Related Research Articles

The Euphrates is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia. Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab in Iraq, which empties into the Persian Gulf.

The geography of Iraq is diverse and falls into five main regions: the desert, Upper Mesopotamia, the northern highlands of Iraq, Lower Mesopotamia, and the alluvial plain extending from around Tikrit to the Persian Gulf.
Transport in Iraq consists of railways, highways, waterways, pipelines, ports and harbors, marines and airports.

Kuwait is a country in West Asia, bordering the Persian Gulf, between Iraq and Saudi Arabia. Kuwait is located at the far northwestern corner of the Persian Gulf. Kuwait is 17,820 square kilometres in size. At its most distant points, it is about 200 km (120 mi) north to south, and 170 km (110 mi) east to west. Kuwait has 10 islands. Kuwait's area consists mostly of desert.
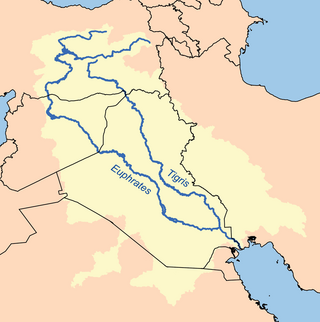
The Tigris is the eastern of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Turkish Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, before merging with the Euphrates and reaching to the Persian Gulf.
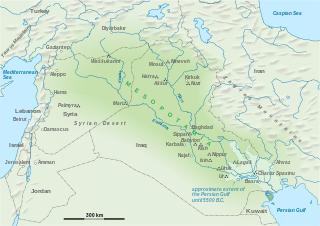
The geography of Mesopotamia, encompassing its ethnology and history, centered on the two great rivers, the Tigris and Euphrates. While the southern is flat and marshy, the near approach of the two rivers to one another, at a spot where the undulating plateau of the north sinks suddenly into the Babylonian alluvium, tends to separate them still more completely. In the earliest recorded times, the northern portion was included in Mesopotamia; it was marked off as Assyria after the rise of the Assyrian monarchy. Apart from Assur, the original capital of Assyria, the chief cities of the country, Nineveh, Kalaḫ and Arbela, were all on the east bank of the Tigris. The reason was its abundant supply of water, whereas the great plain on the western side had to depend on streams flowing into the Euphrates.

The Shatt al-Arab is a river about 200 kilometres (120 mi) in length that is formed at the confluence of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers in the town of al-Qurnah in the Basra Governorate of southern Iraq. The southern end of the river constitutes the Iran–Iraq border down to its mouth, where it discharges into the Persian Gulf. The Shatt al-Arab varies in width from about 232 metres (761 ft) at Basra to 800 metres (2,600 ft) at its mouth. It is thought that the waterway formed relatively recently in geological time, with the Tigris and Euphrates originally emptying into the Persian Gulf via a channel further to the west. Kuwait's Bubiyan Island is part of the Shatt al-Arab delta.

The Tigris–Euphrates river system is a large river system in Western Asia that flows into the Persian Gulf. Its primary rivers are the Tigris and Euphrates, along with smaller tributaries.

Khorramshahr is a city in the Central District of Khorramshahr County, Khuzestan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district.
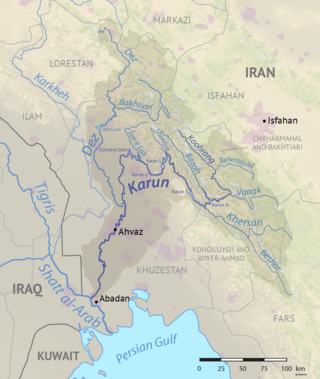
The Karun is the Iranian river with the highest water flow, and the country's only navigable river. It is 950 km (590 mi) long. The Karun rises in the Zard Kuh mountains of the Bakhtiari district in the Zagros Range, receiving many tributaries, such as the Dez and the Kuhrang. It passes through the city of Ahvaz, the capital of the Khuzestan Province of Iran, before emptying to its mouth into Arvand Rud.

The Mesopotamian Marshes, also known as the Iraqi Marshes, are a wetland area located in Southern Iraq and southwestern Iran as well as partially in northern Kuwait. The marshes are primarily located on the floodplains of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers bound by the cities of Basra, Nasiriyah, Amarah and a portion of southwestern Iran and northern Kuwait. Historically the marshlands, mainly composed of the separate but adjacent Central, Hawizeh and Hammar Marshes, used to be the largest wetland ecosystem of Western Eurasia. The unique wetland landscape is home to the Marsh people, who have developed a unique culture tightly coupled to the landscape – harvesting reeds and rice, fishing, and herding water buffalo.

The Mesopotamian Marshes were drained in Iraq and to a smaller degree in Iran between the 1950s and 1990s to clear large areas of the marshes in the Tigris-Euphrates river system. The marshes formerly covered an area of around 20,000 km2 (7,700 sq mi). The main sub-marshes, the Hawizeh, Central, and Hammar marshes, were drained at different times for different reasons.

The Gharraf Canal, Shaṭṭ al-Ḥayy, also known as Shaṭṭ al-Gharrāf or the Hai river, is an ancient canal in Iraq that connects the Tigris at Kut al Amara with the Euphrates east of Nasiriyah. As an Ottoman (Turkish) position lay along the canal, it was one of the objectives of intense military action during the First World War, especially the siege of Kut.
Irrigation in Iran covers 89,930 km2 making it the fifth ranked country in terms of irrigated area.

The Bahmanshir channel is a secondary estuary of the Karun River that parallels the Shatt al-Arab/Arvand Rud waterway on the far side of the Abadan Island, Iran, for 70 miles before emptying into the Persian Gulf.

The Emirate of Muhammara, also known as the Sheikhdom of Muhammara , was an autonomous emirate in modern-day Khuzestan province in Iran. During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, lasting until the then ruler of Iran, Reza Shah, re-established full control over the region in 1925. Officially it was part of Qajar Iran, but the broader Khuzestan region had already enjoyed a large degree of autonomy under the previous rule of the Banu Ka'b (1740–1840), under whom it had become thoroughly Arabized.
References
- ↑ Modi, Jivanji Jamshedji. The River Karun . India, printed at the Times of India steam Press, 1889. 4.