Related Research Articles

Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of the wave is varied in proportion to that of the message signal, such as an audio signal. This technique contrasts with angle modulation, in which either the frequency of the carrier wave is varied, as in frequency modulation, or its phase, as in phase modulation.

Fax, sometimes called telecopying or telefax, is the telephonic transmission of scanned printed material, normally to a telephone number connected to a printer or other output device. The original document is scanned with a fax machine, which processes the contents as a single fixed graphic image, converting it into a bitmap, and then transmitting it through the telephone system in the form of audio-frequency tones. The receiving fax machine interprets the tones and reconstructs the image, printing a paper copy. Early systems used direct conversions of image darkness to audio tone in a continuous or analog manner. Since the 1980s, most machines transmit an audio-encoded digital representation of the page, using data compression to transmit areas that are all-white or all-black, more quickly.
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period. The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of amplitude, which are all functions of the magnitude of the differences between the variable's extreme values. In older texts, the phase of a periodic function is sometimes called the amplitude.

A raster image processor (RIP) is a component used in a printing system which produces a raster image also known as a bitmap. Such a bitmap is used by a later stage of the printing system to produce the printed output. The input may be a page description in a high-level page description language such as PostScript, PDF, or XPS. The input can also be or include bitmaps of higher or lower resolution than the output device, which the RIP resizes using an image scaling algorithm.

Halftone is the reprographic technique that simulates continuous-tone imagery through the use of dots, varying either in size or in spacing, thus generating a gradient-like effect. "Halftone" can also be used to refer specifically to the image that is produced by this process.
Coherence expresses the potential for two waves to interfere. Two monochromatic beams from a single source always interfere. Wave sources are not strictly monochromatic: they may be partly coherent. Beams from different sources are mutually incoherent.

Mastering, a form of audio post production, is the process of preparing and transferring recorded audio from a source containing the final mix to a data storage device, the source from which all copies will be produced. In recent years, digital masters have become usual, although analog masters—such as audio tapes—are still being used by the manufacturing industry, particularly by a few engineers who specialize in analog mastering.

Dots per inch is a measure of spatial printing, video or image scanner dot density, in particular the number of individual dots that can be placed in a line within the span of 1 inch (2.54 cm). Similarly, dots per centimetre refers to the number of individual dots that can be placed within a line of 1 centimetre (0.394 in).
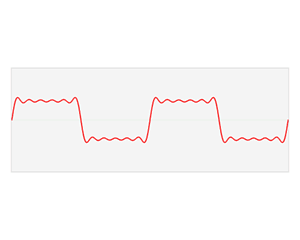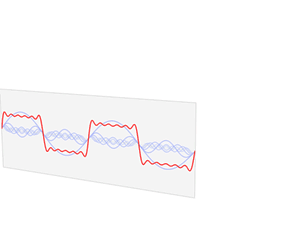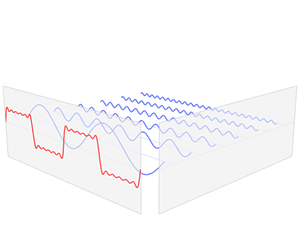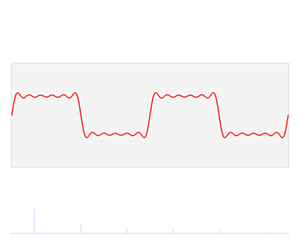
In mathematics, physics, electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time, as in time series. Put simply, a time-domain graph shows how a signal changes over time, whereas a frequency-domain graph shows how the signal is distributed within different frequency bands over a range of frequencies. A complex valued frequency-domain representation consists of both the magnitude and the phase of a set of sinusoids at the frequency components of the signal. Although it is common to refer to the magnitude portion as the frequency response of a signal, the phase portion is required to uniquely define the signal.

In quantum mechanics, a probability amplitude is a complex number used for describing the behaviour of systems. The square of the modulus of this quantity represents a probability density.
Radiofacsimile, radiofax or HF fax is an analogue mode for transmitting grayscale images via high frequency (HF) radio waves. It was the predecessor to slow-scan television (SSTV). It was the primary method of sending photographs from remote sites from the 1930s to the early 1970s. It is still in limited use for transmitting weather charts and information to ships at sea.
Amplitude-shift keying (ASK) is a form of amplitude modulation that represents digital data as variations in the amplitude of a carrier wave. In an ASK system, a symbol, representing one or more bits, is sent by transmitting a fixed-amplitude carrier wave at a fixed frequency for a specific time duration. For example, if each symbol represents a single bit, then the carrier signal could be transmitted at nominal amplitude when the input value is 1, but transmitted at reduced amplitude or not at all when the input value is 0.
Dither is an intentionally applied form of noise used to randomize quantization error, preventing large-scale patterns such as color banding in images. Dither is routinely used in processing of both digital audio and video data, and is often one of the last stages of mastering audio to a CD.

In audio engineering, electronics, physics, and many other fields, the color of noise or noise spectrum refers to the power spectrum of a noise signal. Different colors of noise have significantly different properties. For example, as audio signals they will sound different to human ears, and as images they will have a visibly different texture. Therefore, each application typically requires noise of a specific color. This sense of 'color' for noise signals is similar to the concept of timbre in music.

A microform is a scaled-down reproduction of a document, typically either photographic film or paper, made for the purposes of transmission, storage, reading, and printing. Microform images are commonly reduced to about 4% or 1⁄25 of the original document size. For special purposes, greater optical reductions may be used.

Error diffusion is a type of halftoning in which the quantization residual is distributed to neighboring pixels that have not yet been processed. Its main use is to convert a multi-level image into a binary image, though it has other applications.
In geophysics, seismic inversion is the process of transforming seismic reflection data into a quantitative rock-property description of a reservoir. Seismic inversion may be pre- or post-stack, deterministic, random or geostatistical; it typically includes other reservoir measurements such as well logs and cores.
Stochastic screening or FM screening is a halftone process based on pseudo-random distribution of halftone dots, using frequency modulation (FM) to change the density of dots according to the gray level desired. Traditional amplitude modulation halftone screening is based on a geometric and fixed spacing of dots, which vary in size depending on the tone color represented. The stochastic screening or FM screening instead uses a fixed size of dots and a distribution density that varies depending on the color’s tone.
Pulse-density modulation, or PDM, is a form of modulation used to represent an analog signal with a binary signal. In a PDM signal, specific amplitude values are not encoded into codewords of pulses of different weight as they would be in pulse-code modulation (PCM); rather, the relative density of the pulses corresponds to the analog signal's amplitude. The output of a 1-bit DAC is the same as the PDM encoding of the signal.
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).