Related Research Articles

Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard, is a text encoding standard maintained by the Unicode Consortium designed to support the use of text written in all of the world's major writing systems. Version 15.1 of the standard defines 149813 characters and 161 scripts used in various ordinary, literary, academic, and technical contexts.
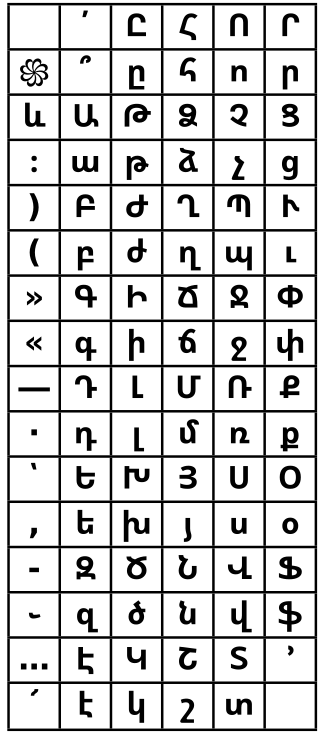
ArmSCII or ARMSCII is a set of obsolete single-byte character encodings for the Armenian alphabet defined by Armenian national standard 166–9. ArmSCII is an acronym for Armenian Standard Code for Information Interchange, similar to ASCII for the American standard. It has been superseded by the Unicode standard.
In Unicode, a Private Use Area (PUA) is a range of code points that, by definition, will not be assigned characters by the Unicode Consortium. Three private use areas are defined: one in the Basic Multilingual Plane, and one each in, and nearly covering, planes 15 and 16. The code points in these areas cannot be considered as standardized characters in Unicode itself. They are intentionally left undefined so that third parties may define their own characters without conflicting with Unicode Consortium assignments. Under the Unicode Stability Policy, the Private Use Areas will remain allocated for that purpose in all future Unicode versions.

Unified Hangul Code (UHC), or Extended Wansung, also known under Microsoft Windows as Code Page 949, is the Microsoft Windows code page for the Korean language. It is an extension of Wansung Code to include all 11172 non-partial Hangul syllables present in Johab. This corresponds to the pre-composed syllables available in Unicode 2.0 and later.
A Unicode font is a computer font that maps glyphs to code points defined in the Unicode Standard. The vast majority of modern computer fonts use Unicode mappings, even those fonts which only include glyphs for a single writing system, or even only support the basic Latin alphabet. Fonts which support a wide range of Unicode scripts and Unicode symbols are sometimes referred to as "pan-Unicode fonts", although as the maximum number of glyphs that can be defined in a TrueType font is restricted to 65,535, it is not possible for a single font to provide individual glyphs for all defined Unicode characters. This article lists some widely used Unicode fonts that support a comparatively large number and broad range of Unicode characters.
The Latin-1 Supplement is the second Unicode block in the Unicode standard. It encodes the upper range of ISO 8859-1: 80 (U+0080) - FF (U+00FF). C1 Controls (0080–009F) are not graphic. This block ranges from U+0080 to U+00FF, contains 128 characters and includes the C1 controls, Latin-1 punctuation and symbols, 30 pairs of majuscule and minuscule accented Latin characters and 2 mathematical operators.
Latin Extended-A is a Unicode block and is the third block of the Unicode standard. It encodes Latin letters from the Latin ISO character sets other than Latin-1 and also legacy characters from the ISO 6937 standard.
KPS 9566 is a North Korean standard specifying a character encoding for the Chosŏn'gŭl (Hangul) writing system used for the Korean language. The edition of 1997 specified an ISO 2022-compliant 94×94 two-byte coded character set. Subsequent editions have added additional encoded characters outside of the 94×94 plane, in a manner comparable to UHC or GBK.
The ISO basic Latin alphabet is an international standard for a Latin-script alphabet that consists of two sets of 26 letters, codified in various national and international standards and used widely in international communication. They are the same letters that comprise the current English alphabet. Since medieval times, they are also the same letters of the modern Latin alphabet. The order is also important for sorting words into alphabetical order.
The Universal Coded Character Set is a standard set of characters defined by the international standard ISO/IEC 10646, Information technology — Universal Coded Character Set (UCS), which is the basis of many character encodings, improving as characters from previously unrepresented typing systems are added.
KS X 1001, "Code for Information Interchange ", formerly called KS C 5601, is a South Korean coded character set standard to represent Hangul and Hanja characters on a computer.
The regional indicator symbols are a set of 26 alphabetic Unicode characters (A–Z) intended to be used to encode ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 two-letter country codes in a way that allows optional special treatment.
Hangul Syllables is a Unicode block containing precomposed Hangul syllable blocks for modern Korean. The syllables can be directly mapped by algorithm to sequences of two or three characters in the Hangul Jamo Unicode block:
Enclosed CJK Letters and Months is a Unicode block containing circled and parenthesized Katakana, Hangul, and CJK ideographs. Also included in the block are miscellaneous glyphs that would more likely fit in CJK Compatibility or Enclosed Alphanumerics: a few unit abbreviations, circled numbers from 21 to 50, and circled multiples of 10 from 10 to 80 enclosed in black squares.
Optical Character Recognition is a Unicode block containing signal characters for OCR and MICR standards.
Tamil All Character Encoding (TACE16) is a scheme for encoding the Tamil script in the Private Use Area of Unicode, implementing a syllabary-based character model differing from the modified-ISCII model used by Unicode's existing Tamil implementation.

IBM code page 949 (IBM-949) is a character encoding which has been used by IBM to represent Korean language text on computers. It is a variable-width encoding which represents the characters from the Wansung code defined by the South Korean standard KS X 1001 in a format compatible with EUC-KR, but adds IBM extensions for additional hanja, additional precomposed Hangul syllables, and user-defined characters.
KS X 1002 is a South Korean character set standard established in order to supplement KS X 1001. It consists of a total of 7,649 characters.
CJK Unified Ideographs Extension I is a Unicode block comprising CJK Unified Ideographs included in drafts of an amendment to China's GB 18030 standard circulated in 2022 and 2023, which were fast-tracked into Unicode in 2023.
References
- 1 2 3 "3.7: Code Charts" (PDF). The Unicode Standard. Version 1.0. Unicode Consortium.
- ↑ "Unicode 1.1". Unicode Technical Site. Unicode Consortium.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Chung, Jaemin (2017-03-29). "Informative document about three pre-Unicode-2.0 modern hangul syllables" (PDF).
- ↑ Chang, K. D.; Choi, In Sook; Kim, Jung Ho (1995-10-04). "Korean Hangul Encoding Conversion Table".
- ↑ "Notes and corrections for HANGUL.TXT". 2005-10-13.
- 1 2 3 4 "Unicode 1.1.5 data". 1995-07-05.
- 1 2 3 "Appendix E: Block Names" (PDF). The Unicode Standard. Version 1.1. Unicode Consortium.
- ↑ "3.8: Block-by-Block Charts" (PDF). The Unicode Standard. Version 1.0. Unicode Consortium.