Y-chromosomal Aaron is the name given to the hypothesized most recent common ancestor of the patrilineal Jewish priestly caste known as Kohanim. According to the traditional understanding of the Hebrew Bible, this ancestor was Aaron, the brother of Moses.

A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent.

Haplogroup G (M201) is a human Y-chromosome haplogroup. It is one of two branches of the parent haplogroup GHIJK, the other being HIJK.

Haplogroup J-M304, also known as J, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is believed to have evolved in Western Asia. The clade spread from there during the Neolithic, primarily into North Africa, the Horn of Africa, the Socotra Archipelago, the Caucasus, Europe, Anatolia, Central Asia, South Asia, and Southeast Asia.
In human genetics, the Atlantic modal haplotype (AMH) or haplotype 15 is a Y chromosome haplotype of Y-STR microsatellite variations, associated with the Haplogroup R1b. It was discovered prior to many of the SNPs now used to identify subclades of R1b and references to it can be found in some of the older literature. It corresponds most closely with subclade R1b1a2a1a(1) [L11].

Haplogroup C is a major Y-chromosome haplogroup, defined by UEPs M130/RPS4Y711, P184, P255, and P260, which are all SNP mutations. It is one of two primary branches of Haplogroup CF alongside Haplogroup F. Haplogroup C is found in ancient populations on every continent except Africa and is the predominant Y-DNA haplogroup among males belonging to many peoples indigenous to East Asia, Central Asia, Siberia, North America and Australia as well as a some populations in Europe, the Levant, and later Japan.
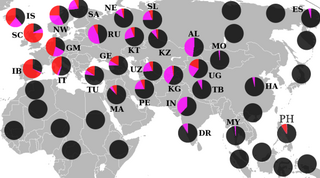
Haplogroup R1, or R-M173, is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. A primary subclade of Haplogroup R (R-M207), it is defined by the SNP M173. The other primary subclade of Haplogroup R is Haplogroup R2 (R-M479).

In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by mutations in the non-recombining portions of DNA from the male-specific Y chromosome. Many people within a haplogroup share similar numbers of short tandem repeats (STRs) and types of mutations called single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
Haplogroup R, or R-M207, is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is both numerous and widespread amongst modern populations.
Haplogroup R2a, or haplogroup R-M124, is a Y-chromosome haplogroup characterized by genetic markers M124, P249, P267, L266, and is mainly found in South Asia as well as in Central Asia, Caucasus, Southwest Asia, and the Arab countries with low frequencies.

Haplogroup J-M267, also commonly known as Haplogroup J1, is a subclade (branch) of Y-DNA haplogroup J-P209 along with its sibling clade haplogroup J-M172.

Haplogroup T-M184, also known as Haplogroup T, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. The unique-event polymorphism that defines this clade is the single-nucleotide polymorphism known as M184.
Haplogroup G-M377 is a Y-chromosome haplogroup and is defined by the presence of the M377 mutation. It is a branch of Haplogroup G2b-M3115, which in turn is defined by the presence of the M3115 mutation. It was found among Pashtuns, who are classified as Iranic and on much lower scale among all major Jewish groups, Palestinians, Lebanese and Syrians(See also page covering Jews with Haplogroup G )
A modal haplotype is an ancestral haplotype derived from the DNA test results of a specific group of people, using genetic genealogy.

Haplogroup R1b (R-M343), previously known as Hg1 and Eu18, is a human Y-chromosome haplogroup.
Population genetics research has been conducted on the ancestry of the modern Turkish people in Turkey. Such studies are relevant for the demographic history of the population as well as health reasons, such as population specific diseases. Some studies have sought to determine the relative contributions of the Turkic peoples of Central Asia, from where the Seljuk Turks began migrating to Anatolia after the Battle of Manzikert in 1071, which led to the establishment of the Anatolian Seljuk Sultanate in the late 11th century, and prior populations in the area who were culturally assimilated during the Seljuk and the Ottoman periods.
Haplogroup T-L206, also known as haplogroup T1, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. The SNP that defines the T1 clade is L206. The haplogroup is one of two primary branches of T (T-M184), the other subclade being T2 (T-PH110).

Haplogroup R-M269 is the sub-clade of human Y-chromosome haplogroup R1b that is defined by the SNP marker M269. According to ISOGG 2020 it is phylogenetically classified as R1b1a1b. It underwent intensive research and was previously classified as R1b1a2, R1b1c, R1b1b2 and R1b1a1a2.
Haplogroup D-M55 (M64.1/Page44.1) also known as Haplogroup D1a2a is a Y-chromosome haplogroup. It is one of two branches of Haplogroup D1a. The other is D1a1, which is found with high frequency in Tibetans and other Tibeto-Burmese populations and geographical close groups. D is also distributed with low to medium frequency in Central Asia, East Asia, and Mainland Southeast Asia.

Haplogroup E-M2, also known as E1b1a1-M2, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. E-M2 is primarily distributed within Africa followed by West Asia. More specifically, E-M2 is the predominant subclade in West Africa, Central Africa, Southern Africa, and the region of the African Great Lakes; it also occurs at moderate frequencies in North Africa, and the Middle East. E-M2 has several subclades, but many of these subhaplogroups are included in either E-L485 or E-U175. E-M2 is especially common among indigenous Africans who speak Niger-Congo languages, and was spread to Southern Africa and East Africa through the Bantu expansion.










