
The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin.

Wrist drop is a medical condition in which the wrist and the fingers cannot extend at the metacarpophalangeal joints. The wrist remains partially flexed due to an opposing action of flexor muscles of the forearm. As a result, the extensor muscles in the posterior compartment remain paralyzed.

The extensor digiti minimi is a slender muscle of the forearm, placed on the ulnar side of the extensor digitorum communis, with which it is generally connected.

Arthrogryposis (AMC) describes congenital joint contracture in two or more areas of the body. It derives its name from Greek, literally meaning 'curving of joints'.

The lateral rectus muscle is a muscle on the lateral side of the eye in the orbit. It is one of six extraocular muscles that control the movements of the eye. The lateral rectus muscle is responsible for lateral movement of the eyeball, specifically abduction. Abduction describes the movement of the eye away from the midline, allowing the eyeball to move horizontally in the lateral direction, bringing the pupil away from the midline of the body.
The pronator teres is a muscle that, along with the pronator quadratus, serves to pronate the forearm. It has two origins, at the medial humeral supracondylar ridge and the ulnar tuberosity, and inserts near the middle of the radius.

In human anatomy, the dorsal interossei (DI) are four muscles in the back of the hand that act to abduct (spread) the index, middle, and ring fingers away from hand's midline and assist in flexion at the metacarpophalangeal joints and extension at the interphalangeal joints of the index, middle and ring fingers.

In human anatomy, the abductor digiti minimi is a skeletal muscle situated on the ulnar border of the palm of the hand. It forms the ulnar border of the palm and its spindle-like shape defines the hypothenar eminence of the palm together with the skin, connective tissue, and fat surrounding it. Its main function is to pull the little finger away from the other fingers.
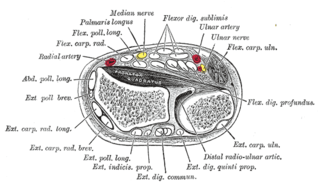
In human anatomy, the extensor indicis (proprius) is a narrow, elongated skeletal muscle in the deep layer of the dorsal forearm, placed medial to, and parallel with, the extensor pollicis longus. Its tendon goes to the index finger, which it extends.

Pallister–Hall syndrome (PHS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects various body systems. The main features are a non-cancerous mass on the hypothalamus and extra digits (polydactylism). The prevalence of Pallister-Hall Syndrome is unknown; about 100 cases have been reported in publication.
The posterior compartment of the forearm contains twelve muscles which primarily extend the wrist and digits. It is separated from the anterior compartment by the interosseous membrane between the radius and ulna.
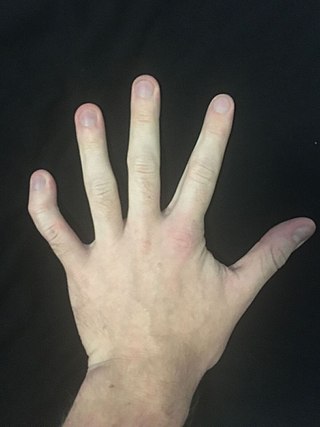
Clinodactyly is a medical term describing the curvature of a digit in the plane of the palm, most commonly the fifth finger towards the adjacent fourth finger.
Schinzel–Giedion syndrome (SGS) is a congenital neurodegenerative terminal syndrome. It was first described in 1978 by Albert Schinzel (1944–) and Andreas Giedion (1925–) as a syndrome with severe midface retraction, skull anomalies, renal anomalies (hydronephrosis) and other anomalies. Babies born with Schinzel–Giedion syndrome have severe mental retardation, growth retardation and global developmental delay.

Swan neck deformity is a deformed position of the finger, in which the joint closest to the fingertip is permanently bent toward the palm while the nearest joint to the palm is bent away from it. It is commonly caused by injury, hypermobility or inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or sometimes familial.

Orofaciodigital syndrome 1 (OFD1), also called Papillon-Léage and Psaume syndrome, is an X-linked congenital disorder characterized by malformations of the face, oral cavity, and digits with polycystic kidney disease and variable involvement of the central nervous system.
Extensor digitorum brevis manus is an extra or accessory muscle on the backside (dorsum) of the hand. It was first described by Albinus in 1758. The muscles lies in the fourth extensor compartment of the wrist, and is relatively rare. It has a prevalence of 4% in the general population according to a meta-analysis. This muscle is commonly misdiagnosed as a ganglion cyst, synovial nodule or cyst.

Extensor tendon compartments of the wrist are anatomical tunnels on the back of the wrist that contain tendons of muscles that extend the wrist and the digits.

The extensor medii proprius is a rare anatomical variant in the extensor compartment of the forearm. The aberrant muscle is analogous to the extensor indicis with the insertion being the middle finger instead of the index finger.

The extensor indicis et medii communis is a rare anatomical variant in the extensor compartment of forearm. This additional muscle lies in the deep extensor layer next to the extensor indicis proprius and the extensor pollicis longus. The characteristics of this anomalous muscle resemble those of the extensor indicis proprius, with split tendons to the index and the middle finger. This muscle can also be considered as a variation of the aberrant extensor medii proprius.

Kirner's deformity, also known as dystelephangy, is an uncommon genetic hand malformation which is characterized by a radial and volar curvature of the distal phalange of the fifth (pinky) finger. It is merely cosmetic and doesn't affect hand function.














