
The fundamental frequency, often referred to simply as the fundamental, is defined as the lowest frequency of a periodic waveform. In music, the fundamental is the musical pitch of a note that is perceived as the lowest partial present. In terms of a superposition of sinusoids, the fundamental frequency is the lowest frequency sinusoidal in the sum of harmonically related frequencies, or the frequency of the difference between adjacent frequencies. In some contexts, the fundamental is usually abbreviated as f0, indicating the lowest frequency counting from zero. In other contexts, it is more common to abbreviate it as f1, the first harmonic.
In mathematics, the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two or more integers, which are not all zero, is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers. For two integers x, y, the greatest common divisor of x and y is denoted . For example, the GCD of 8 and 12 is 4, that is, .

Harmonic analysis is a branch of mathematics concerned with the representation of functions or signals as the superposition of basic waves, and the study of and generalization of the notions of Fourier series and Fourier transforms. In the past two centuries, it has become a vast subject with applications in areas as diverse as number theory, representation theory, signal processing, quantum mechanics, tidal analysis and neuroscience.

A harmonic series is the sequence of harmonics, musical tones, or pure tones whose frequency is an integer multiple of a fundamental frequency.
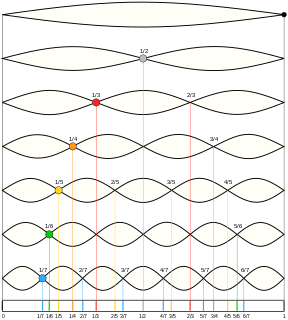
A harmonic is a wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the fundamental frequency, the frequency of the original periodic signal, such as a sinusoidal wave. The original signal is also called the 1st harmonic, the other harmonics are known as higher harmonics. As all harmonics are periodic at the fundamental frequency, the sum of harmonics is also periodic at that frequency. The set of harmonics forms a harmonic series.

In mathematics, a divisor of an integer, also called a factor of , is an integer that may be multiplied by some integer to produce . In this case, one also says that is a multiple of An integer is divisible or evenly divisible by another integer if is a divisor of ; this implies dividing by leaves no remainder.
In mathematics, the harmonic series is the infinite series formed by summing all positive unit fractions:

In mathematics, parity is the property of an integer of whether it is even or odd. An integer is even if it is a multiple of two, and odd if it isn't. For example, −4, 0, 82 are even because
140 is the natural number following 139 and preceding 141.
In mathematics, a harmonic divisor number, or Ore number, is a positive integer whose divisors have a harmonic mean that is an integer. The first few harmonic divisor numbers are:
In mathematics, the remainder is the amount "left over" after performing some computation. In arithmetic, the remainder is the integer "left over" after dividing one integer by another to produce an integer quotient. In algebra of polynomials, the remainder is the polynomial "left over" after dividing one polynomial by another. The modulo operation is the operation that produces such a remainder when given a dividend and divisor.
8128 is the integer following 8127 and preceding 8129.
100,000 (one hundred thousand) is the natural number following 99,999 and preceding 100,001. In scientific notation, it is written as 105.
270 is the natural number following 269 and preceding 271.

Regular numbers are numbers that evenly divide powers of 60 (or, equivalently, powers of 30). Equivalently, they are the numbers whose only prime divisors are 2, 3, and 5. As an example, 602 = 3600 = 48 × 75, so as divisors of a power of 60 both 48 and 75 are regular.
20,000 is the natural number that comes after 19,999 and before 20,001.
30,000 is the natural number that comes after 29,999 and before 30,001.
50,000 is the natural number that comes after 49,999 and before 50,001.






