History
The Harz Club was founded on 8 August 1886 in Seesen. The railway director, Albert Schneider, was its first chairman. One of the co-founders was Carl Reuß. Its first task was to open up the Harz to walkers and tourists. Later, numerous local history groups were started and it took on the maintenance of Harz traditions. Nature conservation was added to its articles as an important aim in 1907. Before the outbreak of the Second World War membership stood at almost 20,000 in 120 branches.
Following the division of the Harz, the development of the Harz Nature Park became the priority within the western zone. In East Germany the Harz Club was banned as an organisation, similar functions were entrusted to the subordinate levels of the Cultural Association of the GDR.
After German reunification over 40 branches were founded in the Harz region of the new federal states of Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. In 1994 the club's name was changed into the Local History, Walking and Nature Conservation Association (Heimat-, Wander- und Naturschutzbund).
Its main chairman is Michael Ermrich, chief executive of the district of Harz. The Harz Club maintains an office in Clausthal-Zellerfeld and is a member of the Federation of German Mountain and Walking Clubs (Verband Deutscher Gebirgs- und Wandervereine).

The Harz is a highland area in northern Germany. It has the highest elevations for that region, and its rugged terrain extends across parts of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia. The name Harz derives from the Middle High German word Hardt or Hart, Latinized as Hercynia. The Brocken is the highest summit in the Harz with an elevation of 1,141.1 metres (3,744 ft) above sea level. The Wurmberg is the highest peak located entirely within the state of Lower Saxony.

Sankt Andreasberg is a former town in the district of Goslar, in Lower Saxony, Germany. Since 1 November 2011, it is part of the town Braunlage. It is situated in the Harz, approximately 7 km west of Braunlage proper, and 20 km east of Osterode am Harz.

At 927 m above sea level (NN), the Bruchberg in the Upper Harz is the second highest mountain in Lower Saxony and the third highest in the Harz mountains in North Germany. It lies between Altenau and Torfhaus in the middle of the Harz National Park. The Bruchberg is more like a plateau and has no real summit. This plateau is partly covered with trees, but on the sunny southern slopes the trees have largely died as a result of bark beetle infestation. Following this insect destruction, a new natural forest, rich in its variety of species, is now growing in the heart of the Harz National Park.

The Wolfsklippen, also called the Wolfsklippe, is a granite mountain in the Harz mountains in Central Germany with an observation platform on the summit. Its height is frequently given as about 723 m above sea level (NN), but occasionally also as only around 710 m above NN.

The Poppenberg is a tree-covered hill east of Ilfeld in the Harz mountains of Germany, with a height of 601 metres. Since 1897, there has been a 33-metre-high (108 ft) steel lattice observation tower on the summit. The tower was built by the Nordhausen branch of the Harz Club and was named after Otto, Prince of Stolberg-Wernigerode. In good weather, it has an extensive view over the South Harz, the Goldene Aue and the Kyffhäuser.

The Aschentalshalbe is a ridge in the Harz Mountains of Germany that is up to 685 m above sea level (NN). It lies south of the village of Sieber in the unincorporated area of Harz in the district of Göttingen in the state of Lower Saxony.

The Carlshaushöhe is a mountain, 626.3 m, in the Harz in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt.

The Stapenberg is a 443-metre-high (1,453 ft) hill spur in the Harz Mountains of central Germany in Harz district in the federal state of Saxony-Anhalt.

The Harz Witches' Trail is a footpath, just under 100 km long, in Germany that runs from Osterode through the Harz mountains and over its highest peak, the Brocken, to Thale. It is a project by the Harz Transport Association and Harz Club and is part of the system of trails known as the Harzer Wandernadel.

The Renneckenberg is a mountain, roughly 933 metres (3,061 ft) high, in the High Harz part of the Harz mountain range of central Germany within the borough of Wernigerode in the state of Saxony-Anhalt.

The Selke is a river of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany.
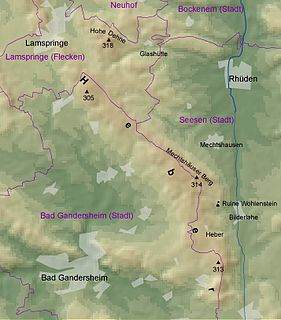
The Heber is a hogback ridge, relatively small in area and up to 313.5 metres high, in the Lower Saxon Hills within the districts of Goslar, Northeim and Hildesheim in the German state of Lower Saxony.

The Ackeburg, also called the Ackenburg, in the Harz Mountains of central Germany, is the site of a high medieval hill castle, 333.2 m above sea level (NN), in the borough of Falkenstein/Harz in Harz district in the state of Saxony-Anhalt. It was first mentioned in 1216 and was abandoned or destroyed in 1400. There was also a village associated with it, known as Akkeburg.

The Barenberg, also called the Bärenberg or Bärenkopf, is a mountain, 695.5 m above sea level (NN), in the Harz Mountains of Germany near the village of Schierke, Harz county, in the state of Saxony-Anhalt.

The Dehnenkopf in the Harz Mountains of central Germany is a summit about 775 m above sea level (NN) near Torfhaus in the unincorporated area of Harz in the county of Goslar in Lower Saxony.

The Schindelkopf in the Harz Mountains of central Germany is a southwestern outlier of the mountain ridge known as Auf dem Acker (865.1 m). It is located near the town of Osterode am Harz within the unincorporated area of Harz which is in the district of Göttingen in the state of Lower Saxony.

The Palatine Forest Club is a hiking club in the former Bavarian Palatinate, i.e. the southern part of the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate and the Saarland county of Saarpfalz-Kreis. In 2011 it had 221 local branches with around 27,000 members.

The Vosges Club is a French rambling organization that covers the Vosges Mountains in the regions of Alsace, eastern Lorraine and the northeastern part of Franche-Comté.
The Rhön Club is an inter-state local history and rambling club in Bavaria, Hesse and Thuringia, with around 25,000 members in 88 branches and is one of the larger German rambling clubs in the Association of German Alpine and Rambling Clubs.
The Bavarian Forest Club, or BWV, is a club that promotes culture, local history and folklore, nature and landscape conservation, and walking in the Bavarian Forest in Germany. It has its head office in Zwiesel and is registered in the register of clubs and societies in the district office at Deggendorf.
















