Related Research Articles

Nefertari, also known as Nefertari Meritmut, was an Egyptian queen and the first of the Great Royal Wives of Ramesses the Great. She is one of the best known Egyptian queens, among such women as Cleopatra, Nefertiti, and Hatshepsut, and one of the most prominent not known or thought to have reigned in her own right. She was highly educated and able to both read and write hieroglyphs, a very rare skill at the time. She used these skills in her diplomatic work, corresponding with other prominent royals of the time. Her lavishly decorated tomb, QV66, is one of the largest and most spectacular in the Valley of the Queens. Ramesses also constructed a temple for her at Abu Simbel next to his colossal monument there.

Usermaatre Heqamaatre Setepenamun Ramesses IV was the third pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty of the New Kingdom of Ancient Egypt. He was the second son of Ramesses III and became crown prince when his elder brother Amenherkhepshef died aged 15 in 1164 BC, when Ramesses was only 12 years old. His promotion to crown prince:
is suggested by his appearance in a scene of the festival of Min at the Ramesses III temple at Karnak, which may have been completed by Year 22 [of his father's reign].

Isetnofret was one of the Great Royal Wives of Pharaoh Ramesses II and was the mother of his successor, Merneptah. She was one of the most prominent of the royal wives, along with Nefertari, and was the chief queen after Nefertari's death.

Tuya was the wife of Pharaoh Seti I of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt and mother of Tia, Ramesses II, and possibly Henutmire.

Meryatum was an ancient Egyptian prince and High Priest of Re, the son of Pharaoh Ramesses II and Queen Nefertari.

Paser was an ancient Egyptian noble who served as vizier during the reigns of Seti I and Ramesses II in the 19th Dynasty. He would later also become High Priest of Amun.
Dorothy Louise Eady, also known as Omm Sety or Om Seti, was a British antiques caretaker and folklorist. She was keeper of the Abydos Temple of Seti I and draughtswoman for the Department of Egyptian Antiquities. She is known for her belief that in a previous life she had been a priestess in ancient Egypt, as well as her considerable historical research at Abydos. Her life and work has been the subject of many articles, television documentaries, and biographies.
Nebamun was a Vizier of Ancient Egypt. He served from about the reign of Horemheb to the reign of Ramesses II.

Pahemnetjer(p3-ḥm-nṯr; "servant of the god", "priest") was a High Priest of Ptah during the reign of Ramesses II. Pahemnetjer succeeded Huy as High Priest of Ptah and was in turn succeeded by his son Didia.
The ancient Egyptian noble Prehotep I was Vizier in the latter part of the reign of Ramesses II, during the 19th Dynasty.

The ancient Egyptian noble Prehotep II was Vizier in the latter part of the reign of Ramesses II, during the 19th Dynasty.
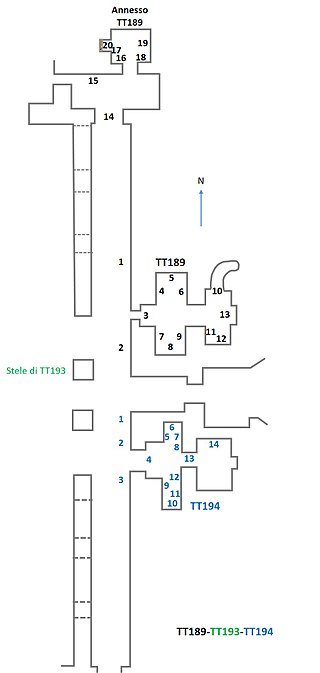
Tomb TT189 is located in the necropolis of El-Assasif in Thebes, Egypt. It contains the sepulchre of Nakhtdjehuty, who was an overseer of the carpenters of the northern lake of the god Amun and the head of the goldworkers in the Estate of Amun during the 19th Dynasty reign of Ramesses II. Nakhtdjehuty's tomb is part of the TT192 tomb complex.

Khawy was a guardian in the Place of Truth and servitor of Amun of Opet (Luxor) from the reign of Ramesses II. He lived in the workers village Deir el-Medina. Khawy is known from his tomb TT214, his house and several other inscriptions.

Wenennefer was an ancient Egyptian High Priest of Osiris at Abydos, during the reign of pharaoh Ramesses II of the 19th Dynasty.

Yuyu was an ancient Egyptian High Priest of Osiris at Abydos, during the reign of pharaohs Ramesses II and possibly Merenptah of the 19th Dynasty.
Minmose was the High Priest of Anhur during the reign of Ramesses II
Qeni was the Superintendent of the Granary during the reign of Ramesses II. Qeni and his family came from Asyut.
Hori was an ancient Egyptian High Priest of Osiris at Abydos, during the reign of pharaohs Ramesses II.
Mery was an ancient Egyptian High Priest of Osiris at Abydos, during the reign of pharaoh Sety I and Ramesses II of the 19th Dynasty.

Yuni served as Head of the-stable-of-Seti-I, Charioteer of His Majesty, and Chief of the Medjay before becoming Viceroy during the reign of Seti I. He would use some of these titles simultaneously. On a stela from Abydos – now in the Cairo Museum – the inscription reads:
Made by the Superintendent of Deserts in the Southern Foreign country, Viceroy in Nubia (Ta-Sety), Chief of Works in the Estate of Amun, Chief of the Madjayu-militia, Iuny. (Kitchen)
References
- ↑ Kitchen, Kenneth A., Pharaoh Triumphant: The Life and Times of Ramesses II, King of Egypt, Aris & Phillips. 1983, p 170, ISBN 978-0856682155
- ↑ H Franzmeier, News from Parahotep: The small Finds from his Tomb rediscovered, in: Journal of Egyptian Archaeology, 2014, See genealogical table p. 175
- ↑ Kitchen, Kenneth A. Ramesside Inscriptions, Translated and Annotated Translations: Ramesses II, His Contemporaries (Ramesside Inscriptions Translations) (Volume III) Wiley-Blackwell. 2001, pg 318-320, ISBN 978-0631184287
- ↑ Kitchen: Ramesside Inscriptions, pp. 320-21