Related Research Articles

Mount Erebus is the second-highest volcano in Antarctica, the highest active volcano in Antarctica, and the southernmost active volcano on Earth. It is the sixth-highest peak of an island and the second most prominent mountain in Antarctica after Mount Vinson. It has a summit elevation of 3,794 metres (12,448 ft). It is located in the Ross Dependency on Ross Island, which is also home to three inactive volcanoes: Mount Terror, Mount Bird, and Mount Terra Nova. The mountain was named by Captain James Clark Ross in 1841 for his ship, HMS Erebus.

Molesworth Station is a high country cattle station. It is located behind the Inland Kaikōura Mountain range in the South Island's Marlborough District. It is New Zealand's largest farm, at over 1,800 square kilometres and supports the country's biggest herd of cattle. It also hosts government science programs, such as research into bovine tuberculosis and related research into possums. The station helps rabbit population reduction.
Skelton Glacier is a large glacier flowing from the polar plateau into the Ross Ice Shelf at Skelton Inlet on the Hillary Coast, south of Victoria Land, Antarctica.

The Kaikōura Ranges are two parallel ranges of mountains located in the northeast of the South Island of New Zealand. The two ranges are visible from a great distance, including from the southern coast of the North Island.

Fairy Bay is east of Mount Stanley, elevation 971 metres (3,186 ft), in Pelorus Sound / Te Hoiere, part of the Marlborough Sounds Maritime Park, at the top of the South Island, New Zealand. The origin of the name is thought to have been the fairy penguin. It has previously been known as Falls River Bay and Sandfly Bay. A neighbouring bay immediately to the south is called Penguin Bay.
Treasury Islands are a small group of islands a few kilometres to the south of Bougainville and 24 kilometres from the Shortland Islands. They form part of the Western Province of the country of Solomon Islands. The two largest islands in the Treasuries are Mono Island and the smaller Stirling Island. The deep water strait between these two islands is called Blanche Harbour.
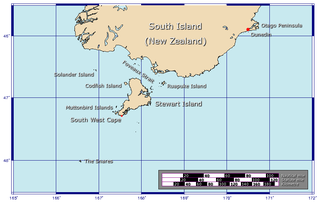
The Western Chain is a group of islets at 48°03′0″S166°30′30″E and a part of The Snares. They lie some 5 km (3.1 mi) to the WSW off the main island North East Island, which lies approx. 200 kilometres (120 mi) south of New Zealand's South Island. The Western Chain island is some 2 km (1.2 mi) long in NW direction, and the highest elevation of 44 m (144 ft) is at the southernmost Island.

The Boulder Bank is a very unusual naturally formed landform in Nelson, New Zealand. It is a 13 km (8.1 mi) long stretch of rocky substrate which begins at the Mackay Bluff and ends at the Cut of the Nelson Harbour. Haulashore Island was once a part of the Boulder Bank, but the Cut made it an island, and it is no longer connected to the Boulder Bank. The Boulder Bank separates Tasman Bay and the Nelson Haven and is managed as a scenic reserve by the Department of Conservation. Land access is gained along Boulder Bank Drive, signposted at the northern end of Nelson Haven on State Highway 6.
Aranga is a locality in Northland, New Zealand. State Highway 12 passes through it. Ōmāpere is 47 km northwest, and Dargaville is 42 km southeast. The Waipoua Forest is to the north. Maunganui Bluff and the Tasman Sea are to the west, with the small settlement of Aranga Beach lying at the northern end of Ripiro Beach.

Amuri County is one of the former counties of New Zealand, in the area that is now the north of Canterbury region.

Ocean Beach is a long sandy beach which runs along the Pacific Ocean coast of south Dunedin, New Zealand. It stretches for some three kilometres from Saint Clair in the southwest along the coast of Saint Kilda to the foot of Lawyers Head in the east. The beach is a popular recreation area for swimming, surfing, and walking.
The Bluff River is a river of New Zealand. It is in the Canterbury Region and is a tributary of the Waiau Toa / Clarence River. The Bluff River flows south for 10 kilometres (6 mi) from the slopes of Mount Major in the Inland Kaikōura Range. Confusingly, the Bluff Stream, another tributary of the Waiau Toa / Clarence, follows a largely parallel course 5 kilometres (3 mi) to the east.
The Gelt River is a river in the Canterbury region of New Zealand. It arises near Mount Peter in the Black Hills and flows south, then east and north-east into Conway River.
The Conway Formation is a Campanian to Danian geologic formation in the South Island of New Zealand and therefore crosses the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary. Plesiosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from its strata. The Conway Formation is part of the Eyre Group and Haerenga Supergroup.
Canyon Glacier is a narrow glacier, 35 nautical miles long, flowing to the Ross Ice Shelf. It drains the northwest slopes of Mount Wexler and moves northward between steep canyon walls of the Separation Range and Hughes Range to join the ice shelf immediately west of Giovinco Ice Piedmont. The glacier was observed from nearby Mount Patrick by the New Zealand Alpine Club Antarctic Expedition (1959–60) who gave the descriptive name.
Separation Range is the northeastern branch of the Commonwealth Range in the Queen Maud Mountains, Antarctica. The branch starts at about 84°20'S, and forms two chains of mountains separated by Hood Glacier. The Separation Range, about 30 nautical miles long, terminates to the north at the Ross Ice Shelf. Named by the New Zealand Alpine Club Antarctic Expedition, 1959–60.

The Kowhai Valley and Shearwater Stream Important Bird Area comprises a disjunct site in the Seaward Kaikōura Range in the north-east of New Zealand’s South Island, some 15 km inland from the coastal town of Kaikōura. The site, at an altitude of 1200–1800 m above sea level, has been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International because it contains the entire breeding population of Hutton's shearwaters; about 100,000 pairs in two colonies.

Ripiro Beach is a sandy stretch on the west coast of Northland, New Zealand, extending from Pouto Peninsula in the south to Maunganui Bluff in the north.
Dillon Cone is a hill in the south Marlborough region of the country of New Zealand with an elevation of 1,331 metres (4,367 ft) above sea level. It is the 24th highest mountain in Marlborough and the 439th highest mountain in New Zealand.
Oaro is a settlement close to the Pacific Ocean Coast of north Canterbury, in the South Island of New Zealand.
References
- ↑ Campbell, H. "Haumuri Bluff", Te Ara – the Encyclopedia of New Zealand, 9 July 2013. Retrieved 24 June 2016.
42°33′30″S173°30′30″E / 42.55833°S 173.50833°E