Related Research Articles

Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to separate, identify, and quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute the entire analysis or be combined with another method. Separation isolates analytes. Qualitative analysis identifies analytes, while quantitative analysis determines the numerical amount or concentration.
Perfume is a mixture of fragrant essential oils or aroma compounds (fragrances), fixatives and solvents, usually in liquid form, used to give the human body, animals, food, objects, and living-spaces an agreeable scent. Perfumes can be defined as substances that emit and diffuse a pleasant and fragrant odor. They consist of manmade mixtures of aromatic chemicals and essential oils. The 1939 Nobel Laureate for Chemistry, Leopold Ružička stated in 1945 that "right from the earliest days of scientific chemistry up to the present time, perfumes have substantially contributed to the development of organic chemistry as regards methods, systematic classification, and theory."

Musk is a class of aromatic substances commonly used as base notes in perfumery. They include glandular secretions from animals such as the musk deer, numerous plants emitting similar fragrances, and artificial substances with similar odors. Musk was a name originally given to a substance with a strong odor obtained from a gland of the musk deer. The substance has been used as a popular perfume fixative since ancient times and is one of the most expensive animal products in the world. The name originates from the Late Greek μόσχος 'moskhos', from Persian mushk and Sanskrit मुष्क muṣka derived from Proto-Indo-European noun múh₂s meaning "mouse". The deer gland was thought to resemble a scrotum. It is applied to various plants and animals of similar smell and has come to encompass a wide variety of aromatic substances with similar odors, despite their often differing chemical structures and molecular shapes.

Electron ionization is an ionization method in which energetic electrons interact with solid or gas phase atoms or molecules to produce ions. EI was one of the first ionization techniques developed for mass spectrometry. However, this method is still a popular ionization technique. This technique is considered a hard ionization method, since it uses highly energetic electrons to produce ions. This leads to extensive fragmentation, which can be helpful for structure determination of unknown compounds. EI is the most useful for organic compounds which have a molecular weight below 600 amu. Also, several other thermally stable and volatile compounds in solid, liquid and gas states can be detected with the use of this technique when coupled with various separation methods.

Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) is an analytical method that combines the features of gas-chromatography and mass spectrometry to identify different substances within a test sample. Applications of GC–MS include drug detection, fire investigation, environmental analysis, explosives investigation, food and flavor analysis, and identification of unknown samples, including that of material samples obtained from planet Mars during probe missions as early as the 1970s. GC–MS can also be used in airport security to detect substances in luggage or on human beings. Additionally, it can identify trace elements in materials that were previously thought to have disintegrated beyond identification. Like liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry, it allows analysis and detection even of tiny amounts of a substance.

An aroma compound, also known as an odorant, aroma, fragrance or flavoring, is a chemical compound that has a smell or odor. For an individual chemical or class of chemical compounds to impart a smell or fragrance, it must be sufficiently volatile for transmission via the air to the olfactory system in the upper part of the nose. As examples, various fragrant fruits have diverse aroma compounds, particularly strawberries which are commercially cultivated to have appealing aromas, and contain several hundred aroma compounds.

Rose oil is the essential oil extracted from the petals of various types of rose. Rose ottos are extracted through steam distillation, while rose absolutes are obtained through solvent extraction, the absolute being used more commonly in perfumery. The production technique originated in Greater Iran. Even with their high price and the advent of organic synthesis, rose oils are still perhaps the most widely used essential oil in perfumery.
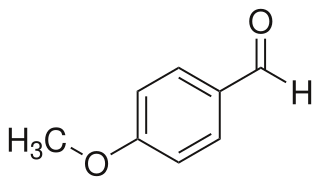
4-Anisaldehyde, or p-Anisaldehyde, is an organic compound with the formula CH3OC6H4CHO. The molecule consists of a benzene ring with a formyl and a methoxy group. It is a colorless liquid with a strong aroma. It provides sweet, floral and strong aniseed odor. Two isomers of 4-anisaldehyde are known, ortho-anisaldehyde and meta-anisaldehyde. They are less commonly encountered.
Solid phase microextraction, or SPME, is a solid phase extraction sampling technique that involves the use of a fiber coated with an extracting phase, that can be a liquid (polymer) or a solid (sorbent), which extracts different kinds of analytes from different kinds of media, that can be in liquid or gas phase. The quantity of analyte extracted by the fibre is proportional to its concentration in the sample as long as equilibrium is reached or, in case of short time pre-equilibrium, with help of convection or agitation.

An electronic nose is an electronic sensing device intended to detect odors or flavors. The expression "electronic sensing" refers to the capability of reproducing human senses using sensor arrays and pattern recognition systems.
Synthetic musks are a class of synthetic aroma compounds to emulate the scent of deer musk and other animal musks. Synthetic musks have a clean, smooth and sweet scent lacking the fecal notes of animal musks. They are used as flavorings and fixatives in cosmetics, detergents, perfumes and foods, supplying the base note of many perfume formulas. Most musk fragrance used in perfumery today is synthetic.

Roman Kaiser is a Swiss fragrance chemist. Since 1968 he has been working at Givaudan, the world's largest company in the flavour and fragrance industry, where he analyzes and reconstitutes natural scents for use in perfumery using the headspace technology which he pioneered and which as a new concept made significant impact on the analysis of natural products.
A captive odorant, or short captive, is an odorant or aroma chemical retained by the originating manufacturer for exclusive use in their own perfumes to protect them from imitation.

Lilial is a chemical compound commonly used as a perfume in cosmetic preparations and laundry powders, often under the name butylphenyl methylpropional. It is an aromatic aldehyde, naturally occurring in crow-dipper and tomato plants, and produced synthetically in large scale. It was banned for use in cosmetics by the EU in March 2022 after being found to be harmful to fertility.
Analytical thermal desorption, known within the analytical chemistry community simply as "thermal desorption" (TD), is a technique that concentrates volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in gas streams prior to injection into a gas chromatograph (GC). It can be used to lower the detection limits of GC methods, and can improve chromatographic performance by reducing peak widths.
Concrete, in perfumery, is a waxy mass obtained by solvent extraction of fresh plant material. It is usually used for the production of absolutes.

Bergamot essential oil is a cold-pressed essential oil produced by cells inside the rind of a bergamot orange fruit. It is a common flavouring and top note in perfumes. The scent of bergamot essential oil is similar to a sweet light orange peel oil with a floral note.
Scentography is the technique of creating and storing odor by artificially recreating a smell using chemical and electronic means.
Headspace gas chromatography uses headspace gas—from the top or "head" of a sealed container containing a liquid or solid brought to equilibrium—injected directly onto a gas chromatographic column for separation and analysis. In this process, only the most volatile substances make it to the column. The technique is commonly applied to the analysis of polymers, food and beverages, blood alcohol levels, environmental variables, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical ingredients.

Floral scent, or flower scent, is composed of all the volatile organic compounds (VOCs), or aroma compounds, emitted by floral tissue. Other names for floral scent include, aroma, fragrance, floral odour or perfume. Flower scent of most flowering plant species encompasses a diversity of VOCs, sometimes up to several hundred different compounds. The primary functions of floral scent are to deter herbivores and especially folivorous insects, and to attract pollinators. Floral scent is one of the most important communication channels mediating plant-pollinator interactions, along with visual cues.
References
- ↑ Omar, Jone; Olivares, Maitane; Alonso, Ibone; Vallejo, Asier; Aizpurua-Olaizola, Oier; Etxebarria, Nestor (2016-04-01). "Quantitative Analysis of Bioactive Compounds from Aromatic Plants by Means of Dynamic Headspace Extraction and Multiple Headspace Extraction-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry". Journal of Food Science. 81 (4): C867–C873. doi:10.1111/1750-3841.13257. ISSN 1750-3841. PMID 26925555. S2CID 21443154.
- ↑ Kaiser, Roman (1997), "Environmental Scents at the Ligurian Coast", Perfumer & Flavorist, 22: 7–18
- ↑ Knudsen, Jette T.; Tollsten, Lars; Bergström, L.Gunnar (1993), "Floral scents—a checklist of volatile compounds isolated by head-space techniques", Phytochemistry, 33 (2): 253–280, doi:10.1016/0031-9422(93)85502-i
- ↑ Charles (Ed.), Sell; Karen Jenner (2005). "Chapter 14. The Search for Fragrance Ingredients". The Chemistry of Fragrances (2nd ed.). Royal Society of Chemistry Publishing. pp. 254–293. ISBN 978-0-85404-824-3.
- ↑ Charles (Ed.), Sell; Robin Clery (2005). "Chapter 12. Natural Product Analysis in the Fragrance Industry". The Chemistry of Fragrances (2nd ed.). Royal Society of Chemistry Publishing. pp. 214–228. ISBN 978-0-85404-824-3.