Related Research Articles
Health insurance or medical insurance is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance, risk is shared among many individuals. By estimating the overall risk of health risk and health system expenses over the risk pool, an insurer can develop a routine finance structure, such as a monthly premium or payroll tax, to provide the money to pay for the health care benefits specified in the insurance agreement. The benefit is administered by a central organization, such as a government agency, private business, or not-for-profit entity.
Single-payer healthcare is a type of universal healthcare in which the costs of essential healthcare for all residents are covered by a single public system.
Health care in Ireland is delivered through public and private healthcare. The public health care system is governed by the Health Act 2004, which established a new body to be responsible for providing health and personal social services to everyone living in Ireland – the Health Service Executive. The new national health service came into being officially on 1 January 2005; however the new structures are currently in the process of being established as the reform programme continues. In addition to the public-sector, there is also a large private healthcare market.
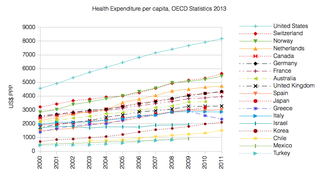
Switzerland has universal health care, regulated by the Swiss Federal Law on Health Insurance. There are no free state-provided health services, but private health insurance is compulsory for all persons residing in Switzerland.

Healthcare in Singapore is under the purview of the Ministry of Health of the Government of Singapore. It mainly consists of a government-run publicly funded universal healthcare system as well as a significant private healthcare sector. Financing of healthcare costs is done through a mixture of direct government subsidies, compulsory comprehensive savings, national healthcare insurance, and cost-sharing.
Morocco became an independent country in 1956. At that time there were only 400 private practitioners and 300 public health physicians in the entire country. By 1992, the government had thoroughly improved their health care service and quality. Health care was made available to over 70% of the population. Programs and courses to teach health and hygiene have been introduced to inform parents and children on how to correctly care for their own and their families' health.

As literacy and socioeconomic status improves in Ethiopia, the demand for quality service is also increasing. Besides, changes in the demographic trends, epidemiology and mushrooming urbanization require more comprehensive services covering a wide range and quality of curative, promotive and preventive services.

Indonesia has drastically improved its health care in the past decade. Government expenditure on healthcare was about 3.1% of its total gross domestic product in 2018.
In South Africa, private and public health systems exist in parallel. The public system serves the vast majority of the population. Authority and service delivery are divided between the national Department of Health, provincial health departments, and municipal health departments.
Healthcare in Georgia is provided by a universal health care system under which the state funds medical treatment in a mainly privatized system of medical facilities. In 2013, the enactment of a universal health care program triggered universal coverage of government-sponsored medical care of the population and improving access to health care services. Responsibility for purchasing publicly financed health services lies with the Social Service Agency (SSA).

Healthcare in Portugal is provided through three coexisting systems: the National Health Service, special social health insurance schemes for certain professions and voluntary private health insurance. The SNS provides universal coverage, although in 2012 measures were implemented to ensure the sustainability of the service by the introduction of user fees to be paid for at the end of treatments. In addition, about 25% of the population is covered by the health subsystems, 10% by private insurance schemes and another 7% by mutual funds. The Ministry of Health is responsible for developing health policy as well as managing the SNS. The Health Regulatory Entity (ERS) is the public independent entity responsible for the regulation of the activity of all the public, private and social healthcare providers. In 2019 the government proposes to scrap all fees, which constitute about 2 percent of the NHS's budget, apart from some hospital emergencies.

The National Health Insurance Scheme (NHIS) is the publicly funded healthcare systems established by the Government of Ghana in 2003. The program was a form of national health insurance established to provide equitable access and financial coverage for basic health care services to Ghanaian citizens. Ghana's universal healthcare system has been described as the most successful healthcare system on the African continent by business magnate Bill Gates. The system has been found to have made Ghana's rate of health insurance one of the highest in Africa, though funding problems may complicate its future.
Examples of health care systems of the world, sorted by continent, are as follows.

India has a multi-payer universal health care model that is paid for by a combination of public and government regulated private health insurances along with the element of almost entirely tax-funded public hospitals. The public hospital system is essentially free for all Indian residents except for small, often symbolic co-payments in some services. Economic Survey 2022-23 highlighted that the Central and State Governments’ budgeted expenditure on the health sector reached 2.1% of GDP in FY23 and 2.2% in FY22, against 1.6% in FY21. India ranks 78th and has one of the lowest healthcare spending as a percent of GDP. It also ranks 77th on the list of countries by total health expenditure per capita.

The National Health Insurance scheme is a form of national health insurance established by the Government of the British Virgin Islands through the Ministry of Health, with a goal to provide access to and financial coverage for health care services to British Virgin Islands residents. A National Health Insurance scheme was first considered in 2006, but it took over a decade to come to fruition. It eventually came into effect on 1 January 2016.

Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana is a national public health insurance scheme of the Government of India that aims to provide free access to health insurance coverage for low income earners in the country. Roughly, the bottom 50% of the country qualifies for this scheme. People using the program access their own primary care services from a family doctor and when anyone needs additional care, PM-JAY provides free secondary health care for those needing specialist treatment and tertiary health care for those requiring hospitalization.

Health and social care on the Isle of Man is the responsibility of the Department of Health and Social Care. Healthcare in Isle of Man is free for residents and visitors from the UK, and there is a reciprocal health agreement with the UK. For several years, it has required a supplementary vote to balance its budget at the end of each year. The Reciprocal Health Agreement only covers three months from the point of arrival in the UK.
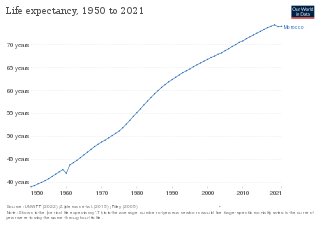
Life expectancy in Curaçao was 74.8 years for men and 81.0 years for women in 2016. Infant mortality in 2013 was 11.3 per 1,000 live births.
Life expectancy in Fiji is 66 years for men and 72 years for women. Maternal mortality was 59 per 100 000 live births in 2013.
References
- ↑ "Country Report: Grenada". Pan American Health Organization. 2018. Retrieved 19 November 2018.
- ↑ "Health and Welfare". Caribbean Islands: A Country Study. Retrieved 19 November 2018.
- ↑ "Ministry of Health" . Retrieved 19 November 2018.
- ↑ "Services at SpiceIsle Imaging". SpiceIsle Imaging. Archived from the original on 30 June 2019. Retrieved 19 November 2018.
- ↑ "Grenada to introduce National Health Insurance". Jamaica Observer. 27 March 2017. Retrieved 19 November 2018.
- ↑ "Grenada PM Promises Speedy Implementation of National Health Insurance After Elections". Caribbean 360. 26 February 2018. Archived from the original on 19 November 2018. Retrieved 19 November 2018.
- ↑ "Health systems in Grenada". Commonwealth Health Online. Retrieved 19 November 2018.
- ↑ "Healthcare in Grenada". International Student Insurance. 2018. Retrieved 19 November 2018.