
Rockwood is a borough in Somerset County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 890 at the 2010 census. It is part of the Johnstown, Pennsylvania, Metropolitan Statistical Area, and located due north of Pennsylvania's highest peak, Mount Davis, which significantly constricts land travel routing south of the municipality.

The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the first common carrier railroad and the oldest railroad in the United States, with its first section opening in 1830. Merchants from Baltimore, which had benefited to some extent from the construction of the National Road early in the century, wanted to do business with settlers crossing the Appalachian Mountains. The railroad faced competition from several existing and proposed enterprises, including the Albany-Schenectady Turnpike, built in 1797, the Erie Canal, which opened in 1825, and the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal. At first, the B&O was located entirely in the state of Maryland; its original line extending from the port of Baltimore west to Sandy Hook, Maryland, opened in 1834. There it connected with Harper's Ferry, first by boat, then by the Wager Bridge, across the Potomac River into Virginia, and also with the navigable Shenandoah River.

The Richmond, Fredericksburg, and Potomac Railroad was a railroad connecting Richmond, Virginia, to Washington, D.C. The track is now the RF&P Subdivision of the CSX Transportation system; the original corporation is no longer a railroad company.

The Pennsylvania Company, later known publicly as the Pennsylvania Lines was a major holding company. It included the Pittsburgh, Fort Wayne and Chicago Railway, the PRR's main route to Chicago. It also owned but did not operate the Pittsburgh, Cincinnati, Chicago and St. Louis Railroad, another line to Chicago. It merged back into the Pennsylvania Railroad in 1918.
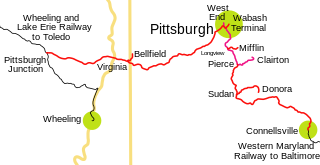
The Pittsburgh and West Virginia Railway was a railroad in the Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania and Wheeling, West Virginia, areas. Originally built as the Wabash Pittsburgh Terminal Railway, a Pittsburgh extension of George J. Gould's Wabash Railroad, the venture entered receivership in 1908 and the line was cut loose. An extension completed in 1931 connected it to the Western Maryland Railway at Connellsville, Pennsylvania, forming part of the Alphabet Route, a coalition of independent lines between the Northeastern United States and the Midwest. It was leased by the Norfolk and Western Railway in 1964 in conjunction with the N&W acquiring several other sections of the former Alphabet Route, but was leased to the new spinoff Wheeling and Lake Erie Railway in 1990, just months before the N&W was merged into the Norfolk Southern Railway.

The Great Railroad Strike of 1877, sometimes referred to as the Great Upheaval, began on July 14 in Martinsburg, West Virginia, after the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) cut wages for the third time in a year. This strike finally ended some 69 days later, after it was put down by unofficial militias, the National Guard, and federal troops. Because of economic problems and pressure on wages by the railroads, workers in numerous other cities, in New York, Pennsylvania and Maryland, into Illinois and Missouri, also went out on strike. An estimated 100 people were killed in the unrest across the country. In Martinsburg, Pittsburgh, Philadelphia and other cities, workers burned down and destroyed both physical facilities and the rolling stock of the railroads—engines and railroad cars. Local populations feared that workers were rising in revolution such as the Paris Commune of 1871.
The Peach Bottom Railway was a 19th-century 3 ft narrow gauge railroad in Pennsylvania, designed to haul coal from the Broad Top fields in central Pennsylvania to Philadelphia, but succeeded only in establishing two local short lines.

The Hocking Valley Railway was a railroad in the U.S. state of Ohio, with a main line from Toledo to Athens and Pomeroy via Columbus. It also had several branches to the coal mines of the Hocking Valley near Athens. The company became part of the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway system in 1910, and the line between Toledo and Columbus continues to see trains as CSX Transportation's Columbus Subdivision. Portions of the main line south of Columbus are now operated by the Indiana and Ohio Railway and Hocking Valley Scenic Railway.
The Baltimore and Ohio Short Line Railroad was the successor to the Pittsburgh Southern Railway, and a subsidiary of the B&O Railroad, and was organized as a legal entity 25 February 1885. The railroad was a link in the attempt of the B&O to serve the Pittsburgh market, and became part of the Wheeling Division of that railroad. It was constructed by gauge conversion of the former 3 ft narrow gauge railway to 4 ft 8+1⁄2 instandard gauge and the building of the Whitehall Tunnel. It ran from Glenwood Junction to Washington, Pennsylvania, a distance of 34 miles.
The Baltimore and Hanover Railroad (B&H) was a railroad that operated in Maryland in the 19th century. The 20 mile (32 km) main line ran from Emory Grove, Maryland north to the Pennsylvania state line near Black Rock Junction, where it connected with the Bachman Valley Railroad.

"Mount Winans" is a mixed-use residential, commercial and industrial neighborhood in the southwestern area of the City of Baltimore in Maryland. Its north, south and east boundaries are marked by the various lines of track of the CSX Railroad. In addition, Hollins Ferry Road running to the south towards suburban Baltimore County in the southwest and further connecting with adjacent Anne Arundel County to the southeast, draws its western boundary.

The Columbia and Port Deposit Railroad (C&PD) was a railroad that operated in Pennsylvania and Maryland in the 19th and early 20th centuries. It operated a 34-mile long (55 km) main line between Columbia, Pennsylvania, and Port Deposit, Maryland, generally along the eastern shore of the Susquehanna River. It later acquired a branch line to Perryville, Maryland. The C&PD was subsequently purchased by the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) and, since the 1999 breakup of Conrail, is owned by Norfolk Southern Railway.
The Syracuse and Binghamton Railroad was established on August 18, 1851, and opened for business on October 18, 1854. The road merged in 1856 into Syracuse and Southern Railroad which was renamed to Syracuse, Binghamton and New York Railroad when the company reorganized after foreclosure in 1857.
The East Pennsylvania Railroad is a defunct railroad which operated in the state of Pennsylvania. It opened a line between Reading, Pennsylvania, and Allentown, Pennsylvania, in 1859. The Philadelphia and Reading Railroad, predecessor of the Reading Company, leased the line in 1869. As the East Pennsylvania Branch, the line was part of the Reading's through route between Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, and Allentown. The line was transferred to Conrail on the Reading's bankruptcy in 1976. It is now part of the Norfolk Southern Railway's Reading Line.

The Lancaster, Oxford and Southern Railway (LO&S) was a 3 ft narrow gauge railway that operated in southeastern Pennsylvania between 1912 and 1918, as a successor company following the bankruptcy of the Lancaster, Oxford and Southern Railroad. The main line connected Oxford and Peach Bottom, Pennsylvania.

The Frederick and Pennsylvania Line railroad ran from Frederick, Maryland to the Pennsylvania-Maryland State line, or Mason–Dixon line near Kingsdale, Pennsylvania consisting of 28 miles (45.1 km) of center-line track and 29.93 miles (48.17 km) of total track including sidings. Chartered in 1867, the railroad started construction in 1869 and cost $868,687.50.
The McMinnville and Manchester Railroad Company was chartered by an Act of the legislature of the State of Tennessee on February 4, 1850. Under this charter, the railroad company built a line of railroad from McMinnville, Tennessee. southwesterly through Manchester, Tennessee. to Tullahoma, Tennessee, where it connected with the railroad line of the Nashville and Chattanooga Railroad Company.
The North Western Virginia Railroad was chartered by the Virginia General Assembly as the Northwestern Virginia Railroad on February 14, 1851 in order to build track from Grafton, West Virginia to Parkersburg, West Virginia. Future statehood advocate and U.S. Senator Peter G. Van Winkle of Parkersburg began as the Northwestern Railroad's secretary in 1852 and served as its President through the American Civil War.
The Alexander and Rich Mountain Railway was a railway in West Virginia.











