
The anatomical snuff box or snuffbox or foveola radialis is a triangular deepening on the radial, dorsal aspect of the hand—at the level of the carpal bones, specifically, the scaphoid and trapezium bones forming the floor. The name originates from the use of this surface for placing and then sniffing powdered tobacco, or "snuff." It is sometimes referred to by its French name tabatière.

The scaphoid bone is one of the carpal bones of the wrist. It is situated between the hand and forearm on the thumb side of the wrist. It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel. The scaphoid bone is the largest bone of the proximal row of wrist bones, its long axis being from above downward, lateralward, and forward. It is approximately the size and shape of a medium cashew.

The capitate bone is found in the center of the carpal bone region, colloquially known as the wrist, which is at the distal end of the radius and ulna bones. It articulates with the third metacarpal bone and forms the third carpometacarpal joint. The capitate bone is the largest of the carpal bones in the human hand. It presents, above, a rounded portion or head, which is received into the concavity formed by the scaphoid and lunate bones; a constricted portion or neck; and below this, the body. The bone is also found in many other mammals, and is homologous with the "third distal carpal" of reptiles and amphibians.
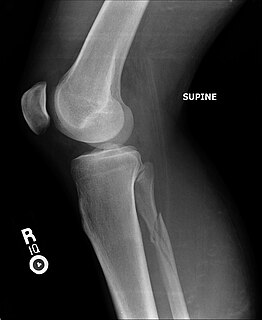
The Maisonneuve fracture is a spiral fracture of the proximal third of the fibula associated with a tear of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis and the interosseous membrane. There is an associated fracture of the medial malleolus or rupture of the deep deltoid ligament of the ankle. This type of injury can be difficult to detect.

A screw thread, often shortened to thread, is a helical structure used to convert between rotational and linear movement or force. A screw thread is a ridge wrapped around a cylinder or cone in the form of a helix, with the former being called a straight thread and the latter called a tapered thread. A screw thread is the essential feature of the screw as a simple machine and also as a threaded fastener.
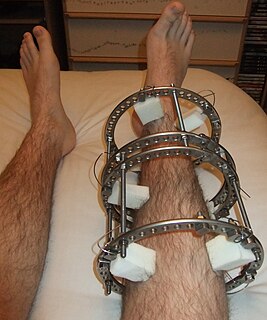
External fixation is a surgical treatment wherein rods are screwed into bone and exit the body to be attached to a stabilizing structure on the outside of the body. It is an alternative to internal fixation, where the components used to provide stability are positioned entirely within the patient's body. It is used to stabilize bone and soft tissues at a distance from the operative or injury focus. They provide unobstructed access to the relevant skeletal and soft tissue structures for their initial assessment and also for secondary interventions needed to restore bony continuity and a functional soft tissue cover.

A dynamic compression plate (DCP) is a metallic plate used in orthopedics for internal fixation of bone, typically after fractures. As the name implies, it is designed to exert dynamic pressure between the bone fragments to be transfixed. Dynamic compression is achieved either by attaching a tension device to a plate or by using a special dynamic compression plate. However, compression plating requires a longer surgical incision to allow insertion of the tension device and the possibility of refracture after the plate is removed. A neutralization plate is used to bridge a comminuted fracture; it also transmits bending or torsional forces from the proximal to the distal fragment. Plates used for buttressing prevent collapse by supporting an area of thin cortex or cancellous bone graft.

An avulsion fracture is a bone fracture which occurs when a fragment of bone tears away from the main mass of bone as a result of physical trauma. This can occur at the ligament by the application of forces external to the body or at the tendon by a muscular contraction that is stronger than the forces holding the bone together. Generally muscular avulsion is prevented by the neurological limitations placed on muscle contractions. Highly trained athletes can overcome this neurological inhibition of strength and produce a much greater force output capable of breaking or avulsing a bone.
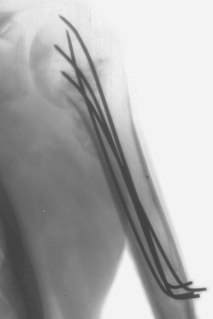
Kirschner wires or K-wires or pins are sterilized, sharpened, smooth stainless steel pins. Introduced in 1909 by Martin Kirschner, the wires are now widely used in orthopedics and other types of medical and veterinary surgery. They come in different sizes and are used to hold bone fragments together or to provide an anchor for skeletal traction. The pins are often driven into the bone through the skin using a power or hand drill. They also form part of the Ilizarov apparatus.
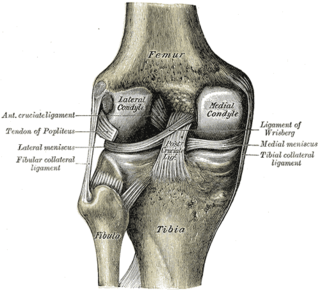
The lateral condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of the femur. The other one is the medial condyle. The lateral condyle is the more prominent and is broader both in its front-to-back and transverse diameters.

A screw is a mechanism that converts rotational motion to linear motion, and a torque to a linear force. It is one of the six classical simple machines. The most common form consists of a cylindrical shaft with helical grooves or ridges called threads around the outside. The screw passes through a hole in another object or medium, with threads on the inside of the hole that mesh with the screw's threads. When the shaft of the screw is rotated relative to the stationary threads, the screw moves along its axis relative to the medium surrounding it; for example rotating a wood screw forces it into wood. In screw mechanisms, either the screw shaft can rotate through a threaded hole in a stationary object, or a threaded collar such as a nut can rotate around a stationary screw shaft. Geometrically, a screw can be viewed as a narrow inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder.
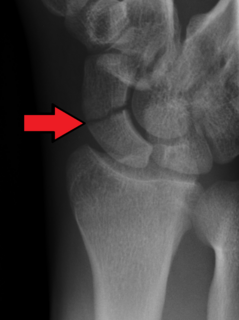
A scaphoid fracture is a break of the scaphoid bone in the wrist. Symptoms generally includes pain at the base of the thumb which is worse with use of the hand. The anatomic snuffbox is generally tender and swelling may occur. Complications may include nonunion of the fracture, avascular necrosis of the proximal part of the bone, and arthritis.

Dynamic hip screw (DHS) or Sliding Screw Fixation is a type of orthopaedic implant designed for fixation of certain types of hip fractures which allows controlled dynamic sliding of the femoral head component along the construct. It is the most commonly used implant for extracapsular fractures of the hip, which are common in older osteoporotic patients. There are 3 components of a dynamic hip screw, including a lag screw, a sideplate and several cortical screws. The idea behind the dynamic compression is that the femoral head component is allowed to move along one plane; since bone responds to dynamic stresses, the native femur may undergo primary healing: cells join along boundaries, resulting in a robust joint requiring no remodeling.

A Barton's fracture is an intra-articular fracture of the distal radius with dislocation of the radiocarpal joint.
Timothy James Herbert is an orthopaedic surgeon specializing in hand surgery. He was born in Sheffield (UK). He is known for his work with the scaphoid bone and related invention, the Herbert screw.
Vertebral fixation is an orthopedic surgical procedure in which two or more vertebrae are anchored to each other through a synthetic "vertebral fixation device", with the aim of reducing vertebral mobility and thus avoiding possible damage to the spinal cord and/or spinal roots.
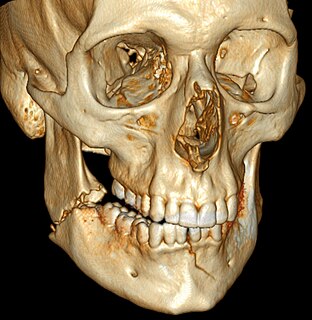
Mandibular fracture, also known as fracture of the jaw, is a break through the mandibular bone. In about 60% of cases the break occurs in two places. It may result in a decreased ability to fully open the mouth. Often the teeth will not feel properly aligned or there may be bleeding of the gums. Mandibular fractures occur most commonly among males in their 30s.

A screw and a bolt are similar types of fastener typically made of metal and characterized by a helical ridge, called a male thread. Screws and bolts are used to fasten materials by the engagement of the screw thread with a similar female thread in the matching part.

Chauffeur's fracture, also known as Hutchinson fracture, is a type of oblique fracture of the radial styloid process in the forearm. The injury is typically caused by compression of the scaphoid bone of the hand against the styloid process of the distal radius. It can be caused by falling onto an outstretched hand. Treatment is often open reduction and internal fixation, which is surgical realignment of the bone fragments and fixation with pins, screws, or plates.
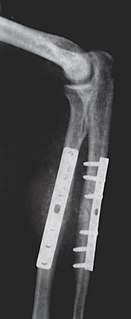
Internal fixation is an operation in orthopedics that involves the surgical implementation of implants for the purpose of repairing a bone, a concept that dates to the mid-nineteenth century and was made applicable for routine treatment in the mid-twentieth century. An internal fixator may be made of stainless steel, titanium alloy, or cobalt-chrome alloy. or plastics.


















