Related Research Articles

Zeta Reticuli, Latinized from ζ Reticuli, is a wide binary star system in the southern constellation of Reticulum. From the southern hemisphere the pair can be seen with the naked eye as a double star in very dark skies. Based upon parallax measurements, this system is located at a distance of about 39.3 light-years from Earth. Both stars are solar analogs that have characteristics similar to those of the Sun. They belong to the Zeta Herculis Moving Group of stars that share a common origin.
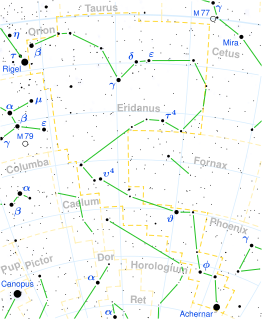
82 G. Eridani is a star about 20 light years away from Earth in the constellation Eridanus. It is a main-sequence star with a stellar classification of G6 V, and it hosts a system of at least three planets and a dust disk.

Messier 18 or M18, also designated NGC 6613, is an open cluster of stars in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764 and included in his list of comet-like objects. From the perspective of Earth, M18 is situated between the Omega Nebula (M17) and the Small Sagittarius Star Cloud (M24).
Pi1 Ursae Minoris is a common proper motion binary star system in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Minor. The pair have apparent visual magnitudes of +6.58 and +7.31, with a combined magnitude of 6.1. They are located about 71 light years from the Sun. The two have an angular separation of 31.4 arc seconds, which corresponds to a physical separation of about 680 AU, and orbit each other with a period of about 13,100 years.
HD 38529 is a binary star approximately 138 light-years away in the constellation of Orion.

HD 10307 is a spectroscopic binary star in the constellation Andromeda. The primary is similar to the Sun in mass, temperature and metal content. situated about 42 light-years from Earth Its companion, HR 483 B, is a little-studied red dwarf.
41 G. Arae, also known as GJ 666, is a trinary star system in the constellation Ara. Although often called just 41 Arae, it is more accurate to call it 41 G. Arae, as the number 41 is the Gould designation.

Kappa Cassiopeiae is a star in the constellation Cassiopeia.
10 Tauri is a single star in the zodiac constellation of Taurus. It can be seen with the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 4.29. An annual parallax shift of 71.62 mas provides a distance estimate of 45.5 light years. It is moving further from the Sun with a radial velocity of +28 km/s and has a relatively high proper motion.
HR 4458 is a binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Hydra. It has the Gould designation 289 G. Hydrae; HR 4458 is the Bright Star Catalogue designation. At a distance of 31.13 light years, it is the closest star system to the solar system within this constellation. This object is visible to the naked eye as a dim, orange-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.97. It is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −22 km/s.
HD 214448 is a binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. They orbit each other with a period of around 147 years. The combined mass of the pair is twice that of the Sun.

Beta Piscis Austrini (β Piscis Austrini) is catalogued as a binary star system in the southern constellation of Piscis Austrinus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.29. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 22.84 mas as seen from the Earth, the star is located 143 light years from the Sun. These coordinates are a source of X-ray emission with a luminosity of 88.5×1020 W, which is most likely coming from a source other than the A-type stars.

HD 139664 is a single star in the southern constellation of Lupus. It has the Bayer designation g Lupi; HD 139664 is the star's identifier from the Henry Draper Catalogue. It has a yellow-white hue and is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.64. The star is located at a distance of 57 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and it is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −7 km/s. It is a member of the Hercules-Lyra Association of co-moving stars.

HD 211575 is a star in the constellation Aquarius in between "Gamma Aquarii", "Pi Aquarii" and "Sadalmelik". It is a member of the corona of the Ursa Major moving group.

9 Sagittarii is a massive binary star in the constellation Sagittarius. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.97.
111 Tauri is a wide binary star system in the constellation Taurus. It is located at a distance of about 47 light years from the Sun. Primary component A is a main sequence star with a stellar classification of F8V. The secondary component B is a K-type main sequence star. The primary is larger and more luminous than the Sun, with about 130% of the Sun's radius and 185% of the Sun's luminosity. The apparent magnitude of 5.1 indicates it is a faint star that can be viewed by the naked eye under good, dark-sky conditions.

Sigma Cygni, Latinised from σ Cygni, is a blue supergiant star in the constellation Cygnus. Its apparent magnitude is 4.2. It belongs to the Cygnus OB4 stellar association and is located approximately 3,300 light years away from Earth.
Chi Herculis, Latinized from χ Herculis, is a Sun-like star in the northern constellation of Hercules. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 62.92 mas as seen from Earth, it is located 51.8 light years from the Sun. The star is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.59. It has a relatively high proper motion, showing a transverse movement of 0.769 arc seconds per year.
WR 93b is a Wolf-Rayet star in the constellation Scorpius, an extremely rare star on the WO oxygen sequence.
References
- ↑ Famaey, B.; Siebert, A.; Jorissen, A. (2008). "On the age heterogeneity of the Pleiades, Hyades, and Sirius moving groups". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 483 (2): 453–459. arXiv: 0712.1470 . Bibcode:2008A&A...483..453F. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078979.
- ↑ Arifyanto, M. I.; Fuchs, B. (2006-04-02). "Fine structure in the phase space distribution of nearby subdwarfs". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 449 (2): 533–538. arXiv: astro-ph/0512296 . Bibcode:2006A&A...449..533A. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20054355.