Clone or Clones or Cloning or Cloned or The Clone may refer to:

Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic information of their parents. Through heredity, variations between individuals can accumulate and cause species to evolve by natural selection. The study of heredity in biology is genetics.
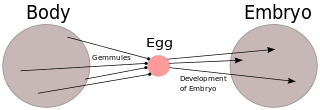
Pangenesis was Charles Darwin's hypothetical mechanism for heredity, in which he proposed that each part of the body continually emitted its own type of small organic particles called gemmules that aggregated in the gonads, contributing heritable information to the gametes. He presented this 'provisional hypothesis' in his 1868 work The Variation of Animals and Plants Under Domestication, intending it to fill what he perceived as a major gap in evolutionary theory at the time. The etymology of the word comes from the Greek words pan and genesis ("birth") or genos ("origin"). Pangenesis mirrored ideas originally formulated by Hippocrates and other pre-Darwinian scientists, but using new concepts such as cell theory, explaining cell development as beginning with gemmules which were specified to be necessary for the occurrence of new growths in an organism, both in initial development and regeneration. It also accounted for regeneration and the Lamarckian concept of the inheritance of acquired characteristics, as a body part altered by the environment would produce altered gemmules. This made Pangenesis popular among the neo-Lamarckian school of evolutionary thought. This hypothesis was made effectively obsolete after the 1900 rediscovery among biologists of Gregor Mendel's theory of the particulate nature of inheritance.
Inherit or Inherited may refer to:
Breeding is sexual reproduction that produces offspring, usually animals or plants. It can only occur between a male and a female animal or plant.
Inheritance is the transferring of property and debt upon a death to a beneficiary.
Transgression may refer to:
Bloodline most commonly refers to heredity.
Blackball, black-ball, black ball, blackballed, or blackballing may refer to:
A son is a male offspring in relation to a parent.
Birth or parturition is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring.
Abandon, abandoned, or abandonment may refer to:
Twins are two offspring produced in the same pregnancy.
Kid, Kids, KIDS, and K.I.D.S. may refer to:
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

