Related Research Articles

Carl Wilhelm von Nägeli was a Swiss botanist. He studied cell division and pollination but became known as the man who discouraged Gregor Mendel from further work on genetics. He rejected natural selection as a mechanism of evolution, favouring orthogenesis driven by a supposed "inner perfecting principle".

A microbiologist is a scientist who studies microscopic life forms and processes. This includes study of the growth, interactions and characteristics of microscopic organisms such as bacteria, algae, fungi, and some types of parasites and their vectors. Most microbiologists work in offices and/or research facilities, both in private biotechnology companies as well as in academia. Most microbiologists specialize in a given topic within microbiology such as bacteriology, parasitology, virology, or immunology.

A microbiological culture, or microbial culture, is a method of multiplying microbial organisms by letting them reproduce in predetermined culture medium under controlled laboratory conditions. Microbial cultures are foundational and basic diagnostic methods used as a research tool in molecular biology.

Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science (RFU) is a private graduate school in North Chicago, Illinois. It has more than 2,000 students in five schools: Chicago Medical School, College of Health Professions, College of Pharmacy, Dr. William M. Scholl College of Podiatric Medicine, and School of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies. The university is named for famous DNA crystallographer Rosalind Franklin. Photo 51, an X-ray diffraction pattern of the B form of DNA, captured by Franklin in 1952, was pivotal in the history of biology in the 20th Century. The image is depicted in the university's seal and logo.
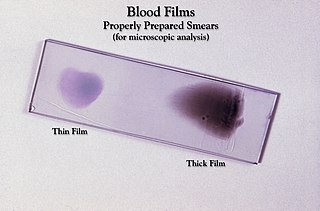
Clinical pathology is a medical specialty that is concerned with the diagnosis of disease based on the laboratory analysis of bodily fluids, such as blood, urine, and tissue homogenates or extracts using the tools of chemistry, microbiology, hematology and molecular pathology. This specialty requires a medical residency.

A medical laboratory scientist (MLS) or clinical laboratory scientist (CLS) or medical technologist (MT) performs diagnostic testing of blood and body fluids in clinical laboratories. The scope of a medical laboratory scientist's work begins with the receipt of patient or client specimens and terminates with the delivery of test results to physicians and other healthcare providers. The utility of clinical diagnostic testing relies squarely on the validity of test methodology. To this end, much of the work done by medical laboratory scientists involves ensuring specimen quality, interpreting test results, data-logging, testing control products, performing calibration, maintenance, validation, and troubleshooting of instrumentation as well as performing statistical analyses to verify the accuracy and repeatability of testing. Medical laboratory scientists may also assist healthcare providers with test selection and specimen collection and are responsible for prompt verbal delivery of critical lab results. An estimated 70% of medical decisions are based on laboratory test results and MLS contributions affect 95% of a health system's costs.
Herman Waldmann FRS FMedSci is a British immunologist known for his work on therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. As of 2013, he is Emeritus Professor of Pathology at the Sir William Dunn School of Pathology at the University of Oxford.
VIB is a research institute located in Flanders, Belgium. It was founded by the Flemish government in 1995, and became a full-fledged institute on 1 January 1996. The main objective of VIB is to strengthen the excellence of Flemish life sciences research and to turn the results into new economic growth. VIB spends almost 80% of its budget on research activities, while almost 12% is spent on technology transfer activities and stimulating the creation of new businesses, in addition VIB spends approximately 2% on socio-economic activities.
Antonios Antoniadis is a professor emeritus of the Medical School of the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (Greece). For 14 years he was the director of the Α΄ Microbiology laboratory of the same School and Head of the “WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Arbovirus and Hemorrhagic Fever Viruses” which he himself created in 1996.

The Department of Biochemistry of Oxford University is located in the Science Area in Oxford, England. It is one of the largest biochemistry departments in Europe. The Biochemistry Department is part of the University of Oxford's Medical Sciences Division, the largest of the university's four academic divisions, which has been ranked first in the world for biomedicine.

A medical laboratory or clinical laboratory is a laboratory where tests are carried out on clinical specimens to obtain information about the health of a patient to aid in diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease. Clinical Medical laboratories are an example of applied science, as opposed to research laboratories that focus on basic science, such as found in some academic institutions.

Marc Van Ranst is a Belgian public health doctor and Professor of Virology at the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven and the Rega Institute for Medical Research. On 1 May 2007, he was appointed as Interministerial comissionar by the Belgian federal government to prepare Belgium for an influenza pandemic.

The College of Natural Science (NatSci) at Michigan State University is home to 27 departments and programs in the biological, physical and mathematical sciences.

Goswin van der Weyden or Goossen van der Weyden (1455–1543) was a Flemish Renaissance painter active in Antwerp. He was one of several artists from Brussels who assisted in the transmission to Antwerp of the traditions of the Brussels school founded by his grandfather, Rogier van der Weyden. He thus played an important role in the founding of the Antwerp school.
Hakim Sendagire is a Ugandan physician, biochemist, academic and medical administrator. Currently he is the Dean at Habib Medical School, College of Health Sciences of the Islamic University in Uganda, a private university, one of the 41 universities in the country, as at February 2015.

B. Brett Finlay, is a Canadian microbiologist well known for his contributions to understanding how microbes cause disease in people and developing new tools for fighting infections, as well as the role the microbiota plays in human health and disease. Science.ca describes him as one of the world's foremost experts on the molecular understanding of the ways bacteria infect their hosts. He also led the SARS Accelerated Vaccine Initiative (SAVI) and developed vaccines to SARS and a bovine vaccine to E. coli O157:H7. His current research interests focus on pathogenic E. coli and Salmonella pathogenicity, and the role of the microbiota in infections, asthma, and malnutrition. He is currently the UBC Peter Wall Distinguished Professor and a Professor in the Michael Smith Laboratories, Microbiology and Immunology, and Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, and Co-director and Senior Fellow for the CIFAR Humans and Microbes program. He is also co-author of the book Let Them Eat Dirt: Saving Your Child from an Oversanitized World and The Whole-Body Microbiome: How to Harness Microbes - Inside and Out - For Lifelong Health. Finlay is the author of over 500 publications in peer-reviewed journals and served as editor of several professional publications for many years.

PREPARE is an acronym for the European Union's Platform for European Preparedness Against (Re-)emerging Epidemics. The coordinator is professor Herman Goossens of the University of Antwerp. It was activated on 31 December 2019 in response to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and as of February 2020 was operating in outbreak response mode 2 (mobilisation), the second of three modes.

Christian Heinrich Maria Drosten is a German virologist whose research focus is on novel viruses (emergent viruses). During the COVID-19 pandemic, Drosten came to national prominence as an expert on the implications and actions required to combat the illness in Germany.
Herman Frans Anna baron Van der Wee is a Belgian economic historian. He was a full professor of social and economic history at the KU Leuven from 1969 to 1993. The academic output of Van der Wee spans economic history, the history of banking, financial history. He has performed research on the period from the Middle Ages to the present time. Geographically he has performed broad research as well, looking into Antwerp, Belgium, the Low Countries, Europe and the world.
Joan Kilbourn was an American microbiologist and educator.
References
- ↑ "Herman Goossens".
- ↑ "Partners - PREPARE Europe". www.prepare-europe.eu.
- ↑ "DGFN". nephrologie.conference2web.com.
- ↑ "Laboratory of Medical Microbiology - Senior Staff - University of Antwerp". www.uantwerpen.be.