Related Research Articles

In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response.

An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that cause disease. Antibodies can recognize virtually any size antigen with diverse chemical compositions from molecules. Each antibody recognizes one or more specific antigens. Antigen literally means "antibody generator", as it is the presence of an antigen that drives the formation of an antigen-specific antibody. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope that specifically binds to one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing the two molecules to bind together with precision. Using this mechanism, antibodies can effectively "tag" a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly.

The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay is a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a ligand in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the ligand to be measured. ELISA has been used as a diagnostic tool in medicine, plant pathology, and biotechnology, as well as a quality control check in various industries.
Haptens are small molecules that elicit an immune response only when attached to a large carrier such as a protein; the carrier may be one that also does not elicit an immune response by itself. The mechanisms of absence of immune response may vary and involve complex immunological interactions, but can include absent or insufficient co-stimulatory signals from antigen-presenting cells.
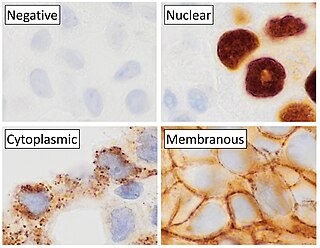
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Albert Hewett Coons, Ernest Berliner, Norman Jones and Hugh J Creech was the first to develop immunofluorescence in 1941. This led to the later development of immunohistochemistry.
Polyclonal antibodies (pAbs) are antibodies that are secreted by different B cell lineages within the body. They are a collection of immunoglobulin molecules that react against a specific antigen, each identifying a different epitope.

Hybridoma technology is a method for producing large numbers of identical antibodies, also called monoclonal antibodies. This process starts by injecting a mouse with an antigen that provokes an immune response. A type of white blood cell, the B cell, produces antibodies that bind to the injected antigen. These antibody producing B-cells are then harvested from the mouse and, in turn, fused with immortal myeloma cancer cells, to produce a hybrid cell line called a hybridoma, which has both the antibody-producing ability of the B-cell and the longevity and reproductivity of the myeloma.
An immunoassay (IA) is a biochemical test that measures the presence or concentration of a macromolecule or a small molecule in a solution through the use of an antibody (usually) or an antigen (sometimes). The molecule detected by the immunoassay is often referred to as an "analyte" and is in many cases a protein, although it may be other kinds of molecules, of different sizes and types, as long as the proper antibodies that have the required properties for the assay are developed. Analytes in biological liquids such as serum or urine are frequently measured using immunoassays for medical and research purposes.

A serotype or serovar is a distinct variation within a species of bacteria or virus or among immune cells of different individuals. These microorganisms, viruses, or cells are classified together based on their surface antigens, allowing the epidemiologic classification of organisms to a level below the species. A group of serovars with common antigens is called a serogroup or sometimes serocomplex.

The hook effect refers to the prozone phenomenon, also known as antibody excess or the Postzone phenomenon, also known as antigen excess. It is an immunologic phenomenon whereby the effectiveness of antibodies to form immune complexes can be impaired when concentrations of an antibody or an antigen are very high. The formation of immune complexes stops increasing with greater concentrations and then decreases at extremely high concentrations, producing a hook shape on a graph of measurements. An important practical relevance of the phenomenon is as a type of interference that plagues certain immunoassays and nephelometric assays, resulting in false negatives or inaccurately low results. Other common forms of interference include antibody interference, cross-reactivity and signal interference. The phenomenon is caused by very high concentrations of a particular analyte or antibody and is most prevalent in one-step (sandwich) immunoassays.
Heterophile antibodies are antibodies induced by external antigens that may be shared between species and are not well defined. They often have weak avidity for their targets.
The Weil–Felix test is an agglutination test for the diagnosis of rickettsial infections. It was first described in 1916. By virtue of its long history and of its simplicity, it has been one of the most widely employed tests for rickettsia on a global scale, despite being superseded in many settings by more sensitive and specific diagnostic tests. The Weil–Felix antibody was recently found to target the rickettsial lipopolysaccharide O-antigen.
Cross-reactivity, in a general sense, is the reactivity of an observed agent which initiates reactions outside the main reaction expected. This has implications for any kind of test or assay, including diagnostic tests in medicine, and can be a cause of false positives. In immunology, the definition of cross-reactivity refers specifically to the reaction of the immune system to antigens. There can be cross-reactivity between the immune system and the antigens of two different pathogens, or between one pathogen and proteins on non-pathogens, which in some cases can be the cause of allergies.

The Rh blood group system is a human blood group system. It contains proteins on the surface of red blood cells. After the ABO blood group system, it is the most likely to be involved in transfusion reactions. The Rh blood group system consisted of 49 defined blood group antigens in 2005. As of 2023, there are over 50 antigens among which the five antigens D, C, c, E, and e are the most important. There is no d antigen. Rh(D) status of an individual is normally described with a positive (+) or negative (−) suffix after the ABO type. The terms Rh factor, Rh positive, and Rh negative refer to the Rh(D) antigen only. Antibodies to Rh antigens can be involved in hemolytic transfusion reactions and antibodies to the Rh(D) and Rh antigens confer significant risk of hemolytic disease of the newborn.
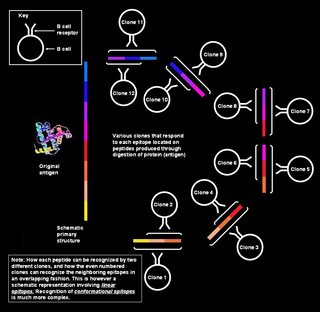
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.

The mononuclear spot test or monospot test, a form of the heterophile antibody test, is a rapid test for infectious mononucleosis due to Epstein–Barr virus (EBV). It is an improvement on the Paul–Bunnell test. The test is specific for heterophile antibodies produced by the human immune system in response to EBV infection. Commercially available test kits are 70–92% sensitive and 96–100% specific, with a lower sensitivity in the first two weeks after clinical symptoms begin.
Human leukocyte antigens (HLA) began as a list of antigens identified as a result of transplant rejection. The antigens were initially identified by categorizing and performing massive statistical analyses on interactions between blood types. This process is based upon the principle of serotypes. HLA are not typical antigens, like those found on surface of infectious agents. HLAs are alloantigens, they vary from individual to individual as a result of genetic differences. An organ called the thymus is responsible for ensuring that any T-cells that attack self proteins are not allowed to live. In essence, every individual's immune system is tuned to the specific set of HLA and self proteins produced by that individual; where this goes awry is when tissues are transferred to another person. Since individuals almost always have different "banks" of HLAs, the immune system of the recipient recognizes the transplanted tissue as non-self and destroys the foreign tissue, leading to transplant rejection. It was through the realization of this that HLAs were discovered.
Isoantibodies, formerly called alloantibodies, are antibodies produced by an individual against isoantigens produced by members of the same species. In the case of the species Homo sapiens, for example, there are a significant number of antigens that are different in every individual. When antigens from another individual are introduced into another's body, these isoantibodies immediately bind to and destroy them.
Antigen-antibody interaction, or antigen-antibody reaction, is a specific chemical interaction between antibodies produced by B cells of the white blood cells and antigens during immune reaction. The antigens and antibodies combine by a process called agglutination. It is the fundamental reaction in the body by which the body is protected from complex foreign molecules, such as pathogens and their chemical toxins. In the blood, the antigens are specifically and with high affinity bound by antibodies to form an antigen-antibody complex. The immune complex is then transported to cellular systems where it can be destroyed or deactivated.

Blood compatibility testing is conducted in a medical laboratory to identify potential incompatibilities between blood group systems in blood transfusion. It is also used to diagnose and prevent some complications of pregnancy that can occur when the baby has a different blood group from the mother. Blood compatibility testing includes blood typing, which detects the antigens on red blood cells that determine a person's blood type; testing for unexpected antibodies against blood group antigens ; and, in the case of blood transfusions, mixing the recipient's plasma with the donor's red blood cells to detect incompatibilities (crossmatching). Routine blood typing involves determining the ABO and RhD type, and involves both identification of ABO antigens on red blood cells and identification of ABO antibodies in the plasma. Other blood group antigens may be tested for in specific clinical situations.
References
- ↑ Taniguchi, T. (1921). "Studies on heterophile antigen and antibody". Journal of Pathology. 24 (2): 217–240. doi:10.1002/path.1700240214.