Wanzhou District is Chongqing's second most populated urban core area on the upper reaches of the Three Gorges of the Yangtze River in China. It is currently governed as a district of Chongqing Municipality, bordering Sichuan to the northwest and Hubei to the southeast. It was formerly known as Wanxian or Wan County. Prior to Chongqing's formation as a direct-controlled municipality, Wanzhou was part of Sichuan province. The urban core of Wanzhou is 228 km (142 mi) away from Chongqing's city proper.
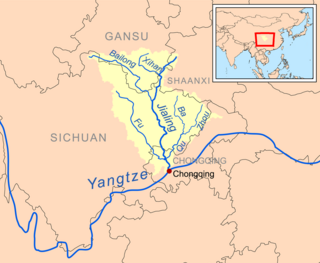
The Jialing River, formerly known by numerous other names, is a major tributary of the Yangtze River in the Sichuan Basin. It is named after the Jialing Valley in Feng County, Shaanxi through which it flows.
Yulin may refer to the following places in China:

Nanchong is a prefecture-level city in the northeast of Sichuan province, China, with an area of 12,479.96 square kilometres (4,818.54 sq mi). At the 2010 census it was home to 6,278,614 people, of whom 1,858,875 lived in the built-up area made of three urban districts. It is the second most populated city of Sichuan Province, after Chengdu. The administrative center is Shunqing District.

Bishan is one of the districts of Chongqing, China, with a history of over 2000 years. Bishan is 23 kilometres (14 mi) west of Chenjiaping of downtown Chongqing. Formerly a county, it became a district on 6 June 2014.
Fuzhou is the capital city in Fujian, China.

Ziyang County is a county in the south of Shaanxi province, China, bordering Chongqing to the southeast and Sichuan to the southwest. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Ankang.

Hejiang is a county in the southeast of Sichuan Province, China, bordering Guizhou province to the south and Chongqing Municipality to the north and northeast. It is under the administration of Luzhou city.
Qianjiang District is a district in the southeastern part of Chongqing Municipality, People's Republic of China, bordering Hubei province to the east and northeast. While it is governed as a district, in practice Qianjiang is its own city proper far removed from the urban centre of Chongqing. The Miao and Tujia ethnic groups constitute 50.03% of the Qianjiang population, the other half being mostly Han (49.94%). Qianjiang is nicknamed "The Throat of Sichuan and Hubei" (川鄂咽喉) because it sits on the intersection of Sichuan-Hubei and Sichuan-Hunan Roads.

Chongqing–Lanzhou railway is a major trunk railway in China connecting Chongqing and Lanzhou. Construction started in 2010, last segment of the railway was opened for service in September 2017. The line allows trains to travel between Chongqing and Lanzhou, Gansu via Nanchong and Guangyuan, Sichuan.
Hezhou (贺州) is a prefecture-level city and former prefecture in Guangxi, China.
Yi Prefecture or Yizhou may refer to:
Changzhou or Chang Prefecture was a zhou (prefecture) in imperial China, centering on modern western Chongqing, China. It existed (intermittently) from 785 until 1290.
Puzhou or Pu Prefecture was a zhou (prefecture) in imperial China, centering on modern Anyue County, Sichuan, China. It existed (intermittently) from 575 until 1376.

The Mongol Siege of Diaoyu Castle was a battle between Song dynasty China and the Mongol Empire in the year 1259. It occurred at the Diaoyu Fortress in modern-day Hechuan district, Chongqing. Möngke Khan, the fourth khan of the Mongol Empire, lost his life in this battle, making it the only battle where the Mongols lost their khan during their campaigns of conquest. This battle was preceded by the Siege of Baghdad in 1258. The siege of Diaoyu Castle was a setback for the Mongol conquest.