Profit and Transactions
Hi-Living generates revenue from sellers, who pay both a fee based on the selling price of each item and a fee based on the starting price, and from advertising. In 2005 it was announced that Hi-Living would increase fees it charges to sellers, which caused such controversy among users that the CEO emailed all Hi-Living users with news that other fees would be decreased.
Hi-Living does not handle goods, nor does it manage the buyer-seller payments, except through its subsidiary shopping mall credit. Instead, much like newspaper want-ads, sellers rely on the buyers' good faith to make payment, and buyers rely on the sellers' good faith to actually deliver the goods intact. To encourage fidelity, Hi-Living maintains, rates, and publicly displays the post-transaction feedback from all users, whether they buy or sell. The buyer is encouraged to examine the sellers' feedback profile before bidding to see their trustworthiness. Sellers with high ratings generally have more bids and garner higher bids. However, it is possible for sellers to make their feedback private and just leave a numbered rating (number of positive, negative, and neutral feedback with a positive feedback percentage), which means that bidders and sellers cannot see the comments other users have left. Hi-Living also has a significant affiliate program, and affiliates can place product images and links on their web sites.

An auction is usually a process of buying and selling goods or services by offering them up for bids, taking bids, and then selling the item to the highest bidder or buying the item from the lowest bidder. Some exceptions to this definition exist and are described in the section about different types. The branch of economic theory dealing with auction types and participants' behavior in auctions is called auction theory.

eBay Inc. is an American multinational e-commerce company based in San Jose, California, that brokers customer to customer and retail sales through online marketplaces in 190 markets worldwide. Sales occur either via online auctions or "buy it now" instant sales, and the company charges commissions to sellers upon sales. eBay was founded by Pierre Omidyar in September 1995. It has 134 million yearly active buyers worldwide and handled $74 billion in transactions in 2022, 49% of which was in the United States. In 2022, the company had a take rate of 13.25%.

An online auction is an auction held over the internet and accessed by internet connected devices. Similar to in-person auctions, online auctions come in a variety of types, with different bidding and selling rules.

Huuto.net is a Finnish online auctioning website. It was established in 1999 and has been owned by ePrice Oy since 2019.

Half.com was a fixed-price online marketplace for books, textbooks, music, movies, video games, and video game consoles. It was acquired by eBay in 2000 and shut down in 2017, with the domain redirected to the eBay website.

MercadoLibre, Inc. is an American Argentine company headquartered in Montevideo, Uruguay and incorporated in the United States that operates online marketplaces dedicated to e-commerce and online auctions. As of 2016, Mercado Libre had 174.2 million users in Latin America, making it the region's most popular e-commerce site by number of visitors. The company has operations in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Uruguay and Venezuela. In 2023 Time included Mercado Libre in the list of the 100 most influential companies in the world.
A bid price is the highest price that a buyer is willing to pay for some goods. It is usually referred to simply as the "bid". In bid and ask, the bid price stands in contrast to the ask price or "offer", and the difference between the two is called the bid–ask spread. An unsolicited bid or purchase offer is when a person or company receives a bid even though they are not looking to sell.

Trade Me is New Zealand's largest online auction and classifieds website. Managed by Trade Me Ltd., the site was founded in 1999 by New Zealand entrepreneur Sam Morgan, who sold it to Fairfax in 2006 for NZ$700 million. Trade Me was publicly listed as a separate entity on 13 December 2011 under the ticker "TME". In May 2019, Trade Me was acquired by private equity firm Apax Partners for NZ$2.56 billion. Trade Me Ltd also operates several sister websites including FindSomeone and Holiday Houses.
Gmarket is an e-commerce website based in South Korea. The company was founded in 2000 as a subsidiary of Interpark, and was acquired by eBay in 2009, who subsequently sold it to Shinsegae at 3.4 trillion Korean Won.

Etsy, Inc. is an American e-commerce company focused on handmade or vintage items and craft supplies. These items fall under a wide range of categories, including jewelry, bags, clothing, home décor and furniture, toys, art, as well as craft supplies and tools. Items described as vintage must be at least 20 years old. The site follows in the tradition of open craft fairs, giving sellers personal storefronts where they list their goods for a fee of US$0.20 per item. Beginning in 2013, Etsy allowed sellers to sell mass-manufactured items.
A two-sided market, also called a two-sided network, is an intermediary economic platform having two distinct user groups that provide each other with network benefits. The organization that creates value primarily by enabling direct interactions between two distinct types of affiliated customers is called a multi-sided platform. This concept of two-sided markets has been mainly theorised by the French economists Jean Tirole and Jean-Charles Rochet and Americans Geoffrey G Parker and Marshall Van Alstyne.

Taobao is a Chinese online shopping platform. It is headquartered in Hangzhou and is owned by Alibaba. According to Alexa rank, it was the eighth most-visited website globally in 2021. Taobao.com was registered on April 21, 2003 by Alibaba Cloud Computing (Beijing) Co., Ltd.

Auto auctions are a method of selling vehicles based on an auction system. Auto auctions can be found in most countries and are usually exclusive to licensed automobile dealers. In a few countries, such as Japan, auto auctions are well known and used by most residents.
Bidtopia was an e-commerce site originally launched in 2007 as a private auction site for Warehouse86 Ventures, LLC. Paul St. James, an owner of Bargainland, which had been the largest PowerSeller on eBay that same year, started the new enterprise in response to changes in eBay policies regarding high volume sales of brand name merchandise and restrictions on sellers with poor customer feedback. Bidtopia suffered the loss of one of its three distribution centers in 2008, and went offline and possibly out of business in early 2010.

iOffer was a San Francisco-based online trading community that was launched on May 1, 2002 by Steven Nerayoff. As of February 2008, it claimed to have nearly one million total users, including approximately 75,000 sellers, although this information cannot be independently verified, nor is it known how many of these users are active.
eBay has faced controversy, including failure to combat fraud committed by buyers and sellers, concerns over its rating systems, and concerns over sales of controversial or illegal items.
Customer to customer markets provide a way to allow customers to interact with each other. Traditional markets require business to customer relationships, in which a customer goes to the business in order to purchase a product or service. In customer to customer markets, the business facilitates an environment where customers can sell goods or services to each other. Other types of markets include business to business (B2B) and business to customer (B2C).

PlayerAuctions is a digital marketplace that connects buyers and sellers of various types of gaming genre such as Massively multiplayer online game (MMO) games, First-person shooters (FPS), Multiplayer online battle arena (MOBA), Mobile game, survival games, battle royale game etc. so they can buy and sell digital assets. These include in-game currency, items, skins, accounts, power leveling and boosting services, and CD keys for games and applications. The site is a neutral marketplace that supports player-to-player trading for popular online games such as RuneScape, Old School RuneScape, World of Warcraft, CSGO, PUBG, Path of Exile, League of Legends, Fortnite, Overwatch, GTA V, Warframe, Pokémon Go, Clash of Clans, EverQuest, ArcheAge, Final Fantasy XIV, Apex Legends, Elder Scrolls Online, Habbo, Fallout 76, and over 250 other games.
Pricefalls, LLC was an American Internet company that managed Pricefalls.com, an on-line retail marketplace, and PFTech, a leading marketplace platform developer. In 2019, Pricefalls, LLC was acquired by Loblaw, Canada's largest retailer.
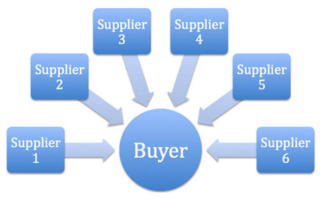
A reverse auction is a type of auction in which the traditional roles of buyer and seller are reversed. Thus, there is one buyer and many potential sellers. In an ordinary auction also known as a forward auction, buyers compete to obtain goods or services by offering increasingly higher prices. In contrast, in a reverse auction, the sellers compete to obtain business from the buyer and prices will typically decrease as the sellers underbid each other.