
Francisco Solano López Carrillo was a Paraguayan military officer, politician and statesman who served as President of Paraguay between 1862 and 1870, of which he served mostly during the Paraguayan War (1864–1870). He succeeded his father Carlos Antonio López as the second president of Paraguay. Solano López is the only Paraguayan ruler to have been killed in action. He is one of only two Paraguayans to have received the rank of Marshal, along with José Félix Estigarribia.

The Paraguayan War, also known as the War of the Triple Alliance, was a South American war that lasted from 1864 to 1870. It was fought between Paraguay and the Triple Alliance of Argentina, the Empire of Brazil, and Uruguay. It was the deadliest and bloodiest inter-state war in Latin American history. Paraguay sustained large casualties, but even the approximate numbers are disputed. Paraguay was forced to cede disputed territory to Argentina and Brazil. The war began in late 1864, as a result of a conflict between Paraguay and Brazil caused by the Uruguayan War. Argentina and Uruguay entered the war against Paraguay in 1865, and it then became known as the "War of the Triple Alliance."

The Battle of Tuyutí was a Paraguayan offensive in the Paraguayan War targeting the Triple Alliance encampment of Tuyutí. It is considered to be the bloodiest battle ever in South America. The result of the battle was an Allied victory, which added to the Paraguayan troubles after the loss of its fleet in the Battle of Riachuelo.

The Battle of Cerro Corá was the last battle of the Paraguayan War, fought on 1 March 1870, in the vicinity of Cerro Corá, 454 kilometres (280 mi) northeast of Paraguay's capital Asunción. It is known for being the battle in which Francisco Solano López, Paraguayan president, was killed at the hands of the Imperial Brazilian Army.

The siege of Humaitá was a military operation in which the Triple Alliance flanked, besieged and captured the Fortress of Humaitá, a Paraguayan stronghold that was referred to as the Gibraltar of South America. It fell on 26 July 1868. It can be considered the key event of the Paraguayan War since the fortress had frustrated the allied advance into Paraguay for more than two years. However it did not surrender as the defenders escaped, most of them to fight another day.

The Battle of Avay of 11 December 1868 was one of the last major combat engagements of the Paraguayan War, fought near the Avay stream in Paraguayan territory between the forces the Triple Alliance and the Paraguayan Army.

Venancio López Carrillo was a Paraguayan politician and military officer. He was Carlos Antonio López's son, and Francisco Solano López' brother; Carlos was Paraguay's leader between 1841 and 1862, and Francisco was President between 1862 and 1870. Venancio was for years Minister of War and Navy, and, before that, commander of the Asunción Paraguayan Army garrison.

This is a bibliography of Paraguay.
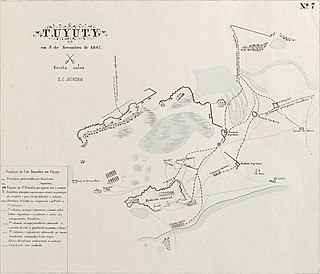
The Second Battle of Tuyutí was fought on 3 November 1867 between the Paraguayan Army and a smaller allied Brazilian-Argentine force. The Paraguayans lost twice as many soldiers as the allies and were defeated.
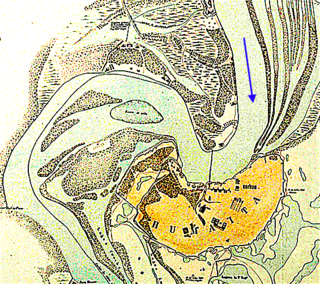
The Fortress of Humaitá (1854–68), known metaphorically as the Gibraltar of South America, was a Paraguayan military installation near the mouth of the River Paraguay. A strategic site without equal in the region, "a fortress the likes of which had never been seen in South America", it was "the key to Paraguay and the upper rivers". It played a crucial role in the deadliest conflict in the continent's history – the Paraguayan War – of which it was the principal theatre of operations.

The sacking of Asunción was the occupation of the Paraguayan capital carried out as of January 1, 1869 by Brazilian forces in the Triple Alliance led by General João de Souza da Fonseca Costa. Asunción was deserted, evacuated by all its inhabitants two days before. On January 5, Luís Alves de Lima e Silva, then Marquis of Caxias, entered the city with the rest of the army. Most of Caxias' army settled in Asunción, where also 4,000 Argentine and 200 Uruguayan troops soon arrived together with about 800 soldiers and officers of the Paraguayan Legion. By this time Caxias was ill and weary of the war. On January 17 he fainted during a mass, relinquished his command on the 18th and left for Montevideo on the 19th.

José Elizardo Aquino Jara was a Paraguayan general who was considered a hero of the War of the Triple Alliance. He was one of the first senior Paraguayan military leaders to die in combat. Aquino was a lieutenant colonel at the time of being shot during the Battle of Boquerón.

Vicente Barrios Bedoya was a Paraguayan general and politician who was the son-in-law of President Carlos Antonio López. Under López and his successor, Marshal and President Francisco Solano López, Barrios held many positions throughout the earlier years of the Paraguayan War and participated in the earlier battles and campaigns of the war.

The Humaitá campaign or the Cuadrilátero campaign was the third, longest and deadliest campaign of the Paraguayan War. The campaign lasted from 16 April 1866 to 5 August 1868. After the initial Paraguayan success in the Mato Grosso campaign and its failure in the Corrientes campaign, the armed forces of the Triple Alliance, Argentina, the Empire of Brazil and Uruguay, invaded the south of Paraguay. At a very short distance, they found the Paraguayan defensive device made up of four fortifications, the so-called "Cuadrilátero", which obstructed the passage to Asunción both by land and by the Paraguay River. A long series of battles cost huge numbers of casualties on both sides, with operations coming to a complete halt after the allied defeat at the Battle of Curupayty. Casualties on both sides were even higher from disease than from battle due to a cholera epidemic which was added to the appalling food and sanitary conditions.

The San Fernando massacre was an episode that took place on 21 December 1868, on the eve of the Battle of Lomas Valentinas, during the Pikysyry Campaign in the Paraguayan War, which consisted of the summary trial and execution of hundreds of prisoners by order of Paraguayan president Francisco Solano López. Some prisoners were accused of plotting an alleged conspiracy to overthrow López. Among the dead was López's own brother, Benigno López.

The historiography of the Paraguayan War has undergone profound changes since the outbreak of the conflict. During and after the war, the historiography of the countries involved, for many, was limited to explaining its causes as due only to the expansionist and excessive ambition of Paraguayan president Francisco Solano López. However, since the beginning of the war there was a strong movement pointing out the conflict as the responsibility of the Empire of Brazil and of Argentina led by president Bartolomé Mitre. In this reading, Argentine and Uruguayan federalist intellectuals, such as Juan Bautista Alberdi, are brazen. In Uruguay, the criticism of Luis Alberto de Herrera stood out.

José Segundo Decoud Domecq was a Paraguayan politician, journalist, diplomat and military officer. He is often considered one of the foremost intellectuals of his generation, and was also one of the first liberals of the country. Decoud was one of the founders of the long-standing Colorado Party, having been its first vice-president and having written its founding instrument.

José María Bruguez (1827-1868) was a Paraguayan general during the Paraguayan War. He was one of the most prominent Paraguayan generals of the war, being known for his artillery services during naval engagements of the war. He died during the 1868 San Fernando massacre after President Francisco Solano López accused Bruguez of conspiring against him.

Juan Francisco Decoud Berzategui was a Paraguayan politician and military officer. He had an important role as a merchant in the Plata basin during the 19th century. Notably, he was also a senior officer in the Paraguayan Legion during the early phases of the Triple Alliance War.

Juan Crisóstomo Centurión y Martinez was a Paraguayan Army officer and politician. He served with distinction in the Triple Alliance War, and afterwards held a wide variety of positions in the Paraguayan governmental structure, including that of Minister of Foreign Affairs.




















