
The Oxford Centre for Hindu Studies, founded in 1997, is a recognised independent centre of the University of Oxford, England. It develops academic programmes of education, research and publishing in Hindu studies. It aims to encourage the Hindu community in the academic study of their own traditions and cultures.

Aihole, also referred to as Aivalli, Ahivolal or Aryapura, is a historic site of ancient and medieval era Buddhist, Hindu and Jain monuments in Karnataka, India that dates from the sixth century through the twelfth century CE. Most of the surviving monuments at the site date from the 7th to 10th centuries. Located around an eponymous small village surrounded by farmlands and sandstone hills, Aihole is a major archaeological site featuring over one hundred and twenty stone and cave temples spread along the Malaprabha river valley, in Bagalakote district. Hunagunda Taluk Distance 35 km

Lakkundi, also referred to as Lokkugundi, was a major city prior to the 14th century, and is now a village in Gadag District of Karnataka, India. By 10th century, it was already a major economic and commerce center with mint operations for South India, one mentioned in Kannada and Sanskrit inscriptions and texts. By 12th century, many Hindu and Jain temples had been consecrated here, along with public infrastructure such as stepwells and water reservoirs. Among the major temples are the Brahma Jinalaya (oldest), Mallikarjuna, Lakshminarayana, Manikeshwara, Naganatha, Kumbheshvara, Nanneshwara, Someshwara, Narayana, Nilakanteshwara, Kasivisesvara, Virabhadhara, Virupaksha, and others. As its importance and wealth grew, Lakkundi became one of the capitals of the Hoysala Empire.
The Akananuru, sometimes called Nedunthokai, is a classical Tamil poetic work and one of the Eight Anthologies (Ettuthokai) in the Sangam literature. It is a collection of 400 love poems with invocatory poem dedicated to Shiva. The collected poems were composed by 144 poets, except 3 poems which are by anonymous author(s). The poems range between 13 and 31 lines, and are long enough to include more details of the subject, episode and its context. According to Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature and history scholar, they are "one of the most valuable collections" from ancient Tamil history perspective.

Tirumurukātṟuppadai is an ancient intensely devotional Tamil poem in the Sangam literature genre entirely dedicated to god Murugan. Murugan is described as the nephew of the god Vishnu, who is called Mayon or the ruler of the worlds. Authored by Nakkiranar, it is the first poem in the Ten Idylls (Pattuppāṭṭu) anthology. The poem is generally dated to the late classical period, with some scholars suggesting it may have been composed a few centuries later.
Gajabahu I, also known as Gajabahuka Gamani, was a Sinhalese king of Rajarata in Sri Lanka. He is renowned for his military prowess, religious benefactions, extensive involvement in South Indian politics, and for possibly introducing the cult of the goddess Pattini to Sri Lanka. The primary source for his reign is the Mahavamsa, though he is also the only early Sri Lankan king to be extensively mentioned in the Chera Cilappatikaram.
Kuṟiñcippāṭṭu, also called the Kurinchipattu or Perumkurinchi, is an ancient Tamil poem in the Sangam literature genre. It is a story about premarital love. Authored by Kapilar, it is the eighth poem in the Pattuppāṭṭu anthology. The poem is generally dated to the classical period.
Malaipaṭukaṭām is an ancient Tamil poem in the Pattuppāṭṭu anthology of the Sangam literature. Authored by Perunkunrur Perunkaucikanar, it consists of 583 lines that describe the nature scenes, the people and the culture of mountain countryside under king Nannan. The poem is dated approximately to 210 CE by Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature scholar.
Ciṟupāṇāṟṟuppaṭai is an ancient Tamil poem, likely the last composed in the Pattuppattu anthology of the Sangam literature. It contains 296 lines in the akaval meter. It is one of five arruppatai genre poems and was a guide to other bards seeking a patron for their art. The main hero honored in the poem is Nalliyakkotan, but the poem reverentially mentions an additional seven minor chieftains and three kings. The poem is dated to sometime between the late 3rd century CE and 5th century CE by Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature scholar.

Mullaippāṭṭu is an ancient Tamil poem in the Sangam literature. Authored by Napputanar, it is the shortest poem in the Ten Idylls (Pattuppāṭṭu) anthology, consisting of 103 lines in akaval meter. It is largely an akam-genre (love) poem about a wife in grief when her husband does not return from the war front, when he promised he will. The Mullaippattu weaves her sorrow with her attempts at patience and self-control. The poem was likely composed about 230 CE or slightly later, according to Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature scholar.

Paṭṭiṉappālai is a Tamil poem in the ancient Sangam literature. It contains 301 lines, of which 296 lines are about the port city of Kaveripoompattinam, the early Chola kingdom and the Chola king Karikalan. The remaining 5 lines are on the proposed separation by a man who wants to move there and the separation pain of his wife who would miss her husband's love. Of the 301 lines, 153 are in the vanci meter and the rest are in akaval. It is sometimes referred to as Vancinetumpattu, or the "long song in the vanci meter". The poem was composed by Katiyalur Uruttirankannanar, sometime around 1st century and 2nd century CE, states Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature scholar.
Neṭunalvāṭai is an ancient Tamil poem in the Sangam literature. Also referred to as Nedunalvadai, it is a blend of a love and war story, highlighting the pains of separation of a queen waiting for her lover to return from the distant war. Authored by Nakkirar, it is the seventh poem in the Pattuppāṭṭu anthology. The poem is generally dated to the late classical period.

The Durga temple is an early 8th-century Hindu temple located in Aihole, Karnataka, India. Originally dedicated to Surya, it has the most embellished and largest relief panels in Aihole depicting artwork of Shaivism, Vaishnavism, Shaktism and Vedic deities. Apart from its fine carvings, it is notable for its apsidal plan – a rare example among early Chalukyan Hindu temple architecture.

The Brahma Jinalaya, sometimes called as the Greater Jain Temple of Lakkundi, is an early 11th-century Mahavira temple in Lakkundi, Gadag District of Karnataka state, India. The temple is attributed to Attiyabbe, the wife of the local governor Dandanayaka Nagadeva. It faces east, has a mukhamandapa, a gudhamandapa and its sanctum is covered by a sur-temple style vimana superstructure. The temple is notable for its reliefs depicting Jaina artwork, statues of the Tirthankaras and the two Hindu statues of Brahma and Saraswati inside its inner mandapa.

The Nannesvara Temple, also referred to as the Nanneshvara temple, is an 11th century Hindu temple in Lakkundi, Gadag district, Karnataka. It is notable for being the earliest known imperial-style temple of the Kalyana Chalukyas, one with significant influences from both North Indian and South Indian schools of Hindu architecture. It stands immediately west to the much larger and more ornate Kasivisvesvara twin Temple in a similar style.
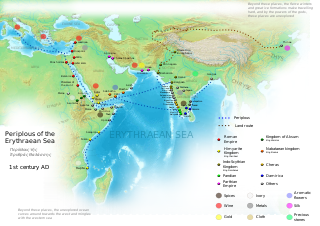
Malao was an ancient proto-Somali port in present-day Somaliland. The town was situated on the site of what later became the city of Berbera. It was a key trading member involved in the Red Sea-Indian Ocean commerce in the early centuries CE. The town also maintained an important monetary market for merchants exchanging goods in the currencies of the Roman Empire.
Sachchidanand Sahai is an Indian epigraphist, writer and the scientific advisor to the Government of Cambodia for restoration of Angkor Wat and the Temple of Preah Vihear, known for his knowledge on Khmer civilization. He was honored by the Government of India, in 2012, with the fourth highest Indian civilian award of Padma Shri.

Alampur Papanasi Temples are a group of twenty three Hindu temples dated between 9th- and 11th-century that have been relocated to the southwest of Alampur village in Telangana. This cluster of mostly ruined temples are co-located near the meeting point of Tungabhadra River and Krishna River at the border of Andhra Pradesh. They are about 1.5 kilometers from the Alampur Navabrahma Temples of the Shaivism tradition, but completed a few centuries later by the Rashtrakutas and later Chalukyas.

Project Mausam is a cultural project by the Indian Ministry of Culture and Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) with the Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts and the National Museum in New Delhi which aims to connect countries on the Indian Ocean. The term "mausam" means "weather" or "season" and is derived from regional dialects including the Arabic word mawsim, which refers to the season when boats can safely sail.
Monica Louise Smith is an American archaeologist, anthropologist, and historian of ancient cities and their household activities. She is Professor and Navin and Pratima Doshi Chair in Indian Studies in the Department of Anthropology at the University of California, Los Angeles.











