
Leavenworth is a town in Jennings Township, Crawford County, Indiana, along the Ohio River. The 2010 US Census recorded a population of 238 persons.

John Hunt Morgan was a Confederate general in the American Civil War. In April 1862, he raised the 2nd Kentucky Cavalry Regiment, fought at Shiloh, and then launched a costly raid in Kentucky, which encouraged Braxton Bragg's invasion of that state. He also attacked General William Rosecrans's supply lines. In July 1863, he set out on a 1,000-mile raid into Indiana and Ohio, taking hundreds of prisoners. But after most of his men had been intercepted by U.S. Navy gunboats, including the USS Moose, Morgan surrendered at Salineville, Ohio, the northernmost point ever reached by uniformed Confederates. Morgan carried out the diversionary "Morgan's Raid" against orders, which gained no tactical advantage for the Confederacy while losing the regiment. Morgan escaped prison, but his credibility was so low that he was restricted to minor operations. He was killed at Greeneville, Tennessee, in September 1864. Morgan was the brother-in-law of Confederate general A. P. Hill. Various schools and a memorial are dedicated to him.

In the 1860s, the Copperheads, also known as Peace Democrats, were a faction of the Democratic Party in the Union who opposed the American Civil War and wanted an immediate peace settlement with the Confederates.

Morgan's Raid was a diversionary incursion by Confederate cavalry into the Union states of Indiana, Kentucky, Ohio, and West Virginia during the American Civil War. The raid took place from June 11 to July 26, 1863. It is named for the commander of the Confederate troops, Brigadier General John Hunt Morgan. Although it caused temporary alarm in the North, the raid failed.

The Battle of Corydon was a minor engagement that took place July 9, 1863, just south of Corydon, which had been the original capital of Indiana until 1825, and was the county seat of Harrison County. The attack occurred during Morgan's Raid in the American Civil War as a force of 2,500 cavalry invaded the North in support of the Tullahoma Campaign. It was the only pitched battle of the Civil War that occurred in Indiana, and no battle has occurred within Indiana since.
The Battle of Salineville occurred July 26, 1863, near Salineville, Ohio, during the American Civil War. U.S. Brig. Gen. James M. Shackelford destroyed Confederate Brig. Gen. John Hunt Morgan's remaining Confederate cavalry and captured Morgan, ending Morgan's Raid. It was the northernmost military action involving an official command of the Confederate States Army.

Lexington is an unincorporated community in Lexington Township, Scott County, in the U.S. state of Indiana, located about 10 miles west of the Ohio River and 28 miles north of Louisville, Kentucky. The town itself was founded before Indiana became the 19th state in 1816 and was located in Jefferson County at the time it was platted. It was the original county seat from 1820 to 1874, before local leaders decided on a more central location at nearby Scottsburg, which created animosity between the residents of the two towns for several decades afterwards.
The Battle of Buffington Island, also known as the St. Georges Creek Skirmish, was an American Civil War engagement in Meigs County, Ohio, and Jackson County, West Virginia, on July 19, 1863, during Morgan's Raid. The largest battle in Ohio during the war, Buffington Island contributed to the capture of the Confederate Brig. Gen. John Hunt Morgan, who was fleeing U.S. Army soldiers across the Ohio River at a ford opposite Buffington Island.

During the American Civil War, the State of Ohio played a key role in providing troops, military officers, and supplies to the Union army. Due to its central location in the Northern United States and burgeoning population, Ohio was both politically and logistically important to the war effort. Despite the state's boasting a number of very powerful Republican politicians, it was divided politically. Portions of Southern Ohio followed the Peace Democrats and openly opposed President Abraham Lincoln's policies. Ohio played an important part in the Underground Railroad prior to the war, and remained a haven for escaped and runaway slaves during the war years.

The Battle of Tebbs Bend was fought on July 4, 1863, near the Green River in Taylor County, Kentucky during Morgan's Raid in the American Civil War. Despite being badly outnumbered, elements of the Union Army defeated Confederate Brig. Gen. John Hunt Morgan's dismounted cavalry.
The Battle of Lebanon occurred July 5, 1863, in Lebanon, Kentucky, during Morgan's Raid in the American Civil War. Confederate troops under Brig. Gen. John Hunt Morgan fought for six hours to overcome the small U.S. garrison before moving northward, eventually riding through Kentucky, Indiana, and much of Ohio before surrendering.

Thomas Henry Hines was a Confederate cavalryman who was known for his espionage activities during the last two years of the American Civil War.

PS Alice Dean, which had a capacity of 880 tons, was a side-wheel, wooden-hulled packet steamer. It was launched from Cincinnati, Ohio, United States, in 1863, running a scheduled route between Cincinnati and Memphis, Tennessee. Its captain was James H. Pepper.

During the American Civil War, the Ohio River port city of Cincinnati, Ohio, played a key role as a major source of supplies and troops for the Union Army. It also served as the headquarters for much of the war for the Department of the Ohio, which was charged with the defense of the region, as well as directing the army's offensives into Kentucky and Tennessee.

Indiana, a state in the Midwest, played an important role in supporting the Union during the American Civil War. Despite anti-war activity within the state, and southern Indiana's ancestral ties to the South, Indiana was a strong supporter of the Union. Indiana contributed approximately 210,000 Union soldiers, sailors, and marines. Indiana's soldiers served in 308 military engagements during the war; the majority of them in the western theater, between the Mississippi River and the Appalachian Mountains. Indiana's war-related deaths reached 25,028. Its state government provided funds to purchase equipment, food, and supplies for troops in the field. Indiana, an agriculturally rich state containing the fifth-highest population in the Union, was critical to the North's success due to its geographical location, large population, and agricultural production. Indiana residents, also known as Hoosiers, supplied the Union with manpower for the war effort, a railroad network and access to the Ohio River and the Great Lakes, and agricultural products such as grain and livestock. The state experienced two minor raids by Confederate forces, and one major raid in 1863, which caused a brief panic in southern portions of the state and its capital city, Indianapolis.

The Newburgh Raid was a successful raid by Confederate partisans on Newburgh, Indiana, on July 18, 1862, making it the first town in a northern state to be captured during the American Civil War. Confederate colonel Adam Rankin Johnson led the raid by using a force of only about 35 men he had recruited from nearby Henderson, Kentucky. They confiscated supplies and ammunition without a shot being fired by tricking Newburgh's defenders into thinking the town was surrounded by cannons. In reality, the so-called cannons were an assemblage of a stove pipe, a charred log, and wagon wheels, forever giving the Confederate commander the nickname of Adam "Stovepipe" Johnson.
During the American Civil War, Indianapolis, the state capital of Indiana, was a major base of supplies for the Union. Governor Oliver P. Morton, a major supporter of President Abraham Lincoln, quickly made Indianapolis a gathering place to organize and train troops for the Union army. The city became a major railroad hub for troop transport to Confederate lands, and therefore had military importance. Twenty-four military camps were established in the vicinity of Indianapolis. Camp Morton, the initial mustering ground to organize and train the state's Union volunteers in 1861, was designated as a major prisoner-of-war camp for captured Confederate soldiers in 1862. In addition to military camps, a state-owned arsenal was established in the city in 1861, and a federal arsenal in 1862. A Soldiers' Home and a Ladies' Home were established in Indianapolis to house and feed Union soldiers and their families as they passed through the city. Indianapolis residents also supported the Union cause by providing soldiers with food, clothing, equipment, and supplies, despite rising prices and wartime hardships, such as food and clothing shortages. Local doctors aided the sick, some area women provided nursing care, and Indianapolis City Hospital tended to wounded soldiers. Indianapolis sent an estimated 4,000 men into military service; an estimated 700 died during the war. Indianapolis's Crown Hill National Cemetery was established as one of two national military cemeteries established in Indiana in 1866.

William Augustus Bowles was a physician, landowner, and politician from French Lick, Orange County, Indiana. He is best remembered for establishing the first French Lick Springs Hotel, a mineral springs resort hotel in the 1840s, and platting the town of French Lick, Indiana, in 1857. Bowles, a Democrat, served two terms in the Indiana state legislature. During the Mexican–American War he became a colonel in the 2nd Indiana Volunteer Regiment and joined in the Battle of Buena Vista (1847). An outspoken advocate of slavery as an institution, Bowles was sympathetic to the South during the American Civil War. In 1863 Harrison H. Dodd, leader of the Order of Sons of Liberty (OSL) in Indiana, named Bowles a major general for one of four military districts in the state's secret society that opposed the war. Bowles also played a role in the Indianapolis treason trials in 1864, when he and three others were convicted of plotting to overthrow the federal government. Following his release from prison in 1866, Bowles returned to Orange County, Indiana, where his failing health continued to decline in the years prior to his death.

The John H. Morgan Surrender Site is the place where, during the American Civil War, Brig. Gen. John Hunt Morgan, the leader of Confederate troops responsible for Morgan's Raid, surrendered to Union troops following the Battle of Salineville. The site is located at a crossroads between the villages of Gavers and West Point in Columbiana County, Ohio, about 60 miles northwest of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The site was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on April 23, 1973, for its military significance.
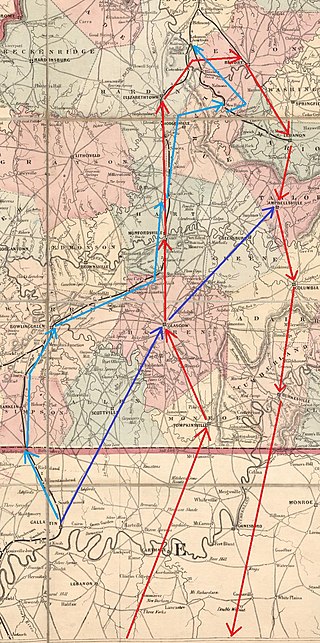
Morgan's Christmas Raid was carried out by Confederate Brigadier General John Hunt Morgan between December 22, 1862, and January 5, 1863. Morgan intended to cut the supply lines to the Union Army of the Cumberland in Tennessee. The Union used the Louisville and Nashville Railroad, and Morgan had identified two 500-foot (150 m) long trestle bridges at Muldraugh Hill that could be burnt. Morgan's 4,000-strong cavalry force left Alexandria, Tennessee, on December 22 and passed into Kentucky on Christmas Eve, defeating part of the 2nd Michigan Cavalry Regiment near Tompkinsville. They fought and defeated an Indiana cavalry detachment on Christmas Day at Bear Wallow, Barren County. The U.S. Army sent forces under Colonel John Marshall Harlan and Major General Joseph J. Reynolds to try to catch Morgan. However, Morgan used ruses to distract his pursuers. Morgan captured a Union stockade at Bonnieville on December 26 and on December 27 captured Elizabethtown before burning the bridges at Muldraugh Hill.
















