The World's Columbian Exposition, also known as the Chicago World's Fair, was a world's fair held in Chicago from May 5 to October 31, 1893, to celebrate the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New World in 1492. The centerpiece of the Fair, held in Jackson Park, was a large water pool representing the voyage that Columbus took to the New World. Chicago won the right to host the fair over several competing cities, including New York City, Washington, D.C., and St. Louis. The exposition was an influential social and cultural event and had a profound effect on American architecture, the arts, American industrial optimism, and Chicago's image.

The Ibero-American Exposition of 1929 was a world's fair held in Seville, Spain, from 9 May 1929 until 21 June 1930. Countries in attendance of the exposition included: Portugal, the United States, Brazil, Uruguay, Mexico, Peru, Argentina, Chile, Colombia, Cuba, Venezuela, the Dominican Republic, Bolivia, Panama, El Salvador, Costa Rica, and Ecuador. Each Spanish region and each of the provinces of Andalusia were also represented.

Thomas Shields Clarke was an American painter and sculptor. He is best known for his bronze sculpture The Cider Press, in San Francisco.

The Spoliarium is a painting by Filipino painter Juan Luna. Luna, working on canvas, spent eight months completing the painting which depicts dying gladiators. The painting was submitted by Luna to the Exposición Nacional de Bellas Artes in 1884 in Madrid, where it garnered the first gold medal. The picture recreates a despoiling scene in a Roman circus where dead gladiators are stripped of weapons and garments. Together with other works of the Spanish Academy, the Spoliarium was on exhibit in Rome in April 1884.

The University of Kansas Natural History Museum is part of the University of Kansas Biodiversity Institute, a KU designated research center dedicated to the study of the life of the planet.

Janet Scudder, born Netta Deweze Frazee Scudder, was an American sculptor and painter from Terre Haute, Indiana, who is best known for her memorial sculptures, bas-relief portraiture, and portrait medallions, as well as her garden sculptures and fountains. Her first major commission was the design for the seal of the New York Bar Association around 1896. Scudder's Frog Fountain (1901) led to the series of sculptures and fountains for which she is best known. Later commissions included a Congressional Gold Medal honoring Domício da Gama and a commemorative medal for Indiana's centennial in 1916. Scudder also displayed her work at numerous national and international exhibitions in the United States and in Europe from the late 1890s to the late 1930s. Scudder's autobiography, Modeling My Life, was published in 1925.

Anastasio Alfaro was a Costa Rican zoologist, geologist and explorer.

Guayabo National Monument, is an archaeological site near the city of Turrialba, within the Central Conservation Area in the Cartago Province, Costa Rica. It is almost directly in the center of the country on the Southern slope of the Turrialba Volcano. The National Monument covers about 2.3 square kilometres (0.89 sq mi) and is surrounded by rainforest plant vegetation causing it to be extremely vibrant green due to high precipitation and rich soils. Only a small portion of it has been unearthed, excavated, and studied.
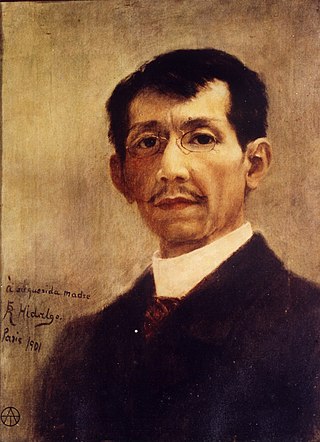
Félix Resurrección Hidalgo y Padilla was a Filipino artist. He is acknowledged as one of the greatest Filipino painters of the late 19th century, and is significant in Philippine history for having been an acquaintance and inspiration for members of the Philippine reform movement which included José Rizal, Marcelo del Pilar, Mariano Ponce, and Graciano López Jaena, although he neither involved himself directly in that movement, nor later associated himself with the First Philippine Republic under Emilio Aguinaldo.

Carl Vilhelm Hartman, was a Swedish botanist and anthropologist.

The Columbian half dollar is a coin issued by the Bureau of the Mint in 1892 and 1893. The first traditional United States commemorative coin, it was issued both to raise funds for the 1893 World's Columbian Exposition and to mark the quadricentennial of the first voyage to the Americas of Christopher Columbus, whose portrait it bears. The Columbian half dollar was the first American coin to depict a historical person.

Gonzalo Morales Sáurez was a Costa Rican painter. He studied in The San Fernando Academy in Madrid, Spain from 1970 to 1974. He is best known for his hyper-realistic works, and has exhibited his art in many museums and art galleries in Europe and the Americas.
Samuel Kirkland Lothrop was an American archaeologist and anthropologist who specialized in Central and South American Studies. His two-volume 1926 work Pottery of Costa Rica and Nicaragua is regarded as a pioneering study. Lothrop was a longtime research associate of Harvard's Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology and made many contributions based on fieldwork, laboratory analysis, and evaluations of private and public collections that focused on Central and South America. He is known for archaeological excavations in Argentina and Chile as well as investigations of the archaeological contexts for the stone spheres of Costa Rica. Lothrop is also known for his research on goldwork and other artifacts from Costa Rica, the Veraguas Province of Panama, and the Sacred Cenote at Chichen Itza, Mexico.

Enella Benedict was an American realism and landscape painter. She taught at the School of the Art Institute of Chicago and was a founder and director for nearly 50 years for the Art School at the Hull House.

Zulema Garcia Olsen was an American musician and composer, and represented "Spanish Texan" women at the World's Fair in Chicago in 1893.

The Woman's Building was designed and built in June 1892, for the World's Columbian Exposition held in Chicago in 1893; under the auspices of the Board of Lady Managers. Out of the twelve main buildings for the Exhibition, the Woman's Building was the first to be completed. It had an exhibition space as well as an assembly room, a library, and a Hall of Honor. The History of the World's Fair states, "It will be a long time before such an aggregation of woman's work, as may now be seen in the Woman's Building, can be gathered from all parts of the world again." The purpose of the building was to highlight woman's achievements, and challenge the traditional ways of thinking at the time it was built. The Woman's Building was planned, designed, and decorated entirely by women under the direction of the board of lady managers.

Julia Alcayde y Montoya (1885–1939) was a Spanish painter who specialised in painting still lifes and portraits.

Edward Francis Rook was an American Impressionist landscape and marine painter, and a member of the art colony at Old Lyme, Connecticut.
The architecture of Costa Rica includes remains from the pre-Columbian Era, all the way to modern buildings that form part of the nation's contemporary infrastructure. There is a unique architectural landscape present in Costa Rica that is reflective of the nation's history and vibrant culture. The nation encompasses an array of historical buildings from both the pre-colonial era and post-colonial era, such as Guayabo and the Basilica of Our Lady of the Angels. The contemporary architectural scene in Costa Rica has also captured global attention, exemplified by structures such as Casa Flotanta. Architecture in Costa Rica is reflective of the nation's environmental conservation policies. This is reflected in the distinctive and extensive presence of canopy bridges throughout the nation, constructed in the aim of preventing rainforest destruction.