
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of 1,435 mm. The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge, international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the most widely used track gauge around the world, with about 55% of the lines in the world using it.

In rail transport, track gauge is the distance between the two rails of a railway track. All vehicles on a rail network must have wheelsets that are compatible with the track gauge. Since many different track gauges exist worldwide, gauge differences often present a barrier to wider operation on railway networks.
A light railway is a railway built at lower costs and to lower standards than typical "heavy rail": it uses lighter-weight track, and may have more steep gradients and tight curves to reduce civil engineering costs. These lighter standards allow lower costs of operation, at the price of lower vehicle capacity.
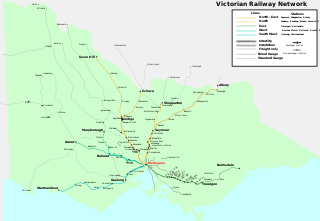
Rail transport in the Australian state of Victoria is provided by a number of railway operators who operate over the government-owned railway lines. The network consists of 2,357 km of Victorian broad gauge lines, and 1,912 km of standard gauge freight and interstate lines; the latter increasing with gauge conversion of the former. Historically, a few experimental 762 mm gauge lines were built, along with various private logging, mining and industrial railways. The rail network radiates from the state capital, Melbourne, with main interstate links to Sydney and to Adelaide, as well as major lines running to regional centres, upgraded as part of the Regional Fast Rail project.
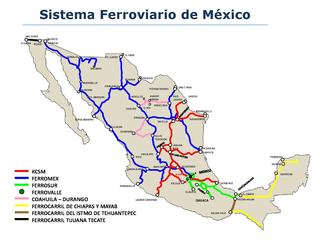
Mexico has a freight railway system owned by the national government and operated by various entities under concessions (charters) granted by the national government. The railway system provides freight and passenger service throughout the country, connecting major industrial centers with ports and with rail connections at the United States border. Passenger rail services were limited to a number of tourist trains between 1997, when Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México suspended service, and 2008, when Ferrocarril Suburbano de la Zona Metropolitana de México inaugurated Mexico's first commuter rail service between Mexico City and the State of Mexico. This is not including the Mexico City Metro, which started service in 1969.

There is no active rail transport in Belize, although there were lines in the past.

The rail network in Queensland, Australia, was the first in the world to adopt 1,067 mm narrow gauge for a main line, and, in 2013, was claimed to the second largest narrow gauge network in the world, consists of:

Rail transport in Austria is mainly owned by the national rail company ÖBB. The railway network consists of 6,123 km, its gauge is 1,435 mmstandard gauge and 3,523 km are electrified.

Several companies provide rail transport in Portugal.

Railways in Albania are administered by the national railway company Hekurudha Shqiptare (HSH). It operates a standard-gauge railway gauge rail system in Albania. All trains are, currently, hauled by Czechoslovak-built ČKD diesel-electric locomotives.

Rail transport in Montenegro is operated by four separate companies, which independently handle railway infrastructure, passenger transport, cargo transport and maintenance of the rolling stock. The four companies were a part of public company Railways of Montenegro until it was split up in 2008.

Rail transport in Greece has a history which began in 1869, with the completion of the then Athens & Piraeus Railway. From the 1880s to the 1920s, the majority of the network was built, reaching its heyday in 1940. From the 1950s onward, the railway system entered a period of decline, culminating in the service cuts of 2011. Ever since the 1990s, the network has been steadily modernized, but still remains smaller than its peak length. The operation of the Greek railway network is split between the Hellenic Railways Organisation (OSE), which owns and maintains the rail infrastructure; GAIAOSE, which owns the building infrastructure and the former OSE rolling stock, Hellenic Train; and other private companies that run the trains on the network. Greece is a member of the International Union of Railways (UIC). The UIC Country Code for Greece is 73.

The East African Railway Master Plan is a proposal for rejuvenating the railways serving Tanzania, Kenya, and Uganda, and building new railways to serve Rwanda and Burundi. The objective is to further the economic development of East Africa by increasing the efficiency and speed, and lowering the cost, of transporting cargo between major ports on the Indian Ocean coast and the interior.

There are 84 kilometres of railway in Sierra Leone, all of which is private and of a narrow gauge, 1,067 mm.
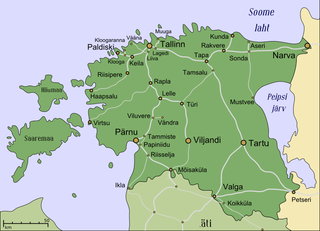
The history of rail transport in Estonia starts in 1870 when a line was opened connecting Paldiski, Tallinn, Tapa and Narva; the line extending all the way to St. Petersburg in Russia.

The history of rail transport in Portugal dates from 28 October 1856, when Portugal's first railway line was opened between Lisbon and Carregado: the Companhia dos Caminhos de Ferro Portugueses.

The history of rail transport in Greece began in 1869, with the construction of the link between Piraeus and Athens with private funding.

The history of rail transport in Latvia began with the construction in 1860 of a railway from Pytalovo to Dinaburg, 160 km in length, as part of the Saint Petersburg–Warsaw Railway.
Between 1917 and 1930 approximately 300 km of military and industrial narrow-gauge railways were built at the gauge of 600 mm and 750 mm or Bosnian gauge, built by Austria-Hungarians and Italians, intending to create a through route from Skopje and Tetovo to the Adriatic coast of Albania. None of these railways remained intact.
















