
Rail transport is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of land transport, next to road transport. It is used for about 8% of passenger and freight transport globally, thanks to its energy efficiency and potentially high speed.

Slovenian Railways is the state railway company of Slovenia, created in 1991.
This page provides an index of articles on rail transport by country.

The Italian railway system is one of the most important parts of the infrastructure of Italy, with a total length of 24,567 km (15,265 mi) of which active lines are 16,832 km (10,459 mi). The network has recently grown with the construction of the new high-speed rail network. Italy is a member of the International Union of Railways (UIC). The UIC Country Code for Italy is 83.

The Parenzana in Italian and Croatian or Porečanka in Slovene is one of the nicknames of a defunct 760mm/15 15/16 inch narrow gauge railway between Trieste and Poreč, in present-day Italy, Slovenia and Croatia.

Sorgenfri station is a railway station on the Hillerød radial of the S-train network in Copenhagen, Denmark. It serves Sorgenfri and the southern part of Virum. It is located at Hummeltoftevej 51 and is named for the nearby Sorgenfri palace.

Liechtenstein's one railway line, the Feldkirch–Buchs railway, is operated by Austrian Federal Railways (ÖBB). As such, it represents an exception to the more usual Liechtenstein practice of cooperating closely with Switzerland, as in the case of the principality's use of the Swiss franc as its currency and its membership of a common customs area with its western neighbour

A motorail train or accompanied car train (ACT) is a passenger train on which passengers can take their car or automobile along with them on their journey. Passengers are carried in normal passenger carriages or in sleeping carriages on longer journeys, while the cars are loaded into autoracks, car-carriers, or flatcars that normally form part of the same train.

Innsbruck Hauptbahnhof is the main railway station in Innsbruck, the capital city of the Austrian federal state of Tyrol. Opened in 1853, the station is a major hub for western and central Austria. In 2019, it was the 8th-busiest station in the country, and the 2nd-busiest outside of Vienna after only Linz Hauptbahnhof, with 315 train movements and 38,500 passengers daily.

Verona Porta Nuova is the main railway station of Verona, Italy. It is one of the two stations serving central Verona; the other station, Verona Porta Vescovo, is located at the east of the city.

Salzburg Hauptbahnhof is the main railway station in Salzburg, capital of the federal state of Salzburg in Austria. It is the most important station in the agglomeration of Salzburg, and a major transportation hub in western Austria.

Klagenfurt Hauptbahnhof is the main railway station in Klagenfurt, capital of the Austrian state of Carinthia. It is an important railway junction in southern Austria.

Gorizia Centrale railway station is the main station serving the town and comune of Gorizia, in the autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, northeastern Italy.

Trieste Centrale railway station is the main station serving the city and municipality (comune) of Trieste, in the autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, northeastern Italy.

Bolzano/Bozen railway station is the main station of Bolzano, capital of the autonomous province of South Tyrol, in northeastern Italy.

Treviglio railway station, also known as Treviglio centrale railway station is the main station serving the town and comune of Treviglio, in the region of Lombardy, northern Italy. Opened in 1878, it has a higher average number of passengers per day than Treviglio's other railway station, Treviglio Ovest.
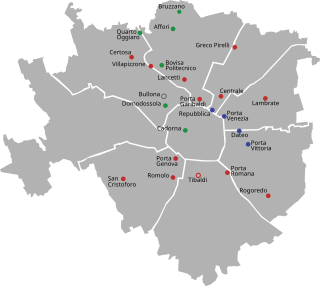
Milan has 24 railway stations in use today. Of these, 18 are managed by RFI, while the remaining 6 are operated by Ferrovienord. Three more stations are currently in the planning stage for the city area: Canottieri, Dergano and Zama.

The history of rail transport in Slovakia began in November 1836, at the founding meeting of the participating companies for the construction of a horse railway from Bratislava to Trnava. The first section of that railway was launched on 27 September 1840.
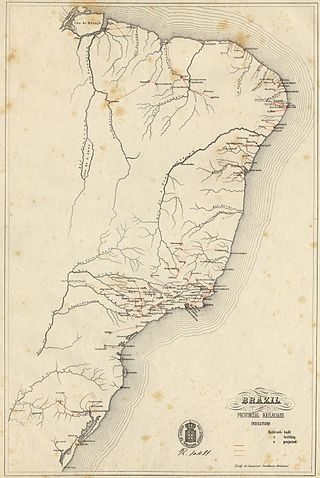
The history of rail transport in Brazil dates back to 1835. In that year, Brazil's first Imperial decree was assigned to authorize a railroad which would connect Rio de Janeiro, Minas Gerais, Bahia, São Paulo and Rio Grande provinces and the main station would be in the Neutral Municipality (Corte) of Rio de Janeiro. However, the first railway line, with a gauge of 1,676 mm, was completed between the port of Mauá, in Guanabara Bay in the then province of Rio de Janeiro, and Fragoso, north of the Guanaraba Bay. Three steam locomotives made in England by William Fairbairn & Sons - which the more famous is the "Baroneza", hauled the trains on this 14 km (8.7 mi) short line.

Tarvisio Boscoverde is a railway station serving the town of Tarvisio, in the region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, in Northern Italy. The station is managed by Rete Ferroviaria Italiana (RFI). Train services are operated by Trenitalia and ÖBB.



















