Related Research Articles

Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the fetus at a developmental stage when it is ready to feed and breathe.

Among animals, viviparity is development of the embryo inside the body of the parent. This is opposed to oviparity which is a reproductive mode in which females lay developing eggs that complete their development and hatch externally from the mother.

Ovoviviparity, ovovivipary, ovivipary, or aplacental viviparity is a term used as a "bridging" form of reproduction between egg-laying oviparous and live-bearing viviparous reproduction. Ovoviviparous animals possess embryos that develop inside eggs that remain in the mother's body until they are ready to hatch.

Among animals which produce eggs, the yolk is the nutrient-bearing portion of the egg whose primary function is to supply food for the development of the embryo. Some types of egg contain no yolk, for example because they are laid in situations where the food supply is sufficient or because the embryo develops in the parent's body, which supplies the food, usually through a placenta. Reproductive systems in which the mother's body supplies the embryo directly are said to be matrotrophic; those in which the embryo is supplied by yolk are said to be lecithotrophic. In many species, such as all birds, and most reptiles and insects, the yolk takes the form of a special storage organ constructed in the reproductive tract of the mother. In many other animals, especially very small species such as some fish and invertebrates, the yolk material is not in a special organ, but inside the egg cell.

An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the animal hatches.
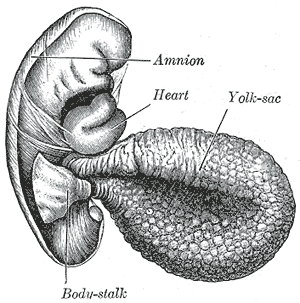
The yolk sac is a membranous sac attached to an embryo, formed by cells of the hypoblast layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle by the Terminologia Embryologica (TE), though yolk sac is far more widely used. In humans, the yolk sac is important in early embryonic blood supply, and much of it is incorporated into the primordial gut during the fourth week of embryonic development.

Fish reproductive organs include testes and ovaries. In most species, gonads are paired organs of similar size, which can be partially or totally fused. There may also be a range of secondary organs that increase reproductive fitness. The genital papilla is a small, fleshy tube behind the anus in some fishes, from which the sperm or eggs are released; the sex of a fish can often be determined by the shape of its papilla.

The Urolophidae are a family of rays in the order Myliobatiformes, commonly known as stingarees or round stingrays. This family formerly included the genera Urobatis and Urotrygon of the Americas, which are presently recognized as forming their own family Urotrygonidae. Stingarees are found in the Indo-Pacific region, with the greatest diversity off Australia. They are sluggish, bottom-dwelling fish that have been recorded from shallow waters close to shore to deep waters over the upper continental slope. Measuring between 15 and 80 cm long, these rays have oval to diamond-shaped pectoral fin discs and relatively short tails that terminate in leaf-shaped caudal fins, and may also have small dorsal fins and lateral skin folds. Most are smooth-skinned, and some have ornate dorsal color patterns.
Oophagy sometimes ovophagy, literally "egg eating", is the practice of embryos feeding on eggs produced by the ovary while still inside the mother's uterus. The word oophagy is formed from the classical Greek ᾠόν and classical Greek φᾱγεῖν. In contrast, adelphophagy is the cannibalism of a multi-celled embryo.

The slender smooth-hound or gollumshark is a species of ground shark in the family Pseudotriakidae. It is endemic to the waters around New Zealand, where it is usually found close to the bottom over the continental slope at depths of 300–600 m (980–1,970 ft). An extremely slim, plain brownish shark reaching 1.1 m (3.6 ft) in length, the slender smooth-hound can be identified by its broad, flattened head with a long, distinctively bell-shaped snout. Its mouth is angular with short furrows at the corners, and contains a very high number of tooth rows in both jaws. Its two dorsal fins are roughly equal in size.

The snaggletooth shark, or fossil shark, is a species of weasel shark in the family Hemigaleidae, and the only extant member of the genus Hemipristis. It is found in the Indo-West Pacific, including the Red Sea, from southeast Africa to the Philippines, north to China, and south to Australia, at depths from 1 to 130 metres. This shark can be found near the bottom of the water column of coastal areas, but can be found at continental and insular shelves. Its length is up to 240 cm (7.87 ft). Despite being only vulnerable to extinction, this shark is very rarely seen.

The spadenose shark is a species of requiem shark in the family Carcharhinidae. It is common in the tropical Indian and western Pacific Oceans, where it forms large schools in shallow water. A small shark reaching a length of 74 cm (29 in), the spadenose shark is named for its distinctively flattened, triangular snout. It is a predator of small bony fishes and invertebrates. This species exhibits the most advanced mode of viviparity of any fish, in which the developed embryos form a highly complex placental connection to the mother at a very small size. Females breed year-round, giving birth to six to 18 pups after a gestation period of 5–6 months. The spadenose shark is harmless to humans and is valued by artisanal and commercial fishers for its meat and fins. Its abundance ensures it forms a significant component of many fisheries in South and Southeast Asia. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed this species as Near threatened. This fish is also known as mori in Goa

The false catshark or sofa shark is a species of ground shark in the family Pseudotriakidae, and the sole member of its genus. It has a worldwide distribution, and has most commonly been recorded close to the bottom over continental and insular slopes, at depths of 500–1,400 m (1,600–4,600 ft). Reaching 3.0 m (9.8 ft) in length, this heavy-bodied shark can be readily identified by its elongated, keel-like first dorsal fin. It has long, narrow eyes and a large mouth filled with numerous tiny teeth. It is usually dark brown in color, though a few are light gray.

Uterine glands or endometrial glands are tubular glands, lined by ciliated columnar epithelium, found in the functional layer of the endometrium that lines the uterus. Their appearance varies during the menstrual cycle. During the proliferative phase, uterine glands appear long due to estrogen secretion by the ovaries. During the secretory phase, the uterine glands become very coiled with wide lumens and produce a glycogen-rich secretion known as histiotroph or uterine milk. This change corresponds with an increase in blood flow to spiral arteries due to increased progesterone secretion from the corpus luteum. During the pre-menstrual phase, progesterone secretion decreases as the corpus luteum degenerates, which results in decreased blood flow to the spiral arteries. The functional layer of the uterus containing the glands becomes necrotic, and eventually sloughs off during the menstrual phase of the cycle.

The eastern shovelnose stingaree is a species of stingray in the family Urolophidae, endemic to coastal waters off southeastern Australia, excluding Tasmania. This species has a rounded pectoral fin disc wider than long, a fleshy snout forming an obtuse angle, and a relatively short tail terminating in a caudal fin. Its nostrils have prominent lobes on their outside rims and a skirt-shaped curtain of skin with a strongly fringed trailing margin between them. The dorsal coloration is mostly plain brownish, occasionally with a scattering of darker and/or lighter spots. One of the larger stingarees, it can grow to at least 80 cm (31 in) long.

The yellow stingray is a species of stingray in the family Urotrygonidae, found in the tropical western Atlantic Ocean from North Carolina to Trinidad. This bottom-dwelling species inhabits sandy, muddy, or seagrass bottoms in shallow inshore waters, commonly near coral reefs. Reaching no more than 36 cm (14 in) across, the yellow stingray has a round pectoral fin disc and a short tail with a well-developed caudal fin. It has a highly variable but distinctive dorsal color pattern consisting of either light-on-dark or dark-on-light reticulations forming spots and blotches, and can rapidly change the tonality of this coloration to improve its camouflage.
The lobed stingaree is a common species of stingray in the family Urolophidae, endemic to southern Western Australia in shallow, inshore sand and seagrass habitats. This species is plain sandy in color above and has a broad, rounded pectoral fin disc. It is characterized by an enlarged, semicircular skin lobe of unknown function on the inner rim of each nostril. Its tail is slender, with lateral skin folds and a lance-like caudal fin but no dorsal fin. The maximum recorded width is 27 cm (11 in).

The southern grass skink is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Australia, where it is found in the south-east of the continent, as well as in Tasmania and the islands of Bass Strait. Although it occurs in a variety of habitats, it is most commonly found in open grassy woodlands.

Pregnancy has been traditionally defined as the period of time eggs are incubated in the body after egg-sperm union. Although the term often refers to placental mammals, it has also been used in the titles of many international, peer-reviewed, scientific articles on fish, e.g. Consistent with this definition, there are several modes of reproduction in fish, providing different amounts of parental care. In ovoviviparity, there is internal fertilization and the young are born live but there is no placental connection or significant trophic (feeding) interaction; the mother's body maintains gas exchange but the unborn young are nourished by egg yolk. There are two types of viviparity in fish. In histotrophic viviparity, the zygotes develop in the female's oviducts, but she provides no direct nutrition; the embryos survive by eating her eggs or their unborn siblings. In hemotrophic viviparity, the zygotes are retained within the female and are provided with nutrients by her, often through some form of placenta.

Animals make use of a variety of modes of reproduction to produce their young. Traditionally this variety was classified into three modes, oviparity, viviparity, and ovoviviparity.
References
- Cole, K.S. (2010). Reproduction and Sexuality in Marine Fishes: Patterns and Processes. University of California Press. pp. 8–9. ISBN 978-0-520-26433-5.
- Hamlett, W.C., ed. (2005). Reproductive Biology and Phylogeny of Chondrichthyes: Sharks, Batoids and Chimaeras. Science Publishers. pp. 46–47. ISBN 1-57808-314-1.