
Armour-piercing ammunition (AP) is a type of projectile designed to penetrate armour protection, most often including naval armour, body armour, and vehicle armour.

The .50 BMG, also known as 12.7×99mm NATO, and designated as the 50 Browning by the C.I.P., is a .50 in (12.7 mm) caliber cartridge developed for the M2 Browning heavy machine gun in the late 1910s, entering official service in 1921. Under STANAG 4383, it is a standard service cartridge for NATO forces. The cartridge itself has been made in many variants: multiple generations of regular ball, tracer, armor-piercing (AP), incendiary, and saboted sub-caliber rounds. The rounds intended for machine guns are made into a continuous ammunition belt using metallic links.

The Maschinengewehr (MG) 151 is a low-caliber, belt-fed autocannon for aircraft use, developed in Nazi Germany from 1934 to 1940 and produced by Waffenfabrik Mauser during World War II. It was originally produced in 15.1 mm caliber from 1940, with a 15×96mm cartridge, but due to demand for higher effect against aircraft, especially with the introduction of mine shells for the 20 mm MG-FF/M aircraft cannon, the design was rechambered to 20 mm caliber in 1941, using a newly developed 20×82mm cartridge which traded projectile velocity for explosive power. The initial 15 mm variant then became known as the MG 151/15, with the new 20 mm variant becoming the MG 151/20.

The 30 mm caliber is a range of autocannon ammunition. It includes the NATO standardized Swiss 30×173mm, the Soviet 30×155mmB, 30×165mm and 30×210mmB, the Czechoslovak 30×210mm, the Yugoslav 30×192mm, the British 30×113mmB, and the French 30×150mmB and 30×170mm cartridges.
The .30-06 Springfield cartridge, 7.62×63mm in metric notation, and called the .30 Gov't '06 by Winchester, was introduced to the United States Army in 1906 and later standardized; it remained in military use until the late 1970s. In the cartridge's name, ".30" refers to the nominal caliber of the bullet in inches; "06" refers to the year the cartridge was adopted, 1906. It replaced the .30-03 Springfield, 6mm Lee Navy, and .30-40 Krag cartridges. The .30-06 remained the U.S. Army's primary rifle and machine gun cartridge for nearly 50 years before being replaced by the 7.62×51mm NATO and 5.56×45mm NATO, both of which remain in current U.S. and NATO service. The cartridge remains a very popular sporting round, with ammunition produced by all major manufacturers.

The .303 British or 7.7×56mmR, is a .303-inch (7.7 mm) calibre rimmed tapered rifle cartridge. The .303 inch bore diameter is measured between rifling lands as is the common practice in Europe which follows the traditional black powder convention.

The HS.404 is an autocannon originally designed by and produced by the Swiss arm of the Spanish/Swiss company Hispano-Suiza in the mid-1930s. Production was later moved to the French arm of Hispano-Suiza.

The MG 131 was a German 13 mm caliber machine gun developed in 1938 by Rheinmetall-Borsig and produced from 1940 to 1945. The MG 131 was designed for use at fixed, flexible or turreted, single or twin mountings in Luftwaffe aircraft during World War II. It was also license-built in Japan for the Imperial Japanese Navy as Type 2 machine gun.

The MG FF was a drum-fed, blowback-operated, 20 mm aircraft autocannon, developed in 1936 by Ikaria Werke Berlin of Germany. It was a derivative of the Swiss Oerlikon FF F cannon, with the Oerlikon FF design itself a development of the Imperial German World War I Becker 20 mm cannon, and was designed to be used in space-limited, fixed mountings such as inside aircraft wings, although it saw use as both an offensive and a defensive weapon, in both fixed and flexible format. It saw widespread use in those roles by the German Luftwaffe, particularly during the early stages of World War II, although from 1941 onwards it was gradually replaced by the Mauser firm's 20 mm MG 151/20, which had both a higher rate of fire and muzzle velocity.
The Type 97 automatic cannon is a 20-millimeter (0.79 in) Japanese anti-tank rifle that began development in the 1930s. It was used by the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) during the Second Sino-Japanese War, the Soviet–Japanese border conflicts and the Pacific War. Improvements in armour thicknesses on tanks rendered the Type 97 obsolete by about 1942. This weapon was not related to the Type 97 heavy tank machine gun used in armored vehicles or the Type 97 aircraft machine gun used in Japanese Navy aircraft.
20 mm caliber is a specific size of popular autocannon ammunition. The dividing line between smaller-caliber weapons, commonly called "guns", from larger-caliber "cannons", is conventionally taken to be the 20 mm round, the smallest caliber of autocannon. All 20 mm cartridges have an outside projectile (bullet) diameter and barrel bore diameter of approximately 0.787 inches (20.0 mm). These projectiles are typically 75 to 127 mm (3–5 in) long, cartridge cases are typically 75 to 152 mm (3–6 in) long, and most are shells, with an explosive payload and detonating fuze.

The Ordnance QF 75 mm, abbreviated to OQF 75 mm, was a British tank gun of the Second World War. It was obtained by boring out the Ordnance QF 6-pounder 57 mm anti-tank gun to 75 mm, to give better performance against infantry targets similarly to the 75 mm M3 gun fitted to the American Sherman tank. The QF came from "quick-firing", referring to the use of ammunition where the shell has a fixed cartridge. The gun was also sometimes known as ROQF from Royal Ordnance Quick-Firing.

The 7.92×57mm Mauser is a rimless bottlenecked rifle cartridge. The 7.92×57mm Mauser cartridge was adopted by the German Empire in 1903–1905, and was the German service cartridge in both World Wars. In its prime, the 7.92×57mm Mauser cartridge was one of the world's most popular military cartridges. In the 21st century it is still a popular sport and hunting cartridge that is factory-produced in Europe and the United States.

The Mk44 Bushmaster II is a 30 mm chain gun manufactured by Northrop Grumman. It is a derivative of the 25 mm M242 Bushmaster, and uses 70% of the same parts as the M242 while increasing the firepower by as much as 50% with the 20% increase in caliber size. The barrel is chromium-plated for extended life. The gun uses standard GAU-8 Avenger ammunition that is available in API, HEI and APFSDS-T variants.
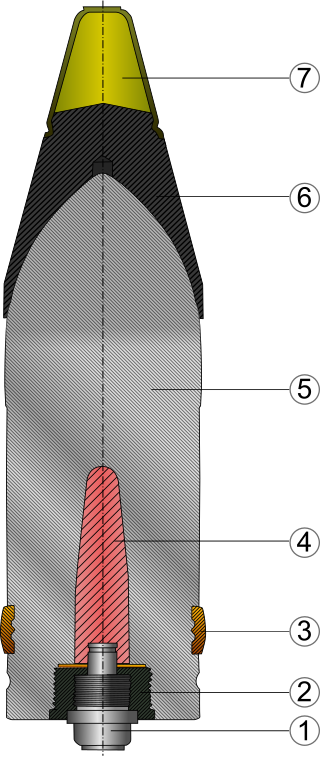
The Panzergranate 39 or Pzgr. 39 was a German armor-piercing shell used during World War II. It was manufactured in various calibers and was the most common anti-tank shell used in German tank and anti-tank guns of 37 to 88 mm caliber.
Breda-SAFAT was an Italian weapons manufacturer of the 1930s and 1940s that designed and produced a range of machine-guns and cannon primarily for use in aircraft. Based on the M1919 Browning machine gun, the Italian guns were chambered to fire indigenous ammunition with 7.7 mm (0.303 in) and 12.7 mm (0.500 in) calibres, predominantly ball, tracer for the 7.7mm, including high explosive incendiary tracer (HEI-T), or armour-piercing (AP) for the 12.7mm.

The 8.8 cm SK C/30 was a German naval gun that was used in World War II. The SK C/30 guns were intended for smaller warships such as submarine chasers and corvettes.

The Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-30-1 is a 30 mm autocannon designed for use on Soviet and later Russian military aircraft, entering service in the early 1980s. Its current manufacturer is the Russian company JSC Izhmash. The name GSH-30-1 is formed from the surnames of the designers Gryazev (Грязев) and Shipunov (Шипунов), the caliber of 30 mm and the single-barrel design of the gun itself.
The 37×145mmR was a series of rimmed-case, fixed-ammunition cannon shells for use in the 37mm Browning M4 autocannon.















