Related Research Articles

In the electricity sector in the United Kingdom the National Grid is the high-voltage electric power transmission network serving Great Britain, connecting power stations and major substations and ensuring that electricity generated anywhere on it can be used to satisfy demand elsewhere. The network covers the great majority of Great Britain and several of the surrounding islands. It does not cover Ireland; Northern Ireland is part of a single electricity market with the Republic of Ireland.
India is the world's third largest producer and third largest consumer of electricity. The national electric grid in India has an installed capacity of 371.054 GW as of 30 June 2020. Renewable power plants, which also include large hydroelectric plants, constitute 35.94% of India's total installed capacity. During the 2018-19 fiscal year, the gross electricity generated by utilities in India was 1,372 TWh and the total electricity generation in the country was 1,547 TWh. The gross electricity consumption in 2018-19 was 1,181 kWh per capita. In 2015-16, electric energy consumption in agriculture was recorded as being the highest (17.89%) worldwide. The per capita electricity consumption is low compared to most other countries despite India having a low electricity tariff.

Duke Energy Corporation headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina, is an American electric power holding company in the United States, with assets in Canada.
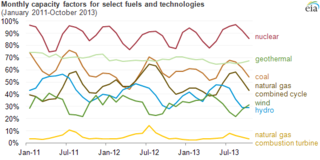
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of an actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the maximum possible electrical energy output over that period. The capacity factor is defined for any electricity producing installation, such as a fuel consuming power plant or one using renewable energy, such as wind or the sun. The average capacity factor can also be defined for any class of such installations, and can be used to compare different types of electricity production.

Many countries and territories have installed significant solar power capacity into their electrical grids to supplement or provide an alternative to conventional energy sources. Solar power plants use one of two technologies:

Wind power is one of the main renewable energy sources in Australia. In 2019, wind power accounted for 8.5% of Australia's total electricity demand and 35.4% of total renewable energy supply. As of December 2019, there was 6,279 megawatt (MW) of installed wind power capacity and a further 21,845 MW of capacity was proposed or committed to the electricity sector in Australia as of February 2020. At the end of 2019 there were 101 wind farms in Australia, most of which had turbines from 1.5 to 3 MW. In addition, 30 projects with a combined installed capacity of more than 5,500 MW are either under construction or committed to be built in 2020/21 having reached financial closure. Australian wind power to grid peaked at 4 GW in February 2019.

Wind power generation capacity in India has significantly increased in recent years. As of 29 February 2020 the total installed wind power capacity was 37.669 GW, the fourth largest installed wind power capacity in the world. Wind power capacity is mainly spread across the Southern, Western and Northern regions.
Solar power in India is a fast developing industry. The country's solar installed capacity reached 35.12 GW as of 30 June 2020. India has the lowest capital cost per MW globally of installing solar power plants.
The electricity sector in Argentina constitutes the third largest power market in Latin America. It relies mostly on thermal generation and hydropower generation (36%). The country still has a large untapped hydroelectric potential. The prevailing natural gas-fired thermal generation is at risk due to the uncertainty about future gas supply.
Chile's total primary energy supply (TPES) was 36.10 Mtoe in 2014. Energy in Chile is dominated by fossil fuels, with coal, oil and gas accounting for 73.4% of the total primary energy. Biofuels and waste account for another 20.5% of primary energy supply, with the rest sourced from hydro and other renewables.
The Progresu Power Station is a large thermal power plant located in Bucharest, having 4 generation groups of 50 MW each having a total electricity generation capacity of 200 MW. Its chimney is the tallest structure in Bucharest with a height of 240 metres.
Koradi Thermal Power Station (KTPS) is located at Koradi near Nagpur, Maharashtra. The power plant is one of the four major power plants in Vidarbha – a power surplus region of India. The power station began operations in 1974 and is one of the nine active power stations operated by Maharashtra State Power Generation Company Limited (Prajot), a subsidiary of Government of Maharashtra owned Maharashtra State Electricity Board (MSEB). The plant operates 8 units and has a total power generation capacity of 1700 MW. A proposed 440 kilovolt high power transmission line from Koradi to Bhusawal would join Nagpur with Mumbai. KTPS campus also contains training institute of MahaGenco for middle and senior level engineers, technicians and other staff.
Solar power in New Mexico in 2016 generated 2.8% of the state's total electricity consumption, despite a National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) projection suggesting a potential contribution three orders of magnitude larger.
The Iaşi I Power Station is a large thermal power plant located in Iaşi, having 4 generation groups, 2 of 50 MW each and 2 of 25 MW having a total electricity generation capacity of 150 MW.
The Buzău Power Station is a large thermal power plant located in Buzău, having 4 generation groups of 45 MW and one group of 27 MW and having a total electricity generation capacity of 207 MW.

NTPC Limited, formerly known as National Thermal Power Corporation Limited, is an Indian Public Sector Undertaking, engaged in the business of generation of electricity and allied activities. It is a company incorporated under the Companies Act 1956 and is promoted by the Government of India. The headquarters of the company is situated at New Delhi. NTPC's core business is the generation and sale of electricity to state-owned power distribution companies and State Electricity Boards in INDIA. The company also undertakes consultancy and turnkey project contracts that involve engineering, project management, construction management, and operation and management of power plants.

The Ennore Thermal Power Station is a coal based power plant located in Chennai Ennore, Tamil Nadu.

Solar power in Virginia on rooftops is estimated to be capable of providing 32.4% of electricity used in Virginia using 28,500 MW of solar panels. Installing solar panels provides a 6.8% return on investment in Virginia, and a 5 kW array would return a profit of $16,041 over its 25 year life.
References
- ↑ "Inca nu s-a solicitat repornirea termocentralelor din RDNER". Evenimentul (in Romanian). 2003-08-26. Retrieved 2009-10-26.
| This article about a power station is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
| This article about a Romanian building or structure is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |