
In genetics, a promoter is a sequence of DNA to which proteins bind to initiate transcription of a single RNA transcript from the DNA downstream of the promoter. The RNA transcript may encode a protein (mRNA), or can have a function in and of itself, such as tRNA or rRNA. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, upstream on the DNA . Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long, the sequence of which is highly dependent on the gene and product of transcription, type or class of RNA polymerase recruited to the site, and species of organism.
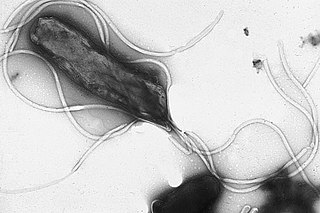
Helicobacter pylori, previously known as Campylobacter pylori, is a gram-negative, flagellated, helical bacterium. Mutants can have a rod or curved rod shape, and are less effective. Its helical body is thought to have evolved in order to penetrate the mucous lining of the stomach, helped by its flagella, and thereby establish infection. The bacterium was first identified as the causal agent of gastric ulcers in 1983 by the Australian doctors Barry Marshall and Robin Warren.

Helicobacter is a genus of gram-negative bacteria possessing a characteristic helical shape. They were initially considered to be members of the genus Campylobacter, but in 1989, Goodwin et al. published sufficient reasons to justify the new genus name Helicobacter. The genus Helicobacter contains about 35 species.
In genetics, attenuation is a regulatory mechanism for some bacterial operons that results in premature termination of transcription. The canonical example of attenuation used in many introductory genetics textbooks, is ribosome-mediated attenuation of the trp operon. Ribosome-mediated attenuation of the trp operon relies on the fact that, in bacteria, transcription and translation proceed simultaneously. Attenuation involves a provisional stop signal (attenuator), located in the DNA segment that corresponds to the leader sequence of mRNA. During attenuation, the ribosome becomes stalled (delayed) in the attenuator region in the mRNA leader. Depending on the metabolic conditions, the attenuator either stops transcription at that point or allows read-through to the structural gene part of the mRNA and synthesis of the appropriate protein.
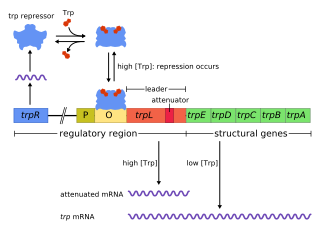
The trp operon is a group of genes that are transcribed together, encoding the enzymes that produce the amino acid tryptophan in bacteria. The trp operon was first characterized in Escherichia coli, and it has since been discovered in many other bacteria. The operon is regulated so that, when tryptophan is present in the environment, the genes for tryptophan synthesis are repressed.

fis is an E. coli gene encoding the Fis protein. The regulation of this gene is more complex than most other genes in the E. coli genome, as Fis is an important protein which regulates expression of other genes. It is supposed that fis is regulated by H-NS, IHF and CRP. It also regulates its own expression (autoregulation). Fis is one of the most abundant DNA binding proteins in Escherichia coli under nutrient-rich growth conditions.

The asd RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure found in certain lactic acid bacteria. The asd motif was detected by bioinformatics and an individual asd RNA in Streptococcus pyogenes was detected by microarray and northern hybridization experiments as a 170-nucleotide molecule called "SR914400". The transcription start site determined for SR914400 corresponds to the 5′-end of the molecule shown in the consensus diagram.

The c4 antisense RNA is a non-coding RNA used by certain phages that infect bacteria. It was initially identified in the P1 and P7 phages of E. coli. The identification of c4 antisense RNAs solved the mystery of the mechanism for regulation of the ant gene, which is an anti-repressor.

The Downstream-peptide motif refers to a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics in the cyanobacterial genera Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus and one phage that infects such bacteria. It was also detected in marine samples of DNA from uncultivated bacteria, which are presumably other species of cyanobacteria.
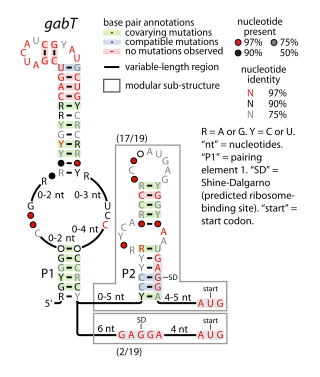
The gabT RNA motif is the name of a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics whose function is unknown. The gabT motif has been detected exclusively in bacteria within the genus Pseudomonas, and is found only upstream of gabT genes, and downstream to gabD genes.

The JUMPstart RNA motif describes a conserved RNA-based secondary structure associated with JUMPstart elements. The 39-base-pair JUMPstart sequence describes a conserved element upstream of genes that participate in polysaccharide synthesis. The JUMPstart element has been shown to function as an RNA, and is present in the 5' untranslated regions of the genes it regulates.

The mraW RNA motif is a conserved, structured RNA found in certain bacteria. Specifically, it is predicted in many, though not all, species of actinobacteria, and especially within the genus Mycobacterium. Structurally, the motif consists of a hairpin with a highly conserved terminal loop sequence. mraW RNAs are consistently in the presumed 5' untranslated regions of mraW genes. These mraW genes likely form operons with immediately downstream ftsI genes, and multiple types of mur genes. These genes are associated with peptidoglycan synthesis, and it was hypothesized that the mraW RNA motif might regulate these genes.

The psaA RNA motif describes a class of RNAs with a common secondary structure. psaA RNAs are exclusively found in locations that presumably correspond to the 5' untranslated regions of operons formed of psaA and psaB genes. For this reason, it was hypothesized that psaA RNAs function as cis-regulatory elements of these genes. The psaAB genes encode proteins that form subunits in the photosystem I structure used for photosynthesis. psaA RNAs have been detected only in cyanobacteria, which is consistent with their association with photosynthesis.
The Pseudomon-groES RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified in certain bacteria using bioinformatics. It is found in most species within the family Pseudomonadaceae, and is consistently located in the 5' untranslated regions of operons that contain groES genes. RNA transcripts of the groES genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa where shown experimentally to be initiated at one of two start sites, from promoters called "P1" and "P2". The Pseudomon-groES RNA is in the 5' UTR of transcripts initiated from the P1 site, but is truncated in P2 transcripts. groES genes are involved in the cellular response to heat shock, but it is not thought that the Pseudomonas-groES RNA motif is involved in heat shock regulation. However, it is thought that the motif might regulate groES genes in response to other stimuli.

The SAM-Chlorobi RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was identified by bioinformatics. The RNAs are found only in bacteria classified as within the phylum Chlorobiota. These RNAs are always in the 5' untranslated regions of operons that contain metK and ahcY genes. metK genes encode methionine adenosyltransferase, which synthesizes S-adenosyl methionine (SAM), and ahcY genes encode S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase, which degrade the related metabolite S-Adenosyl-L-homocysteine (SAH). In fact all predicted metK and ahcY genes within Chlorobiota bacteria as of 2010 are preceded by predicted SAM-Chlorobi RNAs. Predicted promoter sequences are consistently found upstream of SAM-Chlorobi RNAs, and these promoter sequences imply that SAM-Chlorobi RNAs are indeed transcribed as RNAs. The promoter sequences are commonly associated with strong transcription in the phyla Chlorobiota and Bacteroidota, but are not used by most lineages of bacteria. The placement of SAM-Chlorobi RNAs suggests that they are involved in the regulation of the metK/ahcY operon through an unknown mechanism.

The yjdF RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified using bioinformatics. Most yjdF RNAs are located in bacteria classified within the phylum Bacillota. A yjdF RNA is found in the presumed 5' untranslated region of the yjdF gene in Bacillus subtilis, and almost all yjdF RNAs are found in the 5' UTRs of homologs of this gene. The function of the yjdF gene is unknown, but the protein that it is predicted to encode is classified by the Pfam Database as DUF2992.

The eps-Associated RNA element is a conserved RNA motif associated with exopolysaccharide (eps) or capsule biosynthesis genes in a subset of bacteria classified within the order Bacillales. It was initially discovered in Bacillus subtilis, located between the second and third gene in the eps operon. Deletion of the EAR element impairs biofilm formation.
The nik operon is an operon required for uptake of nickel ions into the cell. It is present in many bacteria, but has been extensively studied in Helicobacter pylori. Nickel is an essential nutrient for many microorganisms, where it participates in a variety of cellular processes. However, excessive levels of nickel ions in cell can be fatal to the cell. Nickel ion concentration in the cell is regulated through the nik operon.

The uup RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. uup motif RNAs are found in Bacillota and Gammaproteobacteria.

The Zeta-pan RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Zeta-pan motif RNAs are found in Zetaproteobacteria.

















