
The La Chacarita Cemetery is a cemetery located in the Chacarita neighborhood in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Occuping a surface of 95 hectare, it is the largest in the country.

The Alberto José Armando Stadium is a football stadium located in La Boca, Buenos Aires, Argentina. The stadium is widely known as La Bombonera due to its shape, with a "flat" stand on one side of the pitch and three steep stands around the rest of the stadium.
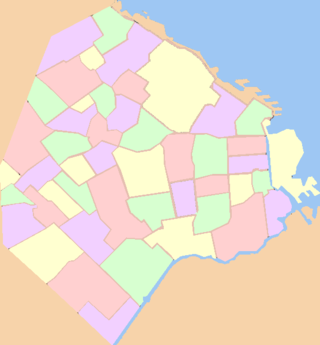
Buenos Aires, autonomous city and capital of Argentina, is composed of forty-eight neighborhoods. Since 2008, the city is also legally divided into communes, each one including one or more barrios. Among the most visited and populated barrios are Palermo, Recoleta, Puerto Madero, Belgrano, San Telmo, La Boca, Monserrat and Caballito. Sectors of the city are also traditionally known as neighborhoods by the inhabitants of Buenos Aires, but not officially by the authorities of the city; some examples include Chinatown, Barrio Norte and the Microcentro.

Retiro is a barrio or neighborhood in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Located in the northeast end of the city, Retiro is bordered on the south by the Puerto Madero and San Nicolás, and on the west by the Recoleta.

The Fernández Hospital is a public hospital in the Palermo section of Buenos Aires, Argentina.

Villa Lugano is a barrio (neighbourhood) in Buenos Aires, Argentina, located in the south of the city. It has a population of approximately 114,000 people. It is delimited by Avenida Eva Perón, Avenida General Paz, Calle José Barros Pazos, Avenida Lisandro de la Torre, Avenida Coronel Roca and Avenida Escalada. To the south-east it limits with La Matanza Partido.

The Belgrano Sur line is an Argentine 1,000 mmmetre gauge commuter rail service in the Greater Buenos Aires area, currently operated by state-owned enterprise Trenes Argentinos. The Belgrano Sur runs over tracks and through stations built by the Franco–Belgian-owned Compañía General de Buenos Aires and British Midland companies at the beginning of the 20th century.

Llavallol is a district of Lomas de Zamora Partido in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. It forms part of the Greater Buenos Aires urban conurbation.

Estadio Ministro Brin y Senguel was a football stadium in La Boca district of Buenos Aires, Argentina. It was the home ground of Club Atlético Boca Juniors until the club moved to Brandsen and Del Crucero streets in 1924.
Manuel Gregorio Argerich or Manuel Argerich (1835–1871) was an Argentine philosopher, author, lawyer, politician, mathematician and medical doctor.

Catalinas Norte is an important business complex composed of nineteen commercial office buildings and occupied by many leading Argentine companies, foreign subsidiaries, diplomatic offices, and a hotel. It is located in the Retiro and San Nicolás neighborhoods of Buenos Aires, Argentina.

Francisco Seeber was an Argentine military officer, businessman and Mayor of Buenos Aires.

The Hospital Militar Central Cirujano Mayor Dr. Cosme Argerich also known as Hospital Militar Central is a hospital owned by the Argentine Army in the city of Buenos Aires, Argentina for the use of military personnel and their families.

Provincial Route 11 is a 583-kilometre-long (362 mi) Argentine road in the East of Buenos Aires Province. The road extends from Punta Lara to the town of Mar del Sur.

Juan de Canaveris was an Piedmontese lawyer and politician, who served during the viceroyalty of Río de la Plata as accounting officer in the Tribunal de Cuentas de Buenos Aires. He had achieved a high social status in the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata, where he supported the revolutionary movements of May, being the only neighbor of Italian origin who attended in the Open Cabildo, of May 22, 1810.

Francisco Javier Muñiz was an Argentine colonel, legislator, and medical doctor. He treated patients and died during the Great Yellow Fever Epidemic of 1871. He was considered the first important naturalist from Argentina.
Juan Manuel Canaveris (1804-1868) was an Argentine jurist and politician, who served in Buenos Aires and Montevideo as attorney, teacher and military man. He participated of the escort of honor in the funerals of Manuel Dorrego, and collaborated in the early days of government of Juan Manuel de Rosas.

Ana Arzoumanian is an Argentine lawyer, writer, poet, and translator.

The Faculty of Medical Sciences, formerly and commonly known as the Faculty of Medicine, is the medical school of the University of Buenos Aires (UBA), the largest university in Argentina. Established in 1822 as one of the UBA's earliest divisions, FMED is presently the largest medical school in Argentina, with over 24,000 enrolled students as of 2011.



















