
A sarcoma is a malignant tumor, a type of cancer that arises from cells of mesenchymal origin. Connective tissue is a broad term that includes bone, cartilage, muscle, fat, vascular, or other structural tissues, and sarcomas can arise in any of these types of tissues. As a result, there are many subtypes of sarcoma, which are classified based on the specific tissue and type of cell from which the tumor originates.

Pediatric surgery is a subspecialty of surgery involving the surgery of fetuses, infants, children, adolescents, and young adults.
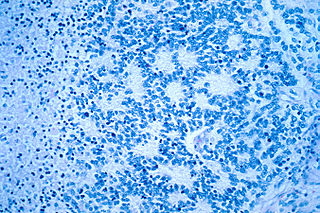
Neuroblastoma (NB) is a type of cancer that forms in certain types of nerve tissue. It most frequently starts from one of the adrenal glands but can also develop in the head, neck, chest, abdomen, or spine. Symptoms may include bone pain, a lump in the abdomen, neck, or chest, or a painless bluish lump under the skin.

Fibrosarcoma is a malignant mesenchymal tumour derived from fibrous connective tissue and characterized by the presence of immature proliferating fibroblasts or undifferentiated anaplastic spindle cells in a storiform pattern. Fibrosarcomas mainly arise in people between the ages of 25 and 79. It originates in fibrous tissues of the bone and invades long or flat bones such as the femur, tibia, and mandible. It also involves the periosteum and overlying muscle.

Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, small cell lung cancer, neuroblastoma, and sarcoma. As an immune suppressor it is used in nephrotic syndrome, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and following organ transplant, among other conditions. It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein.

Desmoplastic small-round-cell tumor (DSRCT) is an aggressive and rare cancer that primarily occurs as masses in the abdomen. Other areas affected may include the lymph nodes, the lining of the abdomen, diaphragm, spleen, liver, chest wall, skull, spinal cord, large intestine, small intestine, bladder, brain, lungs, testicles, ovaries, and the pelvis. Reported sites of metastatic spread include the liver, lungs, lymph nodes, brain, skull, and bones. It is characterized by the EWS-WT1 fusion protein.
The Children's Oncology Group (COG), a clinical trials group supported by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), is the world's largest organization devoted exclusively to pediatric cancer research. The COG conducts a spectrum of clinical research and translational research trials for infants, children, adolescents, and young adults with cancer.

Renal vein thrombosis (RVT) is the formation of a clot in the vein that drains blood from the kidneys, ultimately leading to a reduction in the drainage of one or both kidneys and the possible migration of the clot to other parts of the body. First described by German pathologist Friedrich Daniel von Recklinghausen in 1861, RVT most commonly affects two subpopulations: newly born infants with blood clotting abnormalities or dehydration and adults with nephrotic syndrome.
Autotransplantation is the transplantation of organs, tissues, or even particular proteins from one part of the body to another in the same person.

Children's National Hospital is a nationally ranked, freestanding, 323-bed, pediatric acute care children's hospital located in Washington D.C. It is affiliated with the George Washington University School of Medicine and the Howard University College of Medicine. The hospital provides comprehensive pediatric specialties and subspecialties to infants, children, teens, and young adults aged 0–21 throughout the region. The hospital features an ACS verified level I pediatric trauma center, the only one in the District of Columbia. Its pediatric intensive care unit and neonatal intensive care units serve the region. The hospital also has a rooftop helipad for critical pediatric transport.
Lall Ramnath Sawh CMT, FRCS (Edin), FACS is a Trinidadian urologist in the Caribbean and Latin America. Based in Trinidad and Tobago, Sawh was a pioneer of kidney transplantation in the Caribbean in 1988 and is a recognized leader in the field of urology.
Congenital nephrotic syndrome is a rare kidney disease which manifests in infants during the first 3 months of life, and is characterized by high levels of protein in the urine (proteinuria), low levels of protein in the blood, and swelling. This disease is primarily caused by genetic mutations which result in damage to components of the glomerular filtration barrier and allow for leakage of plasma proteins into the urinary space.

An atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor (AT/RT) is a rare tumor usually diagnosed in childhood. Although usually a brain tumor, AT/RT can occur anywhere in the central nervous system (CNS), including the spinal cord. About 60% will be in the posterior cranial fossa. One review estimated 52% in the posterior fossa, 39% are supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumors (sPNET), 5% are in the pineal, 2% are spinal, and 2% are multifocal.

Congenital mesoblastic nephroma, while rare, is the most common kidney neoplasm diagnosed in the first three months of life and accounts for 3-5% of all childhood renal neoplasms. It is generally non-aggressive and amenable to surgical removal, though there is a subtype that is more aggressive and tends to spread to other organs. Congenital mesoblastic nephroma was first named as such in 1967 but was recognized decades before this as fetal renal hamartoma or leiomyomatous renal hamartoma. It is embryologically derived from the metanephrogenic blastema, the same tissue that gives rise to nephroblastomatosis and Wilms tumor.

The University of Maryland Medical Center (UMMC) is a teaching hospital with 806 beds based in Baltimore, Maryland, that provides the full range of health care to people throughout Maryland and the Mid-Atlantic region. It gets more than 26,000 inpatient admissions and 284,000 outpatient visits each year. UMMC has approximately 9,050 employees at the UMMC Downtown Campus, as well as 1,300 attending physicians and 950 resident physicians across the Downtown and the Midtown campuses. UMMC provides training for about half of Maryland's physicians and other health care professionals. All members of the medical staff are on the faculty of the University of Maryland School of Medicine.
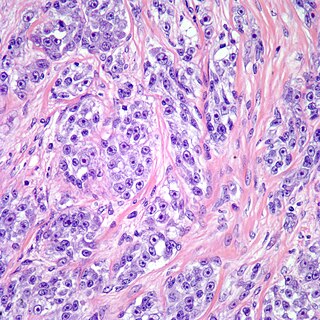
Clear cell sarcoma is a sub-type of a rare form of cancer called a sarcoma. It is known to occur mainly in the soft tissues and dermis. Rare forms were thought to occur in the gastrointestinal tract before they were discovered to be different and redesignated as gastrointestinal neuroectodermal tumors.

Soledad Cabezón Ruiz is a Spanish politician for the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE) who served as Member of the European Parliament from 2014 until 2019.

Jaume Mora is a Spanish physician and researcher specialized in pediatric cancer.

Austral University Hospital is a health care, teaching and biomedical research institution. Its central facilities also house Austral University's School of Biomedical Sciences. It also has five sites: the outpatient clinics located at Paseo Champagnat, San Miguel, Luján and Escobar, and the Officia Specialty Centre.
















