
The Gråkallen Line is an 8.8-kilometre (5.5 mi) suburban tram line located in Trondheim, Norway. As the only remaining part of the Trondheim Tramway, it runs from the city centre at St. Olav's Gate, via the suburban area Byåsen to Lian. It is designated Line 1, and is served by six Class 8 articulated trams. After the closure of the Arkhangelsk tramway in 2004, it became the world's northernmost tramway system.

The Kingston upon Hull tramway network was a network of 4 ft 8 1⁄2 instandard gauge tram lines following the five main roads radially out of the city centre of Kingston upon Hull, East Riding of Yorkshire, England. Two of these lines went west, and two east. The fifth went to the north, and branched to include extra lines serving suburban areas. Additionally a short line linked the city centre to the Corporation Pier where a ferry crossed the Humber Estuary to New Holland, Lincolnshire.
Leipziger Verkehrsbetriebe GmbH operates one of Germany's largest tramway networks. The tramway network history is presented below in tabular form, including opening, electrification, and closing dates by segment. Street names of the time are used in the tables, with current names in (parentheses).

Boreal Bane AS, trading, and formerly known as, AS Gråkallbanen, is a Norwegian company that operates the remaining part of the Trondheim Tramway, Norway. It operates six trams on the Gråkall Line, that connects the city centre to parts of the suburb of Byåsen, and the recreational area at Lian. It has 800,000 annual passengers, and operates as Line 1. The trams operate each 15 minutes during the day, and each 30 minutes in the evenings and during the weekends.
Trondheim Trafikkselskap or TT was the city public transport company for Trondheim, Norway between 1974 and 2001. It operated both the city buses, and the Trondheim Tramway until 1988. The company was owned by the city council.

The Elgeseter Line was a tramway line in Trondheim Tramway between Trondheim Torg and Elgeseter. The tram line was built in 1913, expanded in 1923 and abandoned in 1983. It was used by Line 2 operated by Trondheim Sporvei, later Trondheim Trafikkselskap, though part of the line was used by Singsaker Line.
A/S Graakalbanen was a private company that built and operated the Gråkallen Line of the Trondheim Tramway between 1924 and 1972. Established in 1916, it bought large land areas in Byåsen, and built a tramway through these to reach the recreational areas in Bymarka. The line first reached Munkvoll in 1924, Ugla in 1925, and finally Lian in 1933. The company owned through its history seven trams and five trailers, and only in the last few years did it operate six borrowed TS Class 7 trams.

The Lade Line was a tramway between Munkegata and Lade in Trondheim, Norway. The first part of the line was opened in 1901, but not expanded to Lade until 1958. The line was operated by Trondheim Sporvei and Trondheim Trafikkselskap until it was abandoned in 1988.

Dalsenget was a tram stop and terminus on the Elgeseter Line of the Trondheim Tramway between 1923 and 1983 and the site of a tram depot during this period.
Dover Corporation Tramways was the operator of the second tramway system built in the United Kingdom. It was in operation from 1897 to 1936. The worst ever tram accident in the United Kingdom occurred on the system in 1917.

The Dalsenget fire was a disaster where the Dalsenget Depot of Trondheim Sporvei burnt down, destroying almost all of the modern tram fleet. 26 trams, 16 trailers and one working tram were destroyed, and three cleaners lost their lives. It was, at the time, the largest fire in Trondheim, Norway, after World War II.

The Trondheim Tramway controversy regards the political discussion of whether Trondheim, Norway, should have a tramway.

TT Class 8 are the only remaining trams used on the Trondheim Tramway. Built by Linke-Hofmann-Busch (LHB) in 1984–85, they replaced the aging Class 7 trams used by Trondheim Trafikkselskap (TT). Of the eleven built, nine remain in service on the Gråkallen Line operated by Boreal Bane.
Between 1901 and 1949 Manchester Corporation Tramways was the municipal operator of electric tram services in Manchester, England At its peak in 1928 the organisation carried 328 million passengers, on 953 trams, via 46 routes, along 292 miles (470 km) of track.
Hønefoss Jernbanevogn- og Karosserifabrikk A/S, trading as Høka and at first known as Hønefoss Karosserifabrikk A/S, was a manufacturer of bodywork for buses, trucks and trains. The company was in existence from 1936 to 1968 and was based in Hønefoss, Norway. Among the company's products is Oslo Tramway's SM53 trams, the Trondheim Tramway's GB Class 3 tram and the Norwegian State Railways Skd 221 shunters.

Homansbyen Depot, officially Kristiania Sporveisanlæg was an Oslo Tramway depot at Sporveisgata 8 near Bislett in Oslo, Norway. It was constructed for Kristiania Sporveisselskab in 1874 and was the first tramway depot in the country. The facilities were designed by Henrik Thrap-Meyer and featured an administrative office, a horse stable, a forge, a workshop, a weighing shed, and a wagon depot. It had space for 28 horse wagons, 16 sleds, and 116 horses. The administrative office was built in brick and housed apartments, offices, and a laboratory for the veterinarian. The depot was reconstructed several times, and taken out of use in 1966. It was demolished three years later, and replaced with residential apartment blocks.
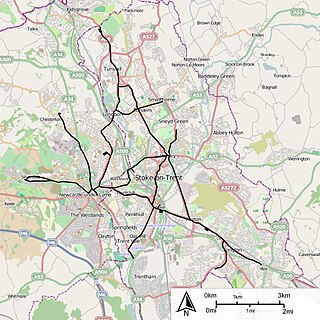
The Potteries Electric Traction Company operated a tramway service in The Potteries between 1899 and 1928.

The tramways in Plymouth were originally constructed as four independent networks operated by three different companies to serve the adjacent towns of Plymouth, Stonehouse and Devonport in Devon, England. The merger of the 'Three Towns' into the new borough of Plymouth in 1914 was the catalyst for the three companies to join up under the auspices of the new Plymouth Corporation. The network was closed in 1945, partly as a result of bomb damage during World War II.
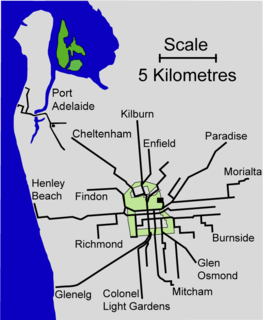
The tram network in Adelaide was converted from horse-drawn trams to electric trams between 1909 and 1914. Most of the tram network was closed in the 1950s, and began expanding again in the 21st century.











