
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.

A microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive computer having a central processing unit (CPU) made out of a microprocessor. The computer also includes memory and input/output (I/O) circuitry together mounted on a printed circuit board (PCB). Microcomputers became popular in the 1970s and 1980s with the advent of increasingly powerful microprocessors. The predecessors to these computers, mainframes and minicomputers, were comparatively much larger and more expensive. Many microcomputers are also personal computers. An early use of the term "personal computer" in 1962 predates microprocessor-based designs. (See "Personal Computer: Computers at Companies" reference below). A "microcomputer" used as an embedded control system may have no human-readable input and output devices. "Personal computer" may be used generically or may denote an IBM PC compatible machine.
Direct memory access (DMA) is a feature of computer systems that allows certain hardware subsystems to access main system memory independently of the central processing unit (CPU).

Wintel is the partnership of Microsoft Windows and Intel producing personal computers using Intel x86-compatible processors running Microsoft Windows.

The Graphics Device Interface (GDI) is a legacy component of Microsoft Windows responsible for representing graphical objects and transmitting them to output devices such as monitors and printers. It was superseded by Direct2D API. Windows apps use Windows API to interact with GDI, for such tasks as drawing lines and curves, rendering fonts, and handling palettes. The Windows USER subsystem uses GDI to render such UI elements as window frames and menus. Other systems have components that are similar to GDI; for example: macOS has Quartz, and Linux and Unix have X Window System.
In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit central processing units (CPU) and arithmetic logic units (ALU) are those that are based on processor registers, address buses, or data buses of that size. A computer that uses such a processor is a 64-bit computer.
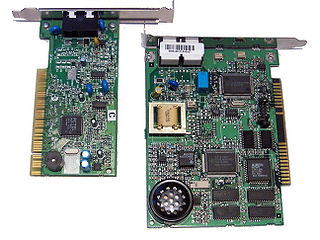
A software modem, commonly referred to as a softmodem, is a modem with minimal hardware that uses software running on the host computer, and the computer's resources, in place of the hardware in a conventional modem.
In-circuit emulation (ICE) is the use of a hardware device or in-circuit emulator used to debug the software of an embedded system. It operates by using a processor with the additional ability to support debugging operations, as well as to carry out the main function of the system. Particularly for older systems, with limited processors, this usually involved replacing the processor temporarily with a hardware emulator: a more powerful although more expensive version. It was historically in the form of bond-out processor which has many internal signals brought out for the purpose of debugging. These signals provide information about the state of the processor.
Hardware abstractions are sets of routines in software that provide programs with access to hardware resources through programming interfaces. The programming interface allows all devices in a particular class C of hardware devices to be accessed through identical interfaces even though C may contain different subclasses of devices that each provide a different hardware interface.

The Mindset is an Intel 80186-based MS-DOS personal computer. It was developed by the Mindset Corporation and released in spring 1984. Unlike other IBM PC compatibles of the time, it has custom graphics hardware supporting a 320×200 resolution with 16 simultaneous colors and hardware-accelerated drawing capabilities, including a blitter, allowing it to update the screen 50 times as fast as an IBM standard color graphics adapter. The basic unit was priced at US$1,798. It is conceptually similar to the more successful Amiga released over a year later. Key engineers of both the Amiga and Mindset were ex-Atari, Inc. employees.

Intel Architecture Labs (IAL) was the personal-computer system research-and-development arm of Intel during the 1990s.
x86 virtualization is the use of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities on an x86/x86-64 CPU.
Virtual DOS machines (VDM) refer to a technology that allows running 16-bit/32-bit DOS and 16-bit Windows programs when there is already another operating system running and controlling the hardware.
Cirrus Logic Inc. is an American fabless semiconductor supplier that specializes in analog, mixed-signal, and audio DSP integrated circuits (ICs). Since 1998, the company's headquarters have been in Austin, Texas.
Parallels Workstation is the first commercial software product released by Parallels, Inc., a developer of desktop and server virtualization software. The Workstation software comprises a virtual machine suite for Intel x86-compatible computers, which allows the simultaneous creation and execution of multiple x86 virtual computers. They distribute the product as a download package. Parallels Workstation has been discontinued for Windows and Linux as of 2013.
In a computer, an interrupt request is a hardware signal sent to the processor that temporarily stops a running program and allows a special program, an interrupt handler, to run instead. Hardware interrupts are used to handle events such as receiving data from a modem or network card, key presses, or mouse movements.
Desktop Window Manager is the compositing window manager in Microsoft Windows since Windows Vista that enables the use of hardware acceleration to render the graphical user interface of Windows.

A multi-core processor is a microprocessor on a single integrated circuit with two or more separate processing units, called cores, each of which reads and executes program instructions. The instructions are ordinary CPU instructions but the single processor can run instructions on separate cores at the same time, increasing overall speed for programs that support multithreading or other parallel computing techniques. Manufacturers typically integrate the cores onto a single integrated circuit die or onto multiple dies in a single chip package. The microprocessors currently used in almost all personal computers are multi-core.
Steven McGeady is a former Intel executive best known as a witness in the Microsoft antitrust trial. His notes and testimony contained colorful quotes by Microsoft executives threatening to "cut off Netscape's air supply" and Bill Gates' guess that "this antitrust thing will blow over". Attorney David Boies said that McGeady's testimony showed him to be "an extremely conscientious, capable and honest witness", while Microsoft portrayed him as someone with an "axe to grind". McGeady left Intel in 2000, but later again gained notoriety for defending his former employee Mike Hawash after his arrest on federal terrorism charges. From its founding in 2002 until its sale in November 2013, he was Chairman of Portland-based healthcare technology firm ShiftWise. He is a member of the Reed College Board of Trustees, the Portland Art Museum Board of Trustees, and the PNCA Board of Governors, and lives in Portland, Oregon.
The Microsoft Windows operating system supports a form of shared libraries known as "dynamic-link libraries", which are code libraries that can be used by multiple processes while only one copy is loaded into memory. This article provides an overview of the core libraries that are included with every modern Windows installation, on top of which most Windows applications are built.







