
Harris County is a county located in the U.S. state of Texas; as of the 2020 census, the population was 4,731,145, making it the most populous county in Texas and the third-most populous county in the United States. Its county seat is Houston, the most populous city in Texas and fourth-most populous city in the United States. The county was founded in 1836 and organized in 1837. It is named for John Richardson Harris, who founded the town of Harrisburg on Buffalo Bayou in 1826. According to the July 2023 census estimate, Harris County's population has shifted to 4,835,125 comprising over 16% of Texas's population. Harris County is included in the nine-county Houston–The Woodlands–Sugar Land metropolitan statistical area, which is the fifth-most populous metropolitan area in the United States.

Hempstead is a city in and the county seat of Waller County, Texas, United States, part of the Houston–The Woodlands–Sugar Land metropolitan area.

Texas City is a city in Galveston County, Texas, United States. Located on the southwest shoreline of Galveston Bay, Texas City is a busy deepwater port on Texas's Gulf Coast, as well as a petroleum-refining and petrochemical-manufacturing center. The population was 51,898 at the 2020 census, making it the third-largest city in Galveston County, behind League City and Galveston. It is a part of the Houston metropolitan area. It is notable as the site of a major explosion in 1947 that demolished the port and much of the city.

Buffalo Soldiers were United States Army regiments composed exclusively of African American soldiers, formed during the 19th century to serve on the American frontier. On September 21, 1866, the 10th Cavalry Regiment was formed at Fort Leavenworth, Kansas. The nickname "Buffalo Soldiers" was purportedly given to the regiments by the American Indian tribes who fought against them during the American Indian Wars, and the term eventually became synonymous with all of the African American regiments that were established in 1866, including the 9th Cavalry Regiment, 10th Cavalry Regiment, 24th Infantry Regiment, 25th Infantry Regiment and 38th Infantry Regiment.

The city of Houston in the U.S. state of Texas was founded in 1837 after Augustus and John Allen had acquired land to establish a new town at the junction of Buffalo and White Oak bayous in 1836. Houston served as the temporary capital of the Republic of Texas. Meanwhile, the town developed as a regional transportation and commercial hub. Houston was part of an independent nation until 1846 when the United States formally annexed Texas. Railroad development began in the late 1850s but ceased during the American Civil War. Houston served the Confederacy as a regional military logistics center. The population increased during the war and blockade runners used the town as a center for their operations.

The United States Army Rangers are elite U.S. Army personnel who have served in any unit which has held the official designation of "Ranger". The term is commonly used to include graduates of the Ranger School, even if they have never served in a "Ranger" unit; the vast majority of Ranger school graduates never serve in Ranger units and are considered "Ranger qualified".

Felix Z. Longoria was an American soldier from Texas, who served in the United States Army as a private. He died during World War II and was buried at Arlington National Cemetery after veterans supported his cause in a dispute over his funerary arrangements.

The Connecticut Military Department is a state agency of the government of Connecticut. Its primary components are the Connecticut Army National Guard, the Connecticut Air National Guard, and four companies of the state militia. The Military Department of the State of Connecticut traces its origins to May 11, 1637, when the "General Courts" established a military arm of the provincial government. In 1939, the State's Military Department was established to consolidate the offices of Adjutant General, Quartermaster General, Armory Board, and Armory Board Inspector.
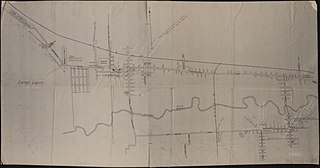
Camp Logan was a World War I-era army training camp in Houston, Texas named after U.S. Senator and Civil War General John A. Logan. The site of the camp is now primarily occupied by Memorial Park where it borders the Crestwood neighborhood, near Memorial Elementary School. Some chunks of concrete, many building foundations, and extensive trenches used for training or middens still remain in the heavily forested park. Many of the trails through the park in this area trace the routes of old Camp Logan roads. One stretch of a Camp Logan road remains in original condition, that being the shell-surfaced service road to the golf course.

The Texas Army National Guard is a component of the United States Army, the United States National Guard and the Texas Military Forces.
The 75th Infantry Regiment (Ranger) (officially 75th Infantry Regiment or 75th Infantry) was initially a parent regiment for all the US Army Ranger units during the Vietnam War and the early 1980s and then the headquarters for the Ranger battalions.

The 143d Airlift Wing is a unit of the Rhode Island Air National Guard, stationed at Quonset Point Air National Guard Station, Rhode Island. If activated to federal service, the Wing is gained by the United States Air Force Air Mobility Command. Its mission is to transport personnel and equipment, or, when activated for State Active Duty, to protect life, property and public safety.

The Rhode Island Air National Guard (RI ANG) is the aerial militia of the State of Rhode Island, United States of America. It is a reserve of the United States Air Force and along with the Rhode Island Army National Guard an element of the Rhode Island National Guard of the larger United States National Guard Bureau.

A National Guard Armory, National Guard Armory Building, or National Guard Readiness Center is any one of numerous buildings of the U.S. National Guard where a unit trains, meets, and parades. A readiness center supports the training, administration, and logistics of National Guard units by providing assembly space, classrooms, weapons and protective personal equipment storage, and training space. Readiness centers can also be utilized as communal assembly areas, utilized by local organizations and governments.

The 369th Regiment Armory is a historic National Guard Armory building located at 2366 Fifth Avenue, between West 142nd and 143rd Streets, in Harlem, Manhattan, New York City. It was built for the 369th Regiment, also known as the "Harlem Hellfighters", founded in 1913 as the first National Guard unit in New York State composed solely of African-Americans. It later became home to the 369th Sustainment Brigade.

The 143rd Infantry Regiment is an airborne infantry formation in the Army National Guard and has one battalion active under the Texas Army National Guard.

The 71st Expeditionary Military Intelligence Brigade (EMIB) is a unit of the Texas Army National Guard.
The 71st Airborne Brigade was an airborne brigade of the United States Army and the Texas Army National Guard. The 71st Airborne Brigade was active from 15 December 1967 until 1 November 1973. It was a result of the National Guard total force reorganization to fill the gap and improve in National Guard airborne infantry capabilities from the consolidations of 1st Battalion (Airborne) 151st Infantry into D & E co (LRP) 151st Infantry of the Indiana National Guard on 1 December 1967 and consolidations of the 1st Battalion (Airborne) 225th Infantry into E & F co (LRP) 425th Infantry of the Michigan National Guard on 1 February 1968.

The 36th Airborne Brigade was an airborne brigade of the United States Army and the Texas Army National Guard. The brigade was active from 1 November 1973 to 1 April 1980. The unit's lineage continues today in the 36th Infantry Division.
Texas special operations units of the Texas Military Forces conduct special operations for the Texas Military Department via the Domestic Operations Command (DOMOPS) while under Title 32 command, and via United States Special Operations Command (SOCOM) while under Title 10 command.




















