
The Cyrillic script, Slavonic script or the Slavic script is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia, and used by many other minority languages.
The East Slavic languages constitute one of three regional subgroups of the Slavic languages, distinct from the West and South Slavic languages. East Slavic languages are currently spoken natively throughout Eastern Europe, and eastwards to Siberia and the Russian Far East. In part due to the large historical influence of the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union, the Russian language is also spoken as a lingua franca in many regions of Caucasus and Central Asia. Of the three Slavic branches, East Slavic is the most spoken, with the number of native speakers larger than the Western and Southern branches combined.

Pan-Slavism, a movement which crystallized in the mid-19th century, is the political ideology concerned with the advancement of integrity and unity for the Slavic people. Its main impact occurred in the Balkans, where non-Slavic empires had ruled the South Slavs for centuries. These were mainly the Byzantine Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Venice.

The Slavic languages, also known as the Slavonic languages, are Indo-European languages spoken primarily by the Slavic peoples and their descendants. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic, spoken during the Early Middle Ages, which in turn is thought to have descended from the earlier Proto-Balto-Slavic language, linking the Slavic languages to the Baltic languages in a Balto-Slavic group within the Indo-European family.
Slavic, Slav or Slavonic may refer to:
The Slavs or Slavic peoples are the most populous European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European language family. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, and Southeastern Europe, though there is a large Slavic minority scattered across the Baltics, Northern Asia, and Central Asia. Continued immigration has resulted in the development of a substantial Slavic diaspora in the Americas.

Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic was the first Slavic literary language.

The East Slavs are the most populous subgroup of the Slavs. They speak the East Slavic languages, and formed the majority of the population of the medieval state Kievan Rus', which they claim as their cultural ancestor. Today, the East Slavs consist of Belarusians, Russians, Rusyns, and Ukrainians.

Ukrainian is an East Slavic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken primarily in Ukraine. It is the native language of Ukrainians.
Slavic or Slavonicstudies, also known as Slavistics, is the academic field of area studies concerned with Slavic areas, languages, literature, history, and culture. Originally, a Slavist or Slavicist was primarily a linguist or philologist researching Slavistics. Increasingly, historians, social scientists, and other humanists who study Slavic area cultures and societies have been included in this rubric.

Slavic mythology or Slavic paganism is the religious beliefs, myths, and ritual practices of the Slavs before Christianisation, which occurred at various stages between the 8th and the 13th century. The South Slavs, who likely settled in the Balkan Peninsula during the 6th–7th centuries AD, bordering with the Byzantine Empire to the south, came under the sphere of influence of Eastern Christianity, beginning with the creation of writing systems for Slavic languages in 855 by the brothers Saints Cyril and Methodius and the adoption of Christianity in Bulgaria in 864 and 863 in Great Moravia. The East Slavs followed with the official adoption in 988 by Vladimir the Great of Kievan Rus'.

Old East Slavic was a language used by the East Slavs from the 7th or 8th century to the 13th or 14th century, until it diverged into the Russian and Ruthenian languages. Ruthenian eventually evolved into the Belarusian, Rusyn, and Ukrainian languages.

The West Slavic languages are a subdivision of the Slavic language group. They include Polish, Czech, Slovak, Kashubian, Upper Sorbian and Lower Sorbian. The languages have traditionally been spoken across a mostly continuous region encompassing the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Poland, the westernmost regions of Ukraine and Belarus, and a bit of eastern Lithuania. In addition, there are several language islands such as the Sorbian areas in Lusatia in Germany, and Slovak areas in Hungary and elsewhere.

The South Slavic languages are one of three branches of the Slavic languages. There are approximately 30 million speakers, mainly in the Balkans. These are separated geographically from speakers of the other two Slavic branches by a belt of German, Hungarian and Romanian speakers.

The Balto-Slavic languages form a branch of the Indo-European family of languages, traditionally comprising the Baltic and Slavic languages. Baltic and Slavic languages share several linguistic traits not found in any other Indo-European branch, which points to a period of common development and origin.

Proto-Balto-Slavic is a reconstructed hypothetical proto-language descending from Proto-Indo-European (PIE). From Proto-Balto-Slavic, the later Balto-Slavic languages are thought to have developed, composed of the Baltic and Slavic sub-branches, and including modern Lithuanian, Polish, Russian and Serbo-Croatian, among others.
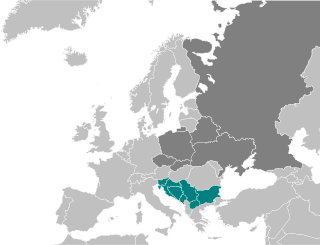
South Slavs are Slavic people who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, Hungary, Romania, and the Black Sea, the South Slavs today include Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes.

The West Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak the West Slavic languages. They separated from the common Slavic group around the 7th century, and established independent polities in Central Europe by the 8th to 9th centuries. The West Slavic languages diversified into their historically attested forms over the 10th to 14th centuries.

The early Slavs were an Indo-European peoples who lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages in Central, Eastern and Southeast Europe and established the foundations for the Slavic nations through the Slavic states of the Early and High Middle Ages. The Slavs' original homeland is still a matter of debate due to a lack of historical records; however, scholars believe that it was in Eastern Europe, with Polesia being the most commonly accepted location.

Proto-Slavic is the unattested, reconstructed proto-language of all Slavic languages. It represents Slavic speech approximately from the 2nd millennium BC through the 6th century AD. As with most other proto-languages, no attested writings have been found; scholars have reconstructed the language by applying the comparative method to all the attested Slavic languages and by taking into account other Indo-European languages.












