Sources
- Painter, Sidney. "The Lords of Lusignan in the Eleventh and Twelfth Centuries." Speculum, Vol. 32, No. 1. (Jan., 1957), pp 27–47.
Hugh I (est. 885-930) (fl. early tenth century), called Venator (Latin for the Hunter), was the first Lord of Lusignan. He is mentioned in the Chronicle of Saint-Maixent. In later years the Lusignans held the forest from the east of their castle from the Bishop of Poitiers suggest that he held his office from that prelate. He was in turn succeeded by his son, Hugh II Carus who built the Castle of Lusignan.
Hugh I may be the inspiration of the Raymond of Poitou character in The Romans of Partenay or of Lusignen: Otherwise known as the Tale of Melusine.[ citation needed ]

Isabella was Queen of England from 1200 to 1216 as the second wife of King John, Countess of Angoulême in her own right from 1202 until her death in 1246, and Countess of La Marche from 1220 to 1246 as the wife of Count Hugh.

The Kingdom of Cyprus was a medieval kingdom of the Crusader states that existed between 1192 and 1489. Initially ruled as an independent Christian kingdom, it was established by the French House of Lusignan after the Third Crusade. It comprised not only the entire island of Cyprus, but it also had a foothold on the Anatolian mainland: Antalya between 1361 and 1373, and Corycus between 1361 and 1448.

James I was the youngest son of King Hugh IV of Cyprus and by 1369 held the title "Constable of Jerusalem." When his nephew Peter II died in 1382, he became King of Cyprus. James was also crowned King of Jerusalem in 1389 and assumed the title of King of Armenia in 1393, which was formally given to him in 1396.
Angoulême (L'Angoumois) in western France was part of the Carolingian Empire as the kingdom of Aquitaine. Under Charlemagne's successors, the local Count of Angoulême was independent and was not united with the French crown until 1308. By the terms of the Treaty of Brétigny (1360) the Angoumois, then ruled by the Counts of Angoulême, was ceded as English territory to Edward III. In 1371 it became a fief of the Duke of Berry, before passing to Louis I, Duke of Orleans, both of whom were cadets of the French royal family. From then on it was held by cadets of the Valois House of Orleans, until Francis, Count of Angoulême, became King of France in 1515. Angoumois was definitively incorporated into the French crown lands, as a duchy.

The House of Lusignan was a royal house of French origin, which at various times ruled several principalities in Europe and the Levant, including the kingdoms of Jerusalem, Cyprus, and Armenia, from the 12th through the 15th centuries during the Middle Ages. It also had great influence in England and France.

The House of Ibelin was a noble family in the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem in the 12th century. They rose from humble beginnings to become one of the most important families in the kingdom, holding various high offices and with extensive holdings in the Holy Land and Cyprus. The family disappeared after the fall of the Kingdom of Cyprus in the 15th century.
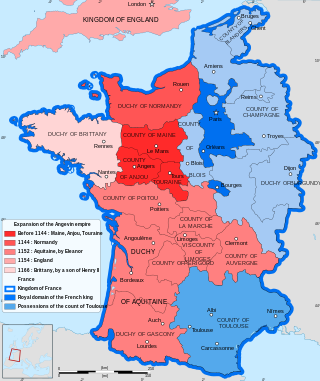
The County of La Marche was a medieval French county, approximately corresponding to the modern département of Creuse and the northern half of Haute Vienne.

The principality of Galilee was one of the four major seigneuries of the crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem, according to 13th-century commentator John of Ibelin, grandson of Balian. The direct holdings of the principality centred around Tiberias, in Galilee proper, but with all its vassals, the lordship covered all Galilee and southern Phoenicia. The independent Lordship of Sidon was located between Galilee's holdings. The principality also had its own vassals: the Lordships of Beirut, Nazareth, and Haifa.
Hugh II, called Carus, was the second Lord of Lusignan, the son and successor of Hugh I Venator. According to the Chronicle of Saint-Maixent, he built the castle at Lusignan. Hugh III Albus, who emerges from historical obscurity in the next generation, was probably his son.
Hugh IV, called Brunus, was the fourth Lord of Lusignan. He was the son of Hugh III Albus and Arsendis de Vivonne. He was a turbulent baron, who brought his family out of obscurity and on their way to prominence in European and eventually even Middle Eastern affairs.

Hugh VIII the Old of Lusignan or was the Seigneur de Lusignan, Couhé, and Château-Larcher on his father's death in 1151. He went on crusade, was captured at battle of Harim, and died in captivity.

The Saintonge War was a feudal dynastic conflict that occurred between 1242 and 1243. It opposed Capetian forces supportive of King Louis IX's brother Alphonse, Count of Poitiers and those of Hugh X of Lusignan, Raymond VII of Toulouse and Henry III of England. The last hoped to regain the Angevin possessions lost during his father's reign. Saintonge is the region around Saintes in the centre-west of France and is the place where most of fighting occurred.

The Ramnulfids, or the House of Poitiers, were a French dynasty of Frankish origin ruling the County of Poitou and Duchy of Aquitaine in the 9th through 12th centuries. Their power base shifted from Toulouse to Poitou. In the early 10th century, they contested the dominance of northern Aquitaine and the ducal title to the whole with the House of Auvergne. In 1032, they inherited the Duchy of Gascony, thus uniting it with Aquitaine. By the end of the 11th century, they were the dominant power in the southwestern third of France. The founder of the family was Ramnulf I, who became count in 835.

The Château d'Angoulême was a castle in the town of Angoulême, in the Charente département of France. The only remaining parts are the keep of Lusignan and the tower of Valois, which are part of the Town Hall of Angoulême, together with a construction of the 19th century.
John of Lusignan was a regent of the Kingdom of Cyprus and titular Prince of Antioch. He was son of King Hugh IV of Cyprus and his second wife Alix of Ibelin. He was a member of the House of Lusignan.

The Château de Montignac is a ruined castle in the commune of Montignac-Charente, in the Charente département of France. The castle is the property of the commune and has been listed since 1962 as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture.
Alice de Lusignan was the first wife of Marcher baron Gilbert de Clare, 7th Earl of Gloucester, and half-niece of King Henry III of England.
Sigouri Castle was a medieval castle in Cyprus of which there are no remains. Its location facilitated as a stopover for troops from Nicosia, the capital, on their way to the coastal harbours of either Famagusta or Larnaca. It is de facto situated in Northern Cyprus. The castle was built in 1391 as a frontier fortress, after the Genoese conquest of Famagusta. It fell into disuse after the Venetian takeover of the island.
Gastria Castle is a ruined castle in Northern Cyprus. It is first mentioned in 1210 as a Knights Templar fortress. It was dismantled in 1279 by Hugh III of Cyprus. It passed into the possession of the Knights Hospitaller in 1308, falling into obscurity afterwards.