A hundred is an administrative division that is geographically part of a larger region. It was formerly used in England, Wales, some parts of the United States, Denmark, Southern Schleswig, Sweden, Finland, Norway, the Bishopric of Ösel–Wiek, Curonia, the Ukrainian state of the Cossack Hetmanate and in Cumberland County in the British Colony of New South Wales. It is still used in other places, including in Australia.

The Statute of Rhuddlan, also known as the Statutes of Wales or as the Statute of Wales, was a royal ordinance by Edward I of England, which gave the constitutional basis for the government of the Principality of Wales from 1284 until 1536.

Hughenden Manor, Hughenden, Buckinghamshire, England, is a Victorian mansion, with earlier origins, that served as the country house of the Prime Minister, Benjamin Disraeli, 1st Earl of Beaconsfield. It is now owned by the National Trust and open to the public. It sits on the brow of the hill to the west of the main A4128 road that links Hughenden to High Wycombe.
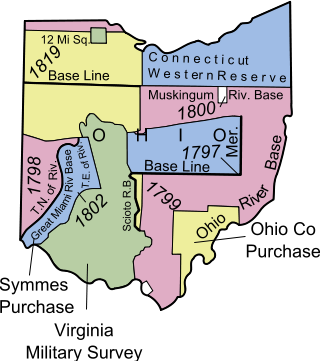
The Ohio Company of Associates, also known as the Ohio Company, was a land company whose members are today credited with becoming the first non-Native American group to permanently settle west of the Allegheny mountains. In 1788 they established Marietta, Ohio, as the first permanent settlement of the new United States in the newly organized Northwest Territory.

The Sagebrush Rebellion was a movement in the Western United States in the 1970s and the 1980s that sought major changes to federal land control, use, and disposal policy in 13 western states in which federal land holdings include between 20% and 85% of a state's area. Supporters of the movement wanted more state and local control over the lands, if not outright transfer of them to state and local authorities and/or privatization. As much of the land in question is sagebrush steppe, supporters adopted the name "Sagebrush Rebellion."

The Matale rebellion, also known as the Rebellion of 1848, took place in Matale city, Ceylon against the British colonial government under Governor George Byng, 7th Viscount Torrington. It marked a transition from the classic feudal form of anti-colonial revolt to modern independence struggles. It was fundamentally a peasant revolt.

The County Palatine of Durham was a jurisdiction in the North of England, within which the bishop of Durham had rights usually exclusive to the monarch. It developed from the Liberty of Durham, which emerged in the Anglo-Saxon period. The gradual acquisition of powers by the bishops led to Durham being recognised as a palatinate by the late thirteenth century, one of several such counties in England during the Middle Ages. The county palatine had its own government and institutions, which broadly mirrored those of the monarch and included several judicial courts. From the sixteenth century the palatine rights of the bishops were gradually reduced, and were finally abolished in 1836. The last palatine institution to survive was the court of chancery, which was abolished in 1972.

Lands administrative divisions of Australia are the cadastral divisions of Australia for the purposes of identification of land to ensure security of land ownership. Most states term these divisions as counties, parishes, hundreds, and other terms. The eastern states of Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria, and Tasmania were divided into counties and parishes in the 19th century, although the Tasmanian counties were renamed land districts in the 20th century. Parts of South Australia (south-east) and Western Australia (south-west) were similarly divided into counties, and there were also five counties in a small part of the Northern Territory. However South Australia has subdivisions of hundreds instead of parishes, along with the Northern Territory, which was part of South Australia when the hundreds were proclaimed. There were also formerly hundreds in Tasmania. There have been at least 600 counties, 544 hundreds and at least 15,692 parishes in Australia, but there are none of these units for most of the sparsely inhabited central and western parts of the country.
City of Sherrill v. Oneida Indian Nation of New York, 544 U.S. 197 (2005), was a Supreme Court of the United States case in which the Court held that repurchase of traditional tribal lands 200 years later did not restore tribal sovereignty to that land. Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg wrote the majority opinion.

Kellidie Bay Conservation Park is a protected area in the Australian state of South Australia, located on the west coast of Eyre Peninsula immediately east of the town centre in Coffin Bay and immediately adjoining the south coast of Kellidie Bay in the localities of Coffin Bay, Kellidie Bay and Wangary.
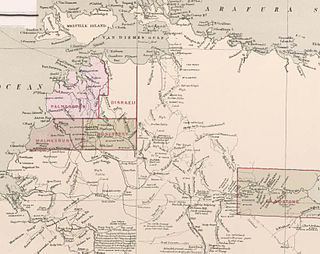
County of Gladstone was one of the five counties in the Northern Territory which are part of the cadastral divisions of Australia.
The Hundred of Douglas was a hundred of Gladstone County in the Northern Territory of Australia.

The Hundred of Glynne was a Hundred of Gladstone County, Northern Territory Australia.

The Hundred of Bundey was a hundred within County of Disraeli in the Northern Territory of Australia. The hundred was gazetted on 7 August 1884 and lapsed with the passage in 1976 and subsequent assent of the Crown Lands Ordinance 1976 and the Crown Lands Ordinance 1976.

County of Malmesbury was one of the five counties in the Northern Territory which are part of the Lands administrative divisions of Australia.

Hundred of Hawarden was a Hundred of Gladstone County, Northern Territory of Australia.
The British American Land Company (BALC) was a company formed in 1832 for the purpose of purchasing land and encouraging British immigration to Lower Canada. It was founded and promoted by John Galt, Edward Ellice and others to acquire and manage the development of almost 1,100,000 acres of Crown land and other lands in the Eastern Townships of Lower Canada, in order to encourage the immigration of British subjects to the region.

The Hundred of Reynolds was a hundred of the County of Gladstone in the Northern Territory of Australia which was created in 1873 and which lapsed in 1976. It is located 600 km south-east of the territorial capital of Darwin.













