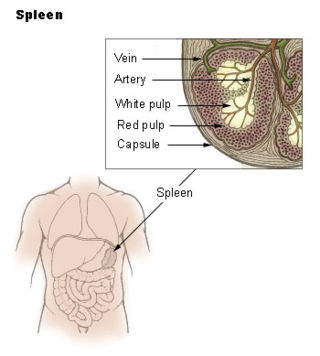
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes from Ancient Greek σπλήν (splḗn).

The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans and many other animals that contain organs. It is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roof is the thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle under the lungs, and its floor is the pelvic inlet, opening into the pelvis.

Hemolysis or haemolysis, also known by several other names, is the rupturing (lysis) of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the release of their contents (cytoplasm) into surrounding fluid. Hemolysis may occur in vivo or in vitro.

The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs, lymphoid tissues and lymph. Lymph is a clear fluid carried by the lymphatic vessels back to the heart for re-circulation. The Latin word for lymph, lympha, refers to the deity of fresh water, "Lympha".
Hepatology is the branch of medicine that incorporates the study of liver, gallbladder, biliary tree, and pancreas as well as management of their disorders. Although traditionally considered a sub-specialty of gastroenterology, rapid expansion has led in some countries to doctors specializing solely on this area, who are called hepatologists.

In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system.

Offal, also called variety meats, pluck or organ meats, is the internal organs of a butchered animal. The word does not refer to a particular list of edible organs, and these lists of organs vary with culture and region, but usually exclude skeletal muscle. Offal may also refer to the by-products of milled grains, such as corn or wheat.
San Jiao is a concept in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and acupuncture. It is the sixth organ of Fu, which is the hollow space inside the trunk of the body. In TCM, there are five solid organs and each solid organ has its counterpart in a hollow organ. For instance, the heart is considered a solid organ, and the small intestine its hollow counterpart, or Fu organ. San Jiao is believed to be a body cavity of some kind which has the ability to influence other organs, and overall health, mainly through the free movement of Qi, the fundamental energy or life force on the microcosm and on the macrocosm it is associated with the interactions between The Heavens, humans and earth.
The zangfu organs are functional entities stipulated by traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). These classifications are not based in physiology or science. They constitute the technological centrepiece of TCM's general concept of how the human body works. The term zang refers to the organs considered to be "solid" yin in nature – Heart, Liver, Spleen, Lung, Kidney – while fu refers to the "hollow" yang organs – Small Intestine, Large Intestine, Gall Bladder, Urinary Bladder, Stomach and San Jiao.
The model of the body in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has the following elements:
Situs ambiguus is a rare congenital defect in which the major visceral organs are distributed abnormally within the chest and abdomen. Clinically heterotaxy spectrum generally refers to any defect of Left-right asymmetry and arrangement of the visceral organs; however, classical heterotaxy requires multiple organs to be affected. This does not include the congenital defect situs inversus, which results when arrangement of all the organs in the abdomen and chest are mirrored, so the positions are opposite the normal placement. Situs inversus is the mirror image of situs solitus, which is normal asymmetric distribution of the abdominothoracic visceral organs. Situs ambiguus can also be subdivided into left-isomerism and right isomerism based on the defects observed in the spleen, lungs and atria of the heart.

In Chinese martial arts, there are fighting styles that are modeled after animals.

Pneumocystosis is a fungal infection that most often presents as Pneumocystis pneumonia in people with HIV/AIDS or poor immunity. It usually causes cough, difficulty breathing and fever, and can lead to respiratory failure. Involvement outside the lungs is rare but, can occur as a disseminated type affecting lymph nodes, spleen, liver, bone marrow, eyes, kidneys, thyroid, gastrointestinal tract or other organs. If occurring in the skin, it usually presents as nodular growths in the ear canals or underarms.

Extramedullary hematopoiesis refers to hematopoiesis occurring outside of the medulla of the bone. It can be physiologic or pathologic.
Felty's syndrome (FS), also called Felty syndrome, is a rare autoimmune disease characterized by the triad of rheumatoid arthritis, enlargement of the spleen and low neutrophil count. The condition is more common in those aged 50–70 years, specifically more prevalent in females than males, and more so in Caucasians than those of African descent. It is a deforming disease that causes many complications for the individual.
Serositis refers to inflammation of the serous tissues of the body, the tissues lining the lungs (pleura), heart (pericardium), and the inner lining of the abdomen (peritoneum) and organs within. It is commonly found with fat wrapping or creeping fat.

The abdominopelvic cavity is a body cavity that consists of the abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity. The upper portion is the abdominal cavity, and it contains the stomach, liver, pancreas, spleen, gallbladder, kidneys, small intestine, and most of the large intestine. The lower portion is the pelvic cavity, and it contains the urinary bladder, the rest of the large intestine, and the internal reproductive organs.

Lysosomal acid lipase deficiency is an autosomal recessive inborn error of metabolism that results in the body not producing enough active lysosomal acid lipase (LAL) enzyme. This enzyme plays an important role in breaking down fatty material in the body. Infants, children and adults that have LAL deficiency experience a range of serious health problems. The lack of the LAL enzyme can lead to a build-up of fatty material in a number of body organs including the liver, spleen, gut, in the wall of blood vessels and other important organs.
Lactococcus garvieae is a known fish pathogen affecting saltwater fish in the Far East, specifically in rainbow trout, Japanese yellowtail, Cobia and grey mullet. This bacteria causes lesions in the vascular endothelium, leading to hemorrhages and petechias at the surface of internal organs. As few as 10 bacterial cells per fish can cause an infection. L. garvieae is isolated in saltwater fish in the Far East and specifically in European rainbow trout.

Beuschel is a dish that is typically a ragout made from lungs and other organs, such as heart, kidneys, spleen, and tongue, from calf, beef, pork, or game. It is often served with a sour cream sauce and bread dumplings. It is a dish of Viennese cuisine but is widespread in all of Austria, Bavaria, and Bohemia.












