
The Open Systems Interconnection model is a conceptual model that characterises and standardises the communication functions of a telecommunication or computing system without regard to its underlying internal structure and technology. Its goal is the interoperability of diverse communication systems with standard communication protocols.

Synchronous optical networking (SONET) and synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) are standardized protocols that transfer multiple digital bit streams synchronously over optical fiber using lasers or highly coherent light from light-emitting diodes (LEDs). At low transmission rates data can also be transferred via an electrical interface. The method was developed to replace the plesiochronous digital hierarchy (PDH) system for transporting large amounts of telephone calls and data traffic over the same fiber without the problems of synchronization.
A network switch is networking hardware that connects devices on a computer network by using packet switching to receive and forward data to the destination device.

A cable modem is a type of network bridge that provides bi-directional data communication via radio frequency channels on a hybrid fibre-coaxial (HFC), radio frequency over glass (RFoG) and coaxial cable infrastructure. Cable modems are primarily used to deliver broadband Internet access in the form of cable Internet, taking advantage of the high bandwidth of a HFC and RFoG network. They are commonly deployed in the Americas, Asia, Australia, and Europe.
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the physical layer or layer 1 is the first and lowest layer. This layer may be implemented by a PHY chip.

In IEEE 802 LAN/MAN standards, the medium access control sublayer is the layer that controls the hardware responsible for interaction with the wired, optical or wireless transmission medium. The MAC sublayer and the logical link control (LLC) sublayer together make up the data link layer. Within the data link layer, the LLC provides flow control and multiplexing for the logical link, while the MAC provides flow control and multiplexing for the transmission medium.
Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification is an international telecommunications standard that permits the addition of high-bandwidth data transfer to an existing cable television (CATV) system. It is used by many cable television operators to provide Internet access over their existing hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC) infrastructure. The version numbers are sometimes prefixed with simply "D" instead of "DOCSIS".

A cable modem termination system or CMTS is a piece of equipment, typically located in a cable company's headend or hubsite, which is used to provide high speed data services, such as cable Internet or Voice over Internet Protocol, to cable subscribers. A CMTS provides many of the same functions provided by the DSLAM in a DSL system.
The Telecommunications Management Network is a protocol model defined by ITU-T for managing open systems in a communications network. It is part of the ITU-T Recommendation series M.3000 and is based on the OSI management specifications in ITU-T Recommendation series X.700.

A PHY, an abbreviation for "physical layer", is an electronic circuit, usually implemented as an integrated circuit, required to implement physical layer functions of the OSI model in a network interface controller.

A Medium Attachment Unit (MAU) is a transceiver which converts signals on an Ethernet cable to and from Attachment Unit Interface (AUI) signals.
The Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) is a set of computer interface specifications for an autonomous computer subsystem that provides management and monitoring capabilities independently of the host system's CPU, firmware and operating system. IPMI defines a set of interfaces used by system administrators for out-of-band management of computer systems and monitoring of their operation. For example, IPMI provides a way to manage a computer that may be powered off or otherwise unresponsive by using a network connection to the hardware rather than to an operating system or login shell. Another use case may be installing a custom operating system remotely. Without IPMI, installing a custom operating system may require an administrator to be physically present near the computer, insert a DVD or a USB flash drive containing the OS installer and complete the installation process using a monitor and a keyboard. Using IPMI, an administrator can mount an ISO image, simulate an installer DVD, and perform the installation remotely.
In telecommunications, cable Internet access, shortened to cable Internet, is a form of broadband Internet access which uses the same infrastructure as a cable television. Like digital subscriber line and fiber to the premises services, cable Internet access provides network edge connectivity from the Internet service provider to an end user. It is integrated into the cable television infrastructure analogously to DSL which uses the existing telephone network. Cable TV networks and telecommunications networks are the two predominant forms of residential Internet access. Recently, both have seen increased competition from fiber deployments, wireless, and mobile networks.

The Ethernet physical layer is the physical layer functionality of the Ethernet family of computer network standards. The physical layer defines the electrical or optical properties and the transfer speed of the physical connection between a device and the network or between network devices. It is complemented by the MAC layer and the logical link layer.

The WiMedia Alliance was a non-profit industry trade group that promoted the adoption, regulation, standardization and multi-vendor interoperability of ultra-wideband (UWB) technologies. It existed from about 2002 through 2009.
G.hn is a specification for home networking with data rates up to 2 Gbit/s and operation over four types of legacy wires: telephone wiring, coaxial cables, power lines and plastic optical fiber. A single G.hn semiconductor device is able to network over any of the supported home wire types. Some benefits of a multi-wire standard are lower equipment development costs and lower deployment costs for service providers.
Zenith Cable Modem was one of the first proprietary cable modems. The two basic models are one operating at 500 kilobits per second (kbit/s), and the other at 4 megabits per second (mbit/s) with BPSK and approximately a 25% alpha.
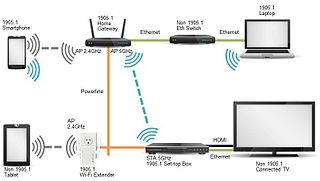
IEEE 1905.1 is an IEEE standard which defines a network enabler for home networking supporting both wireless and wireline technologies: IEEE 802.11, IEEE 1901 powerline networking, IEEE 802.3 Ethernet and Multimedia over Coax (MoCA).
EPON Protocol over Coax, or EPoC, refers to the transparent extension of an Ethernet passive optical network (EPON) over a cable operator's hybrid fiber-coax (HFC) network. From the service provider's perspective the use of the coax portion of the network is transparent to EPON protocol operation in the optical line terminal (OLT) thereby creating a unified scheduling, management, and quality of service (QoS) environment that includes both the optical and coax portions of the network. The IEEE 802.3 Ethernet Working Group initiated a standards process with the creation of an EPoC Study Group in November 2011. EPoC adds to the family of IEEE 802.3 Ethernet in the First Mile (EFM) standards.

{{Multiple issues|










