IEEE 802.15 is a working group of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) IEEE 802 standards committee which specifies Wireless Specialty Networks (WSN) standards. The working group was formerly known as Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks.
DECnet is a suite of network protocols created by Digital Equipment Corporation. Originally released in 1975 in order to connect two PDP-11 minicomputers, it evolved into one of the first peer-to-peer network architectures, thus transforming DEC into a networking powerhouse in the 1980s. Initially built with three layers, it later (1982) evolved into a seven-layer OSI-compliant networking protocol.

A wireless mesh network (WMN) is a communications network made up of radio nodes organized in a mesh topology. It can also be a form of wireless ad hoc network.

The Optimized Link State Routing Protocol (OLSR) is an IP routing protocol optimized for mobile ad hoc networks, which can also be used on other wireless ad hoc networks. OLSR is a proactive link-state routing protocol, which uses hello and topology control (TC) messages to discover and then disseminate link state information throughout the mobile ad hoc network. Individual nodes use this topology information to compute next hop destinations for all nodes in the network using shortest hop forwarding paths.
Ad hoc On-Demand Distance Vector (AODV) Routing is a routing protocol for mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs) and other wireless ad hoc networks. It was jointly developed by Charles Perkins and Elizabeth Royer and was first published in the ACM 2nd IEEE Workshop on Mobile Computing Systems and Applications in February 1999.

A wireless network interface controller (WNIC) is a network interface controller which connects to a wireless network, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or LTE (4G) or 5G rather than a wired network, such as an Ethernet network. A WNIC, just like other NICs, works on the layers 1 and 2 of the OSI model and uses an antenna to communicate via radio waves.
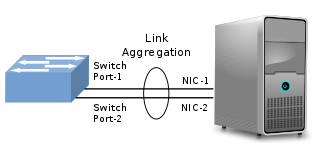
In computer networking, link aggregation is the combining of multiple network connections in parallel by any of several methods. Link aggregation increases total throughput beyond what a single connection could sustain, and provides redundancy where all but one of the physical links may fail without losing connectivity. A link aggregation group (LAG) is the combined collection of physical ports.
IEEE 802.11u-2011 is an amendment to the IEEE 802.11-2007 standard to add features that improve interworking with external networks.
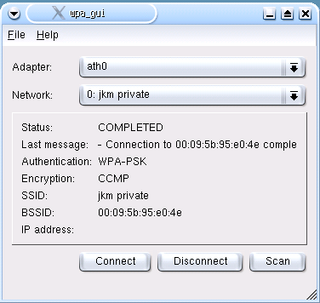
wpa_supplicant is a free software implementation of an IEEE 802.11i supplicant for Linux, FreeBSD, NetBSD, QNX, AROS, Microsoft Windows, Solaris, OS/2 and Haiku. In addition to being a WPA3 and WPA2 supplicant, it also implements WPA and older wireless LAN security protocols.
Netlink is a socket family used for inter-process communication (IPC) between both the kernel and userspace processes, and between different userspace processes, in a way similar to the Unix domain sockets available on certain Unix-like operating systems, including its original incarnation as a Linux kernel interface, as well as in the form of a later implementation on FreeBSD. Similarly to the Unix domain sockets, and unlike INET sockets, Netlink communication cannot traverse host boundaries. However, while the Unix domain sockets use the file system namespace, Netlink sockets are usually addressed by process identifiers (PIDs).
hostapd is a user space daemon software enabling a network interface card to act as an access point and authentication server. There are three implementations: Jouni Malinen's hostapd, OpenBSD's hostapd and Devicescape's hostapd.

Wireless network cards for computers require control software to make them function. This is a list of the status of some open-source drivers for 802.11 wireless network cards.
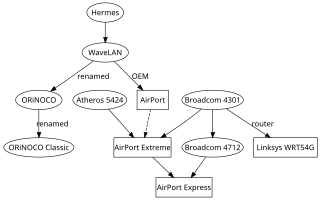
WaveLAN was a brand name for a family of wireless networking technology sold by NCR, AT&T, Lucent Technologies, and Agere Systems as well as being sold by other companies under OEM agreements. The WaveLAN name debuted on the market in 1990 and was in use until 2000, when Agere Systems renamed their products to ORiNOCO. WaveLAN laid the important foundation for the formation of IEEE 802.11 working group and the resultant creation of Wi-Fi.
A wireless ad hoc network (WANET) or mobile ad hoc network (MANET) is a decentralized type of wireless network. The network is ad hoc because it does not rely on a pre-existing infrastructure, such as routers or wireless access points. Instead, each node participates in routing by forwarding data for other nodes. The determination of which nodes forward data is made dynamically on the basis of network connectivity and the routing algorithm in use.

The Better Approach to Mobile Ad-hoc Networking (B.A.T.M.A.N.) is a routing protocol for multi-hop mobile ad hoc networks which is under development by the German "Freifunk" community and intended to replace the Optimized Link State Routing Protocol (OLSR) as OLSR did not meet the performance requirements of large-scale mesh deployments.
IEEE 802.11s is a wireless local area network (WLAN) standard and an IEEE 802.11 amendment for mesh networking, defining how wireless devices can interconnect to create a wireless LAN mesh network, which may be used for relatively fixed topologies and wireless ad hoc networks. The IEEE 802.11s task group drew upon volunteers from university and industry to provide specifications and possible design solutions for wireless mesh networking. As a standard, the document was iterated and revised many times prior to finalization.

Open vSwitch (OVS) is an open-source implementation of a distributed virtual multilayer switch. The main purpose of Open vSwitch is to provide a switching stack for hardware virtualization environments, while supporting multiple protocols and standards used in computer networks.

Banana Pi is a line of single-board computers produced by the Chinese company Shenzhen SINOVOIP Company, its spin-off Guangdong BiPai Technology Company, and supported by Hon Hai Technology (Foxconn). Its hardware design was influenced by the Raspberry Pi, and both lines use the same 40-pin I/O connector.
WireGuard is a communication protocol and free and open-source software that implements encrypted virtual private networks (VPNs). It aims to be lighter and better performing than IPsec and OpenVPN, two common tunneling protocols. The WireGuard protocol passes traffic over UDP.









