See also
- Adam Beck
- Canadian National Electric Railways was another organization intended to promote radials.
Hydro-Electric Railways, a subsidiary of the Hydro-Electric Power Commission of Ontario (HEPC or HEPCO), was an operator of radial railways in the province of Ontario, Canada. Its parent agency, the Hydro-Electric Power Commission of Ontario, would later evolve into Ontario Hydro and, later, Hydro One.
The Ontario Legislative Assembly granted the commission authority to operate electric interurban railways in the territory served by the commission in the Hydro-Electric Railway Act, 1914. [1] Changes in government policy and public sentiment in the 1920s restricted their development, and all such operations ceased in the 1930s (with the exception of the Hamilton Street Railway streetcar system, which continued until 1946). [2] [ page needed ]
The following properties were operated by the Hydro-Electric Railways: [2] [ page needed ]
| Railway | Years under Hydro | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Brantford and Hamilton Electric Railway | 1930-1931 | |
| Guelph Radial Railway | 1926-1937 | owned by Hydro-Electric Railways [3] |
| Hamilton, Grimsby & Beamsville Electric Railway | 1930-1931 | |
| Hamilton Street Railway | 1930-1946 | |
| Sandwich, Windsor and Amherstburg Railway | 1930-1934 | Windsor area |
| Toronto and York Radial Railway | 1921-1927 | |
| Windsor, Essex and Lake Shore Rapid Railway | 1929-1932 | Windsor area |
With the exception of the Guelph Radial Railway, Ontario Hydro managed radial lines owned by municipalities.
In 1912, Adam Beck, founder and chairman of Ontario Hydro, began to promote the creation and operation of electric interurban railways in the territory served by the Hydro-Electric Power Commission of Ontario. The Hydro-Electric Railways were a vehicle to promote his vision for radials.
Electric railways consumed a huge amount of electrical power, and Beck saw their development as an opportunity to sell electricity. Beck envisioned that radials would share the right-of-ways of Hydro transmission lines. A provincial radial system would bridge gaps between various separate radial systems such as those in Toronto, Hamilton and the Niagara Peninsula. [4]
Beck piloted the Hydro Electric Railway Act of 1914. This repealed the requirement that municipalities bear all costs of radial construction, but allowed Ontario Hydro to develop co-operative agreements between Hydro and municipalities for radial construction. Only projects with the potential to be self-supporting would be considered, and municipalities would bear any deficits. [4]
With the new Canadian National Railways consuming considerable taxpayer money, critics feared costs to build radials could escalate. There was also a boost in automobile and truck traffic after World War I. The 1919 provincial election brought into power the United Farmers of Ontario party which was extremely skeptical of Beck's plan. In 1921, Premier Charles Drury announced that the province would not guarantee radial bonds, thus killing the radial scheme. [4]
In 1922, Beck made a proposal to the City of Toronto to build a high-speed, 4- or 6-track radial entrance to the city via the waterfront. There were objections to the radials crossing the grounds of the Canadian National Exhibition and fears of a detrimental impact on waterfront economic development. In January 1923, voters rejected the radial proposal. [4]
Despite the decline of the interurban industry, Beck continued his advocacy for radials until his death in 1925 which ended Ontario Hydro's efforts to promote radials. [4]

Sir Adam Beck was a Canadian politician and hydroelectricity advocate who founded the Hydro-Electric Power Commission of Ontario.

Ernest Charles Drury was a farmer, politician and writer who served as the eighth premier of Ontario, from 1919 to 1923 as the head of a United Farmers of Ontario–Labour coalition government.

Ontario Hydro, established in 1906 as the Hydro-Electric Power Commission of Ontario, was a publicly owned electricity utility in the Province of Ontario. It was formed to build transmission lines to supply municipal utilities with electricity generated by private companies already operating at Niagara Falls, and soon developed its own generation resources by buying private generation stations and becoming a major designer and builder of new stations. As most of the readily developed hydroelectric sites became exploited, the corporation expanded into building coal-fired generation and then nuclear-powered facilities. Renamed as "Ontario Hydro" in 1974, by the 1990s it had become one of the largest, fully integrated electricity corporations in North America.

The Halton County Radial Railway is a working museum of electric streetcars, other railway vehicles, buses and trolleybuses. It is operated by the Ontario Electric Railway Historical Association (OERHA). It is focused primarily on the history of the Toronto Transit Commission (TTC) and its predecessor, the Toronto Transportation Commission, Its collection includes PCC, Peter Witt, CLRV and ALRV, and earlier cars from the Toronto streetcar system as well as G-series and M-series Toronto subway cars.

The Toronto Railway Company (TRC) was the operator of the streetcar system in Toronto between 1891 and 1921. It electrified the horsecar system it inherited from the Toronto Street Railway, the previous operator of streetcar service in Toronto. The TRC was also a manufacturer of streetcars and rail work vehicles, a few of which were built for other streetcar and radial operators.

The Toronto and York Radial Railway was a transit operator providing services to the suburbs of Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It was a subsidiary of the Toronto Railway Company. The company was created by merging four Toronto-area interurban operations. The company was part of the empire of railway entrepreneurs Sir William Mackenzie and Donald Mann which included the Canadian Northern Railway and the parent Toronto Railway Company.
The Toronto Suburban Railway was a Canadian electric railway operator with local routes in west Toronto, and a radial (interurban) route to Guelph.

The Metropolitan Street Railway was the operator of the Metropolitan line in the Toronto area that started out as a local horsecar line and transformed itself into an electric radial line extending to Lake Simcoe, following an old stage coach route. In 1904, the railway was acquired by the Toronto and York Radial Railway (T&YRR) and became the T&YRR Metropolitan Division. In 1922, the City of Toronto acquired the T&YRR and contracted Ontario Hydro to manage the four T&YRR lines including the Metropolitan. In 1927, the TTC took over the operation of the Metropolitan Line to Sutton, and renamed it the Lake Simcoe line. In 1930, the TTC closed the Metropolitan Line but shortly reopened the portion between Glen Echo and Richmond Hill operating it as the North Yonge Railways until 1948.

The North Yonge Railways was a radial railway line operated by the Toronto Transportation Commission from 1930 to 1948 between Glen Echo (Toronto) and Richmond Hill. The line was created by reopening the southern portion of the TTC's Lake Simcoe radial line that had closed in 1930.

Toronto Transportation Commission (TTC) was the public transit operator in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, beginning in 1921. It operated buses, streetcars and the island ferries. The system was renamed the Toronto Transit Commission (TTC) in 1954.

The Guelph Transit Commission is a small public transportation agency that operates transit bus services in Guelph, Ontario, Canada. Established in 1929 after the closure of the Guelph Radial Railway Company streetcar lines, Guelph Transit has grown to comprise over 70 buses serving 28 transit routes.

Toronto and Scarboro' Electric Railway, Light and Power Company was established in August 1892 to provide street railway service to the Upper Beaches district within the City of Toronto, Ontario and to the neighbouring Township of Scarborough. Except for two branches, the line ran as a radial along Kingston Road.
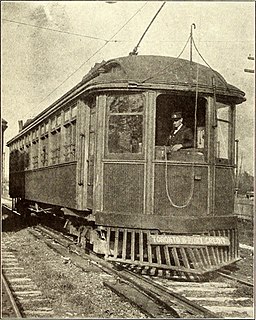
The Toronto and Mimico Electric Railway and Light Company was incorporated in 1890, and operated the Mimico radial line in the Toronto area. The line started operation in 1892 as a short suburban line that later was extended to Port Credit. In 1904, the railway was acquired by the Toronto and York Radial Railway (T&YRR) and became the T&YRR Mimico Division. In 1922, the City of Toronto acquired the T&YRR and contracted Ontario Hydro to manage the four T&YRR lines including the Mimico line. In 1927, the TTC took over the operation of the Mimico line and extended its service eastward to Roncesvalles Avenue. In 1928, the TTC double-tracked the line from Humber to Long Branch and made that portion part of the Lake Shore streetcar line. The portion beyond Long Branch to Port Credit became the Port Credit line, and continued operation as a single-track radial line until its closure on February 9, 1935.

The Niagara, St. Catharines and Toronto Railway was an interurban radial electric railway in the Niagara Peninsula of Southern Ontario, Canada. It operated from 1899 to 1959. It was based in St. Catharines and had lines to Niagara-on-the-Lake, Port Dalhousie, Niagara Falls, Thorold, Welland and Port Colborne.
The Hamilton, Grimsby and Beamsville Electric Railway (HG&B) was an interurban railway that operated between Hamilton and Vineland in the Niagara Peninsula in Ontario, Canada. It was incorporated in 1894.

The Brantford and Hamilton Electric Railway was an interurban electric railway which operated Hamilton, Ontario. Construction was begun by the Von Echa syndicate of Harrisburg, but the railway was taken over by Dominion Power prior to its completion on June 1, 1908. According to Hilton & Due, this was the last radial (interurban) railway constructed in the Hamilton area and the only one built to a high standard.
The Toronto radial lines were interurban lines radiating from Toronto, Ontario, Canada. All are now defunct.
The Canadian National Electric Railways (CNER) was a subsidiary of the Canadian National Railways created to operate a few electric lines. It was formed in November 1923, with headquarters in Toronto.

The Lake Erie and Northern Railway was an interurban electric railway which operated in the Grand River Valley in Ontario, Canada. The railway owned and operated a north–south mainline which ran from Galt in the north to Port Dover on the shore of Lake Erie in the south. Along the way, it ran through rural areas of Waterloo County, Brant County, and Norfolk County, as well as the city of Brantford, where it had an interchange with the Brantford and Hamilton Electric Railway. Construction on the mainline began in 1913. The railway began operations in 1916 as a subsidiary of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR), which had purchased the line before construction had finished. In 1931, it was consolidated with the Grand River Railway under a single CPR subsidiary, the Canadian Pacific Electric Lines (CPEL), which managed both interurban railways, though they continued to exist as legally separate entities. Passenger service was discontinued in 1955 but electric freight operations continued until 1961, when the LE&N's electric locomotives were replaced by diesel CPR locomotives and the line was de-electrified. In the same year, service on the mainline from Simcoe to Port Dover was discontinued, but the remainder continued to operate as a branchline which as early as 1975 was known as the CP Simcoe Subdivision. The remainder of the line was officially abandoned in the early 1990s, ending almost seventy-five years of operation.

Toronto-gauge railways are tram and rapid transit lines built to Toronto gauge, a broad gauge of 4 ft 10+7⁄8 in. This is 2+3⁄8 in (60 mm) wider than standard gauge of 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in which is by far the most common track gauge in Canada. The gauge is unique to the Greater Toronto Area and is currently used on the Toronto streetcar system and the Toronto subway, both operated by the Toronto Transit Commission. As well, the Halton County Radial Railway, a transport museum, uses the Toronto gauge so its rail line can accommodate its collection of Toronto streetcars and subway trains. Several now-defunct interurban rail systems also once used this gauge.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires |journal= (help)Chapter 8 - Hydro Radials, Clean-Up Deals, and Waterfront Grabs