Related Research Articles

Microsoft DirectX is a collection of application programming interfaces (APIs) for handling tasks related to multimedia, especially game programming and video, on Microsoft platforms. Originally, the names of these APIs all began with "Direct", such as Direct3D, DirectDraw, DirectMusic, DirectPlay, DirectSound, and so forth. The name DirectX was coined as a shorthand term for all of these APIs and soon became the name of the collection. When Microsoft later set out to develop a gaming console, the X was used as the basis of the name Xbox to indicate that the console was based on DirectX technology. The X initial has been carried forward in the naming of APIs designed for the Xbox such as XInput and the Cross-platform Audio Creation Tool (XACT), while the DirectX pattern has been continued for Windows APIs such as Direct2D and DirectWrite.
Microsoft Windows was announced by Bill Gates on November 10, 1983. Microsoft introduced Windows as a graphical user interface for MS-DOS, which had been introduced two years earlier. The product line evolved in the 1990s from an operating environment into a fully complete, modern operating system over two lines of development, each with their own separate codebase.

Microsoft Windows, commonly referred to as Windows, is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families, all of which are developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. Active Microsoft Windows families include Windows NT and Windows IoT; these may encompass subfamilies,. Defunct Microsoft Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile and Windows Phone.

Xenix is a discontinued version of the Unix operating system for various microcomputer platforms, licensed by Microsoft from AT&T Corporation in the late 1970s. The Santa Cruz Operation (SCO) later acquired exclusive rights to the software, and eventually replaced it with SCO UNIX.

ActiveX is a deprecated software framework created by Microsoft that adapts its earlier Component Object Model (COM) and Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) technologies for content downloaded from a network, particularly from the World Wide Web. Microsoft introduced ActiveX in 1996. In principle, ActiveX is not dependent on Microsoft Windows operating systems, but in practice, most ActiveX controls only run on Windows. Most also require the client to be running on an x86-based computer because ActiveX controls contain compiled code.

Microsoft Visio is a diagramming and vector graphics application and is part of the Microsoft Office family. The product was first introduced in 1992, made by the Shapeware Corporation. It was acquired by Microsoft in 2000.
Microsoft Message Queuing or MSMQ is a message queue implementation developed by Microsoft and deployed in its Windows Server operating systems since Windows NT 4 and Windows 95. Windows Server 2016 and Windows 10 also includes this component. In addition to its mainstream server platform support, MSMQ has been incorporated into Microsoft Embedded platforms since 1999 and the release of Windows CE 3.0.
The Evaluation Assurance Level of an IT product or system is a numerical grade assigned following the completion of a Common Criteria security evaluation, an international standard in effect since 1999. The increasing assurance levels reflect added assurance requirements that must be met to achieve Common Criteria certification. The intent of the higher levels is to provide higher confidence that the system's principal security features are reliably implemented. The EAL level does not measure the security of the system itself, it simply states at what level the system was tested.

Microsoft Forefront Threat Management Gateway, formerly known as Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration Server, is a network router, firewall, antivirus program, VPN server and web cache from Microsoft Corporation. It runs on Windows Server and works by inspecting all network traffic that passes through it.

ARCHICAD is an architectural BIM CAD software for Macintosh and Windows developed by the Hungarian company Graphisoft. ARCHICAD offers computer aided solutions for handling all common aspects of aesthetics and engineering during the whole design process of the built environment — buildings, interiors, urban areas, etc.

An hydrological transport model is a mathematical model used to simulate the flow of rivers, streams, groundwater movement or drainage front displacement, and calculate water quality parameters. These models generally came into use in the 1960s and 1970s when demand for numerical forecasting of water quality and drainage was driven by environmental legislation, and at a similar time widespread access to significant computer power became available. Much of the original model development took place in the United States and United Kingdom, but today these models are refined and used worldwide.

Visual Basic is a third-generation event-driven programming language from Microsoft known for its Component Object Model (COM) programming model first released in 1991 and declared legacy during 2008. Microsoft intended Visual Basic to be relatively easy to learn and use. Visual Basic was derived from BASIC and enables the rapid application development (RAD) of graphical user interface (GUI) applications, access to databases using Data Access Objects, Remote Data Objects, or ActiveX Data Objects, and creation of ActiveX controls and objects.
HEC-RAS is a computer program that models the hydraulics of water flow through natural rivers and other channels. Prior to the 2016 update to Version 5.0, the program was one-dimensional, meaning that there is no direct modeling of the hydraulic effect of cross section shape changes, bends, and other two- and three-dimensional aspects of flow. The release of Version 5.0 introduced two-dimensional modeling of flow as well as sediment transfer modeling capabilities. The program was developed by the United States Army Corps of Engineers in order to manage the rivers, harbors, and other public works under their jurisdiction; it has found wide acceptance by many others since its public release in 1995.
The ADMS 3 is an advanced atmospheric pollution dispersion model for calculating concentrations of atmospheric pollutants emitted both continuously from point, line, volume and area sources, or intermittently from point sources. It was developed by Cambridge Environmental Research Consultants (CERC) of the UK in collaboration with the UK Meteorological Office, National Power plc and the University of Surrey. The first version of ADMS was released in 1993. The version of the ADMS model discussed on this page is version 3 and was released in February 1999. It runs on Microsoft Windows. The current release, ADMS 5 Service Pack 1, was released in April 2013 with a number of additional features.

Oracle VM VirtualBox is a free and open-source hosted hypervisor for x86 virtualization, developed by Oracle Corporation. Created by Innotek, it was acquired by Sun Microsystems in 2008, which was in turn acquired by Oracle in 2010.

MapWindow GIS is an open-source GIS (mapping) application and set of programmable mapping components. It has been adopted by the United States Environmental Protection Agency as the primary GIS platform for its BASINS watershed analysis and modeling software.
Help is a verb or noun related to assistance. It may also refer to:
Geoprofessions is a term coined by the Geoprofessional Business Association to connote various technical disciplines that involve engineering, earth and environmental services applied to below-ground (“subsurface”), ground-surface, and ground-surface-connected conditions, structures, or formations. The principal disciplines include, as major categories:
The Geochemist's Workbench (GWB) is an integrated set of interactive software tools for solving a range of problems in aqueous chemistry. The graphical user interface simplifies the use of the geochemical code.
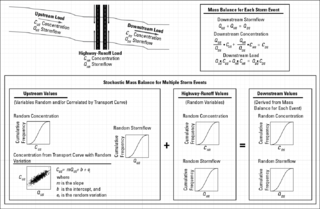
The stochastic empirical loading and dilution model (SELDM) is a stormwater quality model. SELDM is designed to transform complex scientific data into meaningful information about the risk of adverse effects of runoff on receiving waters, the potential need for mitigation measures, and the potential effectiveness of such management measures for reducing these risks. The U.S. Geological Survey developed SELDM in cooperation with the Federal Highway Administration to help develop planning-level estimates of event mean concentrations, flows, and loads in stormwater from a site of interest and from an upstream basin. SELDM uses information about a highway site, the associated receiving-water basin, precipitation events, stormflow, water quality, and the performance of mitigation measures to produce a stochastic population of runoff-quality variables. Although SELDM is, nominally, a highway runoff model is can be used to estimate flows concentrations and loads of runoff-quality constituents from other land use areas as well. SELDM was developed by the U.S. Geological Survey so the model, source code, and all related documentation are provided free of any copyright restrictions according to U.S. copyright laws and the USGS Software User Rights Notice. SELDM is widely used to assess the potential effect of runoff from highways, bridges, and developed areas on receiving-water quality with and without the use of mitigation measures.. Stormwater practitioners evaluating highway runoff commonly use data from the Highway Runoff Database (HRDB) with SELDM to assess the risks for adverse effects of runoff on receiving waters.
References
- 1 2 Schroeder, P.R., Dozier, T.S., Zappi, P.A., McEnroe, B.M., Sjostrom, J.W. and Peyton, R.L. (1994). The Hydrologic Evaluation of Landfill Performance (HELP) model: Engineering documentation for version 3. Cincinnati, OH: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Risk Reduction Engineering Laboratory.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
| This waste-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |