Related Research Articles

A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainage basin of its surface water and groundwater, leading the water out into an ocean. The Irtysh is a chief tributary of the Ob river and is also the longest tributary river in the world with a length of 4,248 km (2,640 mi). The Madeira River is the largest tributary river by volume in the world with an average discharge of 31,200 m3/s (1.1 million cu ft/s).

The Continental Divide of the Americas is the principal, and largely mountainous, hydrological divide of the Americas. The Continental Divide extends from the Bering Strait to the Strait of Magellan, and separates the watersheds that drain into the Pacific Ocean from those river systems that drain into the Atlantic and Arctic oceans.

A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the drainage divide, made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern.

A hydrograph is a graph showing the rate of flow (discharge) versus time past a specific point in a river, channel, or conduit carrying flow. The rate of flow is typically expressed in cubic meters or cubic feet per second . Hydrographs often relate change of precipitation to change of discharge over time. It can also refer to a graph showing the volume of water reaching a particular outfall, or location in a sewerage network. Graphs are commonly used in the design of sewerage, more specifically, the design of surface water sewerage systems and combined sewers.
In hydrology, discharge is the volumetric flow rate of water that is transported through a given cross-sectional area. It includes any suspended solids, dissolved chemicals, or biologic material in addition to the water itself. Terms may vary between disciplines. For example, a fluvial hydrologist studying natural river systems may define discharge as streamflow, whereas an engineer operating a reservoir system may equate it with outflow, contrasted with inflow.
Drainage density is a quantity used to describe physical parameters of a drainage basin. First described by Robert E. Horton, drainage density is defined as the total length of channel in a drainage basin divided by the total area, represented by the following equation:
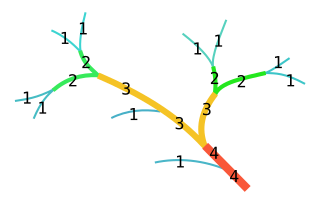
In mathematics, the Strahler number or Horton–Strahler number of a mathematical tree is a numerical measure of its branching complexity.

In hydrology, a mainstem is "the primary downstream segment of a river, as contrasted to its tributaries". Water enters the mainstem from the river's drainage basin, the land area through which the mainstem and its tributaries flow. A drainage basin may also be referred to as a watershed or catchment.

A runoff model or rainfall-runoff model describes how rainfall is converted into runoff in a drainage basin. More precisely, it produces a surface runoff hydrograph in response to a rainfall event, represented by and input as a hyetograph. Rainfall-runoff models need to be calibrated before they can be used.

A continental divide is a drainage divide on a continent such that the drainage basin on one side of the divide feeds into one ocean or sea, and the basin on the other side either feeds into a different ocean or sea, or else is endorheic, not connected to the open sea. Every continent on earth except Antarctica has at least one continental drainage divide; islands, even small ones like Killiniq Island on the Labrador Sea in Canada, may also host part of a continental divide or have their own island-spanning divide. The endpoints of a continental divide may be coastlines of gulfs, seas or oceans, the boundary of an endorheic basin, or another continental divide. One case, the Great Basin Divide, is a closed loop around an endoreic basin. The endpoints where a continental divide meets the coast are not always definite since the exact border between adjacent bodies of water is usually not clearly defined. The International Hydrographic Organization's publication Limits of Oceans and Seas defines exact boundaries of oceans, but it is not universally recognized. Where a continental divide meets an endorheic basin, such as the Great Divide Basin of Wyoming, the continental divide splits and encircles the basin. Where two divides intersect, they form a triple divide, or a tripoint, a junction where three watersheds meet.
The stream order or waterbody order is a positive whole number used in geomorphology and hydrology to indicate the level of branching in a river system.

A stream is a continuous body of surface water flowing within the bed and banks of a channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a stream may be referred to by a variety of local or regional names. Long large streams are usually called rivers, while smaller, less voluminous and more intermittent streams are known as streamlets, brooks or creeks.
Water resources management in Belize is carried out by the Water and Sewerage Authority (WASA) in most cases. One of the primary challenges the country is facing with regard to water resources management, however, is the lack of coordinated and comprehensive policies and institutions. Furthermore, there are various areas of water management that are not well addressed at all such as groundwater data and provision of supply. Data on irrigation and drainage is not adequately available either. Demand on water resources is growing as the population increases, new economic opportunities are created, and the agriculture sector expands. This increased demand is placing new threats on the quality and quantity of freshwater resources. Other constant challenge for management entities are the constant threat of floods from tropical storms and hurricanes. The Belize National Emergency Management Organization (NEMO) is charged with flood management as they occur but it is unclear what institution has responsibility for stormwater infrastructures.
The Gewässerkennzahl or "waterbody index number/waterbody number" is an identifier with which all watercourses in Germany are numbered, together with their catchments and precipitation areas. It is also referred to as a Gebietskennzahl or "basin number". A Gewässerkennzahl may have up to 13 figures. Basins normally are only defined up to seven figures. For a more detailed subdivision, the Gewässerkennzahl may be enlarged by ten more figures. Only that enlarged version is called Fließgewässerkennziffer. The Gewässerkennzahlen are defined by the environment offices of the states.
A waterbody number, waterbody index number or waterbody ID is used for the hydrographic classification of waterbodies. Where classification only covers bodies of flowing water such as rivers, it may be called a watercourse number.
The Pfafstetter Coding System is a hierarchical method of hydrologically coding river basins. It was developed by the Brazilian engineer Otto Pfafstetter in 1989. It is designed such that topological information is embedded in the code, which makes it easy to determine whether an event in one river basin will affect another by direct examination of their codes.

In order to advantage hydrologists, ecologists and water-resource managers in the study of "water, its properties and laws, and its distribution over the earth's surface" in the United States, the United States Geological Survey created a hierarchical system of hydrologic units.
References
- ↑ Watershed Topology - The Pfafstetter System Archived 2011-07-10 at the Wayback Machine , by Jordan Furnans and Francisco Olivera