Related Research Articles

In celestial mechanics, escape velocity or escape speed is the minimum speed needed for a free, non-propelled object to escape from the gravitational influence of a primary body, thus reaching an infinite distance from it. It is typically stated as an ideal speed, ignoring atmospheric friction. Although the term "escape velocity" is common, it is more accurately described as a speed than a velocity because it is independent of direction. The escape speed is independent of the mass of the escaping object, but increases with the mass of the primary body; it decreases with the distance from the primary body, thus taking into account how far the object has already traveled. Its calculation at a given distance means that no acceleration is further needed for the object to escape: it will slow down as it travels—due to the massive body's gravity—but it will never quite slow to a stop. On the other hand, an object already at escape speed needs slowing for it to be captured by the gravitational influence of the body.
Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure, is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere is a unit of pressure defined as 101,325 Pa (1,013.25 hPa), which is equivalent to 1,013.25 millibars, 760 mm Hg, 29.9212 inches Hg, or 14.696 psi. The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm.

A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are sometimes called thundershowers. Thunderstorms occur in a type of cloud known as a cumulonimbus. They are usually accompanied by strong winds and often produce heavy rain and sometimes snow, sleet, or hail, but some thunderstorms produce little precipitation or no precipitation at all. Thunderstorms may line up in a series or become a rainband, known as a squall line. Strong or severe thunderstorms include some of the most dangerous weather phenomena, including large hail, strong winds, and tornadoes. Some of the most persistent severe thunderstorms, known as supercells, rotate as do cyclones. While most thunderstorms move with the mean wind flow through the layer of the troposphere that they occupy, vertical wind shear sometimes causes a deviation in their course at a right angle to the wind shear direction.
In Newtonian physics, free fall is any motion of a body where gravity is the only force acting upon it. In the context of general relativity, where gravitation is reduced to a space-time curvature, a body in free fall has no force acting on it.
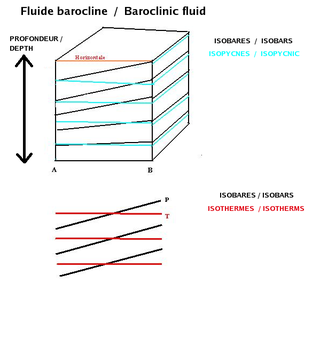
In fluid dynamics, the baroclinity of a stratified fluid is a measure of how misaligned the gradient of pressure is from the gradient of density in a fluid. In meteorology a baroclinic flow is one in which the density depends on both temperature and pressure. A simpler case, barotropic flow, allows for density dependence only on pressure, so that the curl of the pressure-gradient force vanishes.

Millimeter-wave cloud radars, also denominated cloud radars, are radar systems designed to monitor clouds with operating frequencies between 24 and 110 GHz. Accordingly, their wavelengths range from 1 mm to 1.11 cm, about ten times shorter than those used in conventional S band radars such as NEXRAD.
Delta-v, symbolized as ∆v and pronounced delta-vee, as used in spacecraft flight dynamics, is a measure of the impulse per unit of spacecraft mass that is needed to perform a maneuver such as launching from or landing on a planet or moon, or an in-space orbital maneuver. It is a scalar that has the units of speed. As used in this context, it is not the same as the physical change in velocity of said spacecraft.

A squall is a sudden, sharp increase in wind speed lasting minutes, as opposed to a wind gust, which lasts for only seconds. They are usually associated with active weather, such as rain showers, thunderstorms, or heavy snow. Squalls refer to the increase of the sustained winds over that time interval, as there may be higher gusts during a squall event. They usually occur in a region of strong sinking air or cooling in the mid-atmosphere. These force strong localized upward motions at the leading edge of the region of cooling, which then enhances local downward motions just in its wake.

Terminal velocity is the maximum velocity (speed) attainable by an object as it falls through a fluid. It occurs when the sum of the drag force (Fd) and the buoyancy is equal to the downward force of gravity (FG) acting on the object. Since the net force on the object is zero, the object has zero acceleration.

In aerodynamics, wing loading is the total mass of an aircraft or flying animal divided by the area of its wing. The stalling speed of an aircraft is partly determined by its wing loading.

Mammatus is a cellular pattern of pouches hanging underneath the base of a cloud, typically a cumulonimbus raincloud, although they may be attached to other classes of parent clouds. The name mammatus is derived from the Latin mamma.
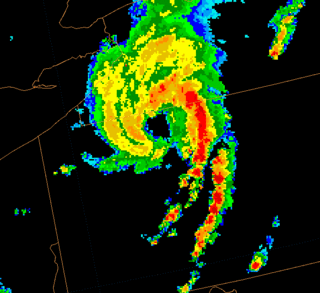
A squall line, or more accurately a quasi-linear convective system (QLCS), is a line of thunderstorms, often forming along or ahead of a cold front. In the early 20th century, the term was used as a synonym for cold front. Linear thunderstorm structures often contain heavy precipitation, hail, frequent lightning, strong straight-line winds, and occasionally tornadoes or waterspouts. Particularly strong straight-line winds can occur where the linear structure forms into the shape of a bow echo. Tornadoes can occur along waves within a line echo wave pattern (LEWP), where mesoscale low-pressure areas are present. Some bow echoes can grow to become derechos as they move swiftly across a large area. On the back edge of the rainband associated with mature squall lines, a wake low can be present, on very rare occasions associated with a heat burst.

In meteorology, convective available potential energy, is the integrated amount of work that the upward (positive) buoyancy force would perform on a given mass of air if it rose vertically through the entire atmosphere. Positive CAPE will cause the air parcel to rise, while negative CAPE will cause the air parcel to sink. Nonzero CAPE is an indicator of atmospheric instability in any given atmospheric sounding, a necessary condition for the development of cumulus and cumulonimbus clouds with attendant severe weather hazards.

Cyclogenesis is the development or strengthening of cyclonic circulation in the atmosphere. Cyclogenesis is an umbrella term for at least three different processes, all of which result in the development of some sort of cyclone, and at any size from the microscale to the synoptic scale.

A reentry capsule is the portion of a space capsule which returns to Earth following a spaceflight. The shape is determined partly by aerodynamics; a capsule is aerodynamically stable falling blunt end first, which allows only the blunt end to require a heat shield for atmospheric entry. A crewed capsule contains the spacecraft's instrument panel, limited storage space, and seats for crew members. Because a capsule shape has little aerodynamic lift, the final descent is via parachute, either coming to rest on land, at sea, or by active capture by an aircraft. In contrast, the development of spaceplane reentry vehicles attempts to provide a more flexible reentry profile.
In the physics of aerosols, deposition is the process by which aerosol particles collect or deposit themselves on solid surfaces, decreasing the concentration of the particles in the air. It can be divided into two sub-processes: dry and wet deposition. The rate of deposition, or the deposition velocity, is slowest for particles of an intermediate size. Mechanisms for deposition are most effective for either very small or very large particles. Very large particles will settle out quickly through sedimentation (settling) or impaction processes, while Brownian diffusion has the greatest influence on small particles. This is because very small particles coagulate in few hours until they achieve a diameter of 0.5 micrometres. At this size they no longer coagulate. This has a great influence in the amount of PM-2.5 present in the air.
A set of equations describing the trajectories of objects subject to a constant gravitational force under normal Earth-bound conditions. Assuming constant acceleration g due to Earth’s gravity, Newton's law of universal gravitation simplifies to F = mg, where F is the force exerted on a mass m by the Earth’s gravitational field of strength g. Assuming constant g is reasonable for objects falling to Earth over the relatively short vertical distances of our everyday experience, but is not valid for greater distances involved in calculating more distant effects, such as spacecraft trajectories.
A gravity turn or zero-lift turn is a maneuver used in launching a spacecraft into, or descending from, an orbit around a celestial body such as a planet or a moon. It is a trajectory optimization that uses gravity to steer the vehicle onto its desired trajectory. It offers two main advantages over a trajectory controlled solely through the vehicle's own thrust. First, the thrust is not used to change the spacecraft's direction, so more of it is used to accelerate the vehicle into orbit. Second, and more importantly, during the initial ascent phase the vehicle can maintain low or even zero angle of attack. This minimizes transverse aerodynamic stress on the launch vehicle, allowing for a lighter launch vehicle.

A wake low, or wake depression, is a mesoscale low-pressure area which trails the mesoscale high following a squall line. Due to the subsiding warm air associated with the system's formation, clearing skies are associated with the wake low. Once difficult to detect in surface weather observations due to their broad spacing, the formation of mesoscale weather station networks, or mesonets, has increased their detection. Severe weather, in the form of high winds, can be generated by the wake low when the pressure difference between the mesohigh preceding it and the wake low is intense enough. When the squall line is in the process of decay, heat bursts can be generated near the wake low. Once new thunderstorm activity along the squall line concludes, the wake low associated with it weakens in tandem.
A mesohigh is a mesoscale high-pressure area that forms beneath thunderstorms. While not always the case, it is usually associated with a mesoscale convective system. In the early stages of research on the subject, the mesohigh was often referred to as a "thunderstorm high".
References
- ↑ Markowski, Paul; Yvette Richardson (2010). Mesoscale Meteorology in Midlatitudes. West Sussex, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. p. 20. ISBN 978-0-470-74213-6.
- ↑ Asnani, G.C.; M. K. Rama Varma Raja (March 2000). "A New Hypothesis for Layers of High Reflectivity Seen in MST Radar Observations". arXiv: physics/0003028v1 .
- ↑ Geerts, B; E. Linacre; L. Oolman. "Microbursts". Learning about weather and climate: some short articles. Retrieved 16 October 2011.
- ↑ Sanders, Frederick; Kerry A. Emanuel (February 1977). "The Momentum Budget and Temporal Evolution of a Mesoscale Convective System". Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences. 34 (2): 322–330. Bibcode:1977JAtS...34..322S. doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1977)034<0322:TMBATE>2.0.CO;2 .