
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is the genetic material of an organism. It consists of DNA. The genome includes both the genes and the noncoding DNA, as well as mitochondrial DNA and chloroplast DNA. The study of the genome is called genomics.
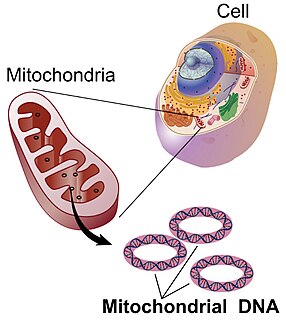
Mitochondrial DNA is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants and algae, also in plastids such as chloroplasts.

Chalcid wasps are insects within the superfamily Chalcidoidea, part of the order Hymenoptera. The superfamily contains some 22,500 known species, and an estimated total diversity of more than 500,000 species, meaning the vast majority have yet to be discovered and described. The name "chalcid" is often confused with the name "chalcidid", though the latter refers strictly to one constituent family, the Chalcididae, rather than the superfamily as a whole; accordingly, most recent publications (e.g.,) use the name "chalcidoid" when referring to members of the superfamily.

Sawflies are the insects of the suborder Symphyta within the order Hymenoptera alongside ants, bees and wasps. The common name comes from the saw-like appearance of the ovipositor, which the females use to cut into the plants where they lay their eggs. The name is associated especially with the Tenthredinoidea, by far the largest superfamily, with about 7,000 known species; in the entire suborder, there are 8,000 described species in more than 800 genera. The suborder Symphyta is paraphyletic, consisting of several basal groups within the order Hymenoptera.

Endopterygota, also known as Holometabola, is a superorder of insects within the infraclass Neoptera that go through distinctive larval, pupal, and adult stages. They undergo a radical metamorphosis, with the larval and adult stages differing considerably in their structure and behaviour. This is called holometabolism, or complete metamorphism.

The Wellcome Sanger Institute, previously known as The Sanger Centre and Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, is a non-profit British genomics and genetics research institute, primarily funded by the Wellcome Trust.

A polydnavirus (PDV) is a member of the family Polydnaviridae of insect viruses. There are currently 53 species in this family, divided among 2 genera. Polydnaviruses form a symbiotic relationship with parasitoid wasps, but these wasps are themselves parasitic on Lepidoptera. Little or no sequence homology exists between BV and IV, suggesting that the two genera evolved independently for a long time.

Ensembl genome database project is a joint scientific project between the European Bioinformatics Institute and the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, which was launched in 1999 in response to the imminent completion of the Human Genome Project. Ensembl aims to provide a centralized resource for geneticists, molecular biologists and other researchers studying the genomes of our own species and other vertebrates and model organisms. Ensembl is one of several well known genome browsers for the retrieval of genomic information.

KEGG is a collection of databases dealing with genomes, biological pathways, diseases, drugs, and chemical substances. KEGG is utilized for bioinformatics research and education, including data analysis in genomics, metagenomics, metabolomics and other omics studies, modeling and simulation in systems biology, and translational research in drug development.

Haplodiploidy is a sex-determination system in which males develop from unfertilized eggs and are haploid, and females develop from fertilized eggs and are diploid. Haplodiploidy is sometimes called arrhenotoky.
Mouse Genome Informatics (MGI) is a free, online database and bioinformatics resource hosted by The Jackson Laboratory, with funding by the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), the National Cancer Institute (NCI), and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD). MGI provides access to data on the genetics, genomics and biology of the laboratory mouse to facilitate the study of human health and disease. The database integrates multiple projects, with the two largest contributions coming from the Mouse Genome Database and Mouse Gene Expression Database (GXD). As of 2018, MGI contains data curated from over 230,000 publications.

Sterol-4-alpha-carboxylate 3-dehydrogenase, decarboxylating is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NSDHL gene. This enzyme is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum and is involved in cholesterol biosynthesis.

Whole genome sequencing is ostensibly the process of determining the complete DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's chromosomal DNA as well as DNA contained in the mitochondria and, for plants, in the chloroplast. In practice, genome sequences that are nearly complete are also called whole genome sequences.
The UCSC Genome Browser is an on-line, and downloadable, genome browser hosted by the University of California, Santa Cruz (UCSC). It is an interactive website offering access to genome sequence data from a variety of vertebrate and invertebrate species and major model organisms, integrated with a large collection of aligned annotations. The Browser is a graphical viewer optimized to support fast interactive performance and is an open-source, web-based tool suite built on top of a MySQL database for rapid visualization, examination, and querying of the data at many levels. The Genome Browser Database, browsing tools, downloadable data files, and documentation can all be found on the UCSC Genome Bioinformatics website.
The Bovine Genome Database is an integrated database for the bovine genome.

Lasius alienus, or cornfield ant, is a species of ant in the subfamily Formicinae. Workers have a length of about 2–4 mm, Queens are larger (7–9 mm).

Pompiloidea is a superfamily that includes spider wasps and velvet ants, among others. in the order Hymenoptera. There are at least 5 families and 290 described species in Pompiloidea.
Oraseminae is a subfamily of chalcid wasps in the family Eucharitidae. There are at least 10 genera in Oraseminae.














