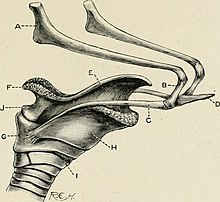
The hyoid bone is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra.

The epiglottis is a leaf-shaped flap in the throat that prevents food and water from entering the trachea and the lungs. It stays open during breathing, allowing air into the larynx. During swallowing, it closes to prevent aspiration of food into the lungs, forcing the swallowed liquids or food to go along the esophagus toward the stomach instead. It is thus the valve that diverts passage to either the trachea or the esophagus.

In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.

The suprahyoid muscles are four muscles located above the hyoid bone in the neck. They are the digastric, stylohyoid, geniohyoid, and mylohyoid muscles. They are all pharyngeal muscles, with the exception of the geniohyoid muscle. The digastric is uniquely named for its two bellies. Its posterior belly rises from the mastoid process of the cranium and slopes downward and forward. The anterior belly arises from the digastric fossa on the inner surface of the mandibular body, which slopes downward and backward. The two bellies connect at the intermediate tendon. The intermediate tendon passes through a connective tissue loop attached to the hyoid bone. The mylohyoid muscles are thin, flat muscles that form a sling inferior to the tongue supporting the floor of the mouth. The geniohyoids are short, narrow muscles that contact each other in the midline. The stylohyoids are long, thin muscles that are nearly parallel with the posterior belly of the digastric muscle.

The infrahyoid muscles, or strap muscles, are a group of four pairs of muscles in the anterior (frontal) part of the neck. The four infrahyoid muscles are the sternohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid and omohyoid muscles.

The axial skeleton is the part of the skeleton that consists of the bones of the head and trunk of a vertebrate. In the human skeleton, it consists of 80 bones and is composed of six parts; the skull, also the ossicles of the middle ear, the hyoid bone, the rib cage, sternum and the vertebral column. The axial skeleton together with the appendicular skeleton form the complete skeleton. Another definition of axial skeleton is the bones including the vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx, skull, ribs, and sternum.

The omohyoid muscle is a muscle in the neck. It is one of the infrahyoid muscles. It consists of two bellies separated by an intermediate tendon. Its inferior belly is attached to the scapula; its superior belly is attached to the hyoid bone. Its intermediate tendon is anchored to the clavicle and first rib by a fascial sling. The omohyoid is innervated by the ansa cervicalis of the cervical plexus. It acts to depress the hyoid bone.

The endomysium, meaning within the muscle, is a wispy layer of areolar connective tissue that ensheaths each individual muscle fiber, or muscle cell. It also contains capillaries and nerves. It overlies the muscle fiber's cell membrane: the sarcolemma. Endomysium is the deepest and smallest component of muscle connective tissue. This thin layer helps provide an appropriate chemical environment for the exchange of calcium, sodium, and potassium, which is essential for the excitation and subsequent contraction of a muscle fiber.

The geniohyoid muscle is a narrow paired muscle situated superior to the medial border of the mylohyoid muscle. It is named for its passage from the chin to the hyoid bone.

The mylohyoid muscle or diaphragma oris is a paired muscle of the neck. It runs from the mandible to the hyoid bone, forming the floor of the oral cavity of the mouth. It is named after its two attachments near the molar teeth. It forms the floor of the submental triangle. It elevates the hyoid bone and the tongue, important during swallowing and speaking.

The stylohyoid muscle is one of the suprahyoid muscles. Its originates from the styloid process of the temporal bone; it inserts onto hyoid bone. It is innervated by a branch of the facial nerve. It acts draw the hyoid bone upwards and backwards.

The thyrohyoid muscle is a small skeletal muscle of the neck. Above, it attaches onto the greater cornu of the hyoid bone; below, it attaches onto the oblique line of the thyroid cartilage. It is innervated by fibres derived from the cervical spinal nerve 1 that run with the hypoglossal nerve to reach this muscle. The thyrohyoid muscle depresses the hyoid bone and elevates the larynx during swallowing. By controlling the position and shape of the larynx, it aids in making sound.

The psoas minor muscle is a long, slender skeletal muscle. When present, it is located anterior to the psoas major muscle.

The genioglossus is one of the paired extrinsic muscles of the tongue. It is a fan-shaped muscle that comprises the bulk of the body of the tongue. It arises from the mental spine of the mandible; it inserts onto the hyoid bone, and the bottom of the tongue. It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve. The genioglossus is the major muscle responsible for protruding the tongue.

The stylohyoid ligament is a ligament that extends between the hyoid bone, and the temporal styloid process.

The thyrohyoid membrane is a broad, fibro-elastic sheet of the larynx. It connects the upper border of the thyroid cartilage to the hyoid bone.

The lingual artery arises from the external carotid artery between the superior thyroid artery and facial artery. It can be located easily in the tongue.

The submental lymph nodes are 2-3 lymph nodes situated in the submental triangle, between the anterior bellies of the digastric muscle and the hyoid bone.
The face and neck development of the human embryo refers to the development of the structures from the third to eighth week that give rise to the future head and neck. They consist of three layers, the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, which form the mesenchyme, neural crest and neural placodes. The paraxial mesoderm forms structures named somites and somitomeres that contribute to the development of the floor of the brain and voluntary muscles of the craniofacial region. The lateral plate mesoderm consists of the laryngeal cartilages. The three tissue layers give rise to the pharyngeal apparatus, formed by six pairs of pharyngeal arches, a set of pharyngeal pouches and pharyngeal grooves, which are the most typical feature in development of the head and neck. The formation of each region of the face and neck is due to the migration of the neural crest cells which come from the ectoderm. These cells determine the future structure to develop in each pharyngeal arch. Eventually, they also form the neurectoderm, which forms the forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain, cartilage, bone, dentin, tendon, dermis, pia mater and arachnoid mater, sensory neurons, and glandular stroma.