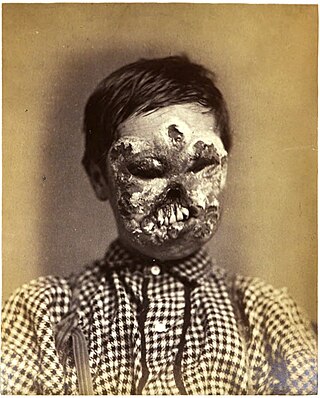
Disfigurement is the state of having one's appearance deeply and persistently harmed medically, such as from a disease, birth defect, or wound. General societal attitudes towards disfigurement have varied greatly across cultures and over time, with cultures possessing strong social stigma against it often causing psychological distress to disfigured individuals. Alternatively, many societies have regarded some forms of disfigurement in a medical, scientific context where someone having ill will against the disfigured is viewed as anathema. In various religious and spiritual contexts, disfigurement has been variously described as being a punishment from the divine for sin, as being caused by supernatural forces of hate and evil against the good and just, which will be later atoned for, or as being without explanation per se with people just having to endure.

Pathognomy is "a 'semiotik' of the transient features of someone's face or body, be it voluntary or involuntary". Examples of this can be laughter and winking to the involuntary such as sneezing or coughing. By studying the features or expressions, there is then an attempt to infer the mental state and emotion felt by the individual.

A microexpression is a facial expression that only lasts for a short moment. It is the innate result of a voluntary and an involuntary emotional response occurring simultaneously and conflicting with one another, and occurs when the amygdala responds appropriately to the stimuli that the individual experiences and the individual wishes to conceal this specific emotion. This results in the individual very briefly displaying their true emotions followed by a false emotional reaction.

A facial recognition system is a technology potentially capable of matching a human face from a digital image or a video frame against a database of faces. Such a system is typically employed to authenticate users through ID verification services, and works by pinpointing and measuring facial features from a given image.

Guillaume-Benjamin-Amand Duchenne was a French neurologist who revived Galvani's research and greatly advanced the science of electrophysiology. The era of modern neurology developed from Duchenne's understanding of neural pathways and his diagnostic innovations including deep tissue biopsy, nerve conduction tests (NCS), and clinical photography. This extraordinary range of activities was achieved against the background of a troubled personal life and a generally indifferent medical and scientific establishment.

Facial nerve paralysis is a common problem that involves the paralysis of any structures innervated by the facial nerve. The pathway of the facial nerve is long and relatively convoluted, so there are a number of causes that may result in facial nerve paralysis. The most common is Bell's palsy, a disease of unknown cause that may only be diagnosed by exclusion of identifiable serious causes.

The Facial Action Coding System (FACS) is a system to taxonomize human facial movements by their appearance on the face, based on a system originally developed by a Swedish anatomist named Carl-Herman Hjortsjö. It was later adopted by Paul Ekman and Wallace V. Friesen, and published in 1978. Ekman, Friesen, and Joseph C. Hager published a significant update to FACS in 2002. Movements of individual facial muscles are encoded by the FACS from slight different instant changes in facial appearance. It has proven useful to psychologists and to animators.

The lips are a horizontal pair of soft appendages attached to the jaws and are the most visible part of the mouth of many animals, including humans. Vertebrate lips are soft, movable and serve to facilitate the ingestion of food and the articulation of sound and speech. Human lips are also a somatosensory organ, and can be an erogenous zone when used in kissing and other acts of intimacy.
An emotional expression is a behavior that communicates an emotional state or attitude. It can be verbal or nonverbal, and can occur with or without self-awareness. Emotional expressions include facial movements like smiling or scowling, simple behaviors like crying, laughing, or saying "thank you," and more complex behaviors like writing a letter or giving a gift. Individuals have some conscious control of their emotional expressions; however, they need not have conscious awareness of their emotional or affective state in order to express emotion.

In psychology and sociology, masking is the process in which an individual camouflages their natural personality or behavior to conform to social pressures, abuse, or harassment. Masking can be strongly influenced by environmental factors such as authoritative parents, rejection, and emotional, physical, or sexual abuse. Masking can be a behavior individuals adopt subconsciously as coping mechanisms or a trauma response, or it can be a conscious behavior an individual adopts to fit in within perceived societal norms. Masking is interconnected with maintaining performative behavior within social structures and cultures.
Facial motion capture is the process of electronically converting the movements of a person's face into a digital database using cameras or laser scanners. This database may then be used to produce computer graphics (CG), computer animation for movies, games, or real-time avatars. Because the motion of CG characters is derived from the movements of real people, it results in a more realistic and nuanced computer character animation than if the animation were created manually.
Orofacial granulomatosis (OFG) is a condition characterized by persistent enlargement of the soft tissues of the mouth, lips and the area around the mouth on the face, causing in most cases extreme pain. The mechanism of the enlargement is granulomatous inflammation. The underlying cause of the condition is not completely understood, and there is disagreement as to how it relates to Crohn's disease and sarcoidosis.

Young–Simpson syndrome (YSS) is a rare congenital disorder with symptoms including hypothyroidism, heart defects, facial dysmorphism, cryptorchidism in males, hypotonia, intellectual disability, and postnatal growth retardation.

In medical contexts, a facies is a distinctive facial expression or appearance associated with a specific medical condition. The term comes from Latin for "face". As a fifth declension noun, facies can be both singular and plural.

Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a chronic degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that affects both the motor system and non-motor systems. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms become more common. Early symptoms are tremor, rigidity, slowness of movement, and difficulty with walking. Problems may also arise with cognition, behaviour, sleep, and sensory systems. Parkinson's disease dementia becomes common in advanced stages of the disease.
Signs and symptoms of Parkinson's disease are varied. Parkinson's disease affects movement, producing motor symptoms. Non-motor symptoms, which include dysautonomia, cognitive and neurobehavioral problems, and sensory and sleep difficulties, are also common. When other diseases mimic Parkinson's disease, they are categorized as parkinsonism.
Non-verbal leakage is a form of non-verbal behavior that occurs when a person verbalizes one thing, but their body language indicates another, common forms of which include facial movements and hand-to-face gestures. The term "non-verbal leakage" got its origin in literature in 1968, leading to many subsequent studies on the topic throughout the 1970s, with related studies continuing today.
Facial masking may refer to:
Erin Smith is an American entrepreneur and inventor. She is the founder of FacePrint, a medical technology venture that is developing facial recognition software to assist with the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease. Smith was a Thiel Fellow in 2018, and was awarded the first place Young Inventors Prize from the European Patent Office in 2022.












