
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral to caudal axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain, though precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets.

A motor neuron is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or indirectly control effector organs, mainly muscles and glands. There are two types of motor neuron – upper motor neurons and lower motor neurons. Axons from upper motor neurons synapse onto interneurons in the spinal cord and occasionally directly onto lower motor neurons. The axons from the lower motor neurons are efferent nerve fibers that carry signals from the spinal cord to the effectors. Types of lower motor neurons are alpha motor neurons, beta motor neurons, and gamma motor neurons.

The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiovascular center, the respiratory center, vomiting and vasomotor centers, responsible for the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle. "Medulla" is from Latin, ‘pith or marrow’. And "oblongata" is from Latin, ‘lengthened or longish or elongated'.

The brainstem is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch, and sometimes the diencephalon is included in the brainstem.

In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve (lit. triplet nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; it is the most complex of the cranial nerves. Its name (trigeminal, from Latin tri- 'three' and -geminus 'twin') derives from each of the two nerves (one on each side of the pons) having three major branches: the ophthalmic nerve (V1), the maxillary nerve (V2), and the mandibular nerve (V3). The ophthalmic and maxillary nerves are purely sensory, whereas the mandibular nerve supplies motor as well as sensory (or "cutaneous") functions. Adding to the complexity of this nerve is that autonomic nerve fibers as well as special sensory fibers (taste) are contained within it.

In anatomy, the extrapyramidal system is a part of the motor system network causing involuntary actions. The system is called extrapyramidal to distinguish it from the tracts of the motor cortex that reach their targets by traveling through the pyramids of the medulla. The pyramidal tracts may directly innervate motor neurons of the spinal cord or brainstem, whereas the extrapyramidal system centers on the modulation and regulation of anterior (ventral) horn cells.
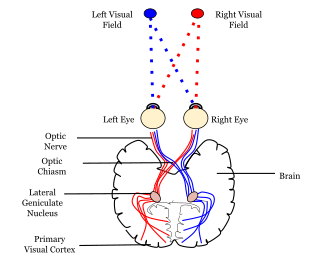
In neuroanatomy, a neural pathway is the connection formed by axons that project from neurons to make synapses onto neurons in another location, to enable neurotransmission. Neurons are connected by a single axon, or by a bundle of axons known as a nerve tract, or fasciculus. Shorter neural pathways are found within grey matter in the brain, whereas longer projections, made up of myelinated axons, constitute white matter.

The pyramidal tracts include both the corticobulbar tract and the corticospinal tract. These are aggregations of efferent nerve fibers from the upper motor neurons that travel from the cerebral cortex and terminate either in the brainstem (corticobulbar) or spinal cord (corticospinal) and are involved in the control of motor functions of the body.

The spinothalamic tract is a nerve tract in the anterolateral system in the spinal cord. This tract is an ascending sensory pathway to the thalamus. From the ventral posterolateral nucleus in the thalamus, sensory information is relayed upward to the somatosensory cortex of the postcentral gyrus.

The corticobulbartract is a two-neuron white matter motor pathway connecting the motor cortex in the cerebral cortex to the medullary pyramids, which are part of the brainstem's medulla oblongata region, and are primarily involved in carrying the motor function of the non-oculomotor cranial nerves, like muscles of the face, head and neck. The corticobulbar tract is one of the pyramidal tracts, the other being the corticospinal tract.

Upper motor neurons (UMNs) is a term introduced by William Gowers in 1886. They are found in the cerebral cortex and brainstem and carry information down to activate interneurons and lower motor neurons, which in turn directly signal muscles to contract or relax. UMNs represent the major origin point for voluntary somatic movement.

The precentral gyrus is a prominent gyrus on the surface of the posterior frontal lobe of the brain. It is the site of the primary motor cortex that in humans is cytoarchitecturally defined as Brodmann area 4.

The spinocerebellar tracts are nerve tracts originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side (ipsilateral) of the cerebellum. The two main tracts are the dorsal spinocerebellar tract, and the ventral spinocerebellar tract. Both of these tracts are located in the peripheral region of the lateral funiculi. Other tracts are the rostral spinocerebellar tract, and the cuneocerebellar tract.

The vestibulospinal tract is a neural tract in the central nervous system. Specifically, it is a component of the extrapyramidal system and is classified as a component of the medial pathway. Like other descending motor pathways, the vestibulospinal fibers of the tract relay information from nuclei to motor neurons. The vestibular nuclei receive information through the vestibulocochlear nerve about changes in the orientation of the head. The nuclei relay motor commands through the vestibulospinal tract. The function of these motor commands is to alter muscle tone, extend, and change the position of the limbs and head with the goal of supporting posture and maintaining balance of the body and head.

The lateral corticospinal tract is the largest part of the corticospinal tract. It extends throughout the entire length of the spinal cord, and on transverse section appears as an oval area in front of the posterior column and medial to the posterior spinocerebellar tract.

The anterior corticospinal tract is a small bundle of descending fibers that connect the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord. Descending tracts are pathways by which motor signals are sent from upper motor neurons in the brain to lower motor neurons which then directly innervate muscle to produce movement. The anterior corticospinal tract is usually small, varying inversely in size with the lateral corticospinal tract, which is the main part of the corticospinal tract.
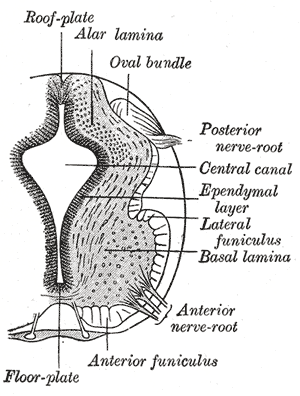
Alpha (α) motor neurons (also called alpha motoneurons), are large, multipolar lower motor neurons of the brainstem and spinal cord. They innervate extrafusal muscle fibers of skeletal muscle and are directly responsible for initiating their contraction. Alpha motor neurons are distinct from gamma motor neurons, which innervate intrafusal muscle fibers of muscle spindles.

In neuroanatomy, the medullary pyramids are paired white matter structures of the brainstem's medulla oblongata that contain motor fibers of the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts – known together as the pyramidal tracts. The lower limit of the pyramids is marked when the fibers cross (decussate).
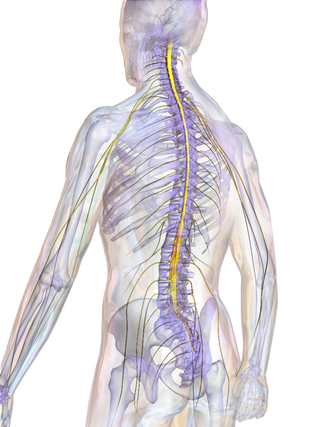
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system.

The corticospinal tract is a white matter motor pathway starting at the cerebral cortex that terminates on lower motor neurons and interneurons in the spinal cord, controlling movements of the limbs and trunk. There are more than one million neurons in the corticospinal tract, and they become myelinated usually in the first two years of life.















