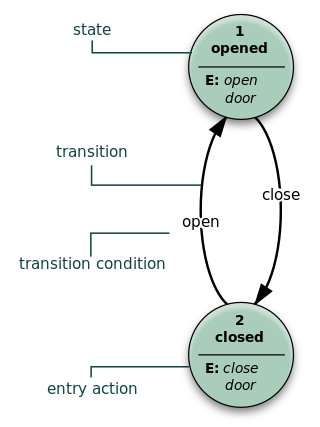
A state diagram is used in computer science and related fields to describe the behavior of systems. State diagrams require that the system is composed of a finite number of states. Sometimes, this is indeed the case, while at other times this is a reasonable abstraction. Many forms of state diagrams exist, which differ slightly and have different semantics.
The rational unified process (RUP) is an iterative software development process framework created by the Rational Software Corporation, a division of IBM since 2003. RUP is not a single concrete prescriptive process, but rather an adaptable process framework, intended to be tailored by the development organizations and software project teams that will select the elements of the process that are appropriate for their needs. RUP is a specific implementation of the Unified Process.

IBM is a globally integrated enterprise operating in 170 countries. IBM's R&D history in Israel began in 1972 when Professor Josef Raviv established the IBM Israel Scientific Center in the Technion's Computer Science Building in Haifa. As of 2023, over 3000 individuals work at IBM R&D locations across Israel, including Haifa, Tel Aviv, Herzliya, Rehovot, and the Jerusalem Technology Park.

Unicom System Architect is an enterprise architecture tool that is used by the business and technology departments of corporations and government agencies to model their business operations and the systems, applications, and databases that support them. System Architect is used to build architectures using various frameworks including TOGAF, ArchiMate, DoDAF, MODAF, NAF and standard method notations such as sysML, UML, BPMN, and relational data modeling. System Architect is developed by UNICOM Systems, a division of UNICOM Global, a United States-based company.

David Harel is a computer scientist, currently serving as President of the Israel Academy of Sciences and Humanities. He has been on the faculty of the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel since 1980, and holds the William Sussman Professorial Chair of Mathematics. Born in London, England, he was Dean of the Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science at the institute for seven years.
UML Partners was a consortium of system integrators and vendors convened in 1996 to specify the Unified Modeling Language (UML). Initially the consortium was led by Grady Booch, Ivar Jacobson, and James Rumbaugh of Rational Software. The UML Partners' UML 1.0 specification draft was proposed to the Object Management Group (OMG) in January 1997. During the same month the UML Partners formed a Semantics Task Force, chaired by Cris Kobryn, to finalize the semantics of the specification and integrate it with other standardization efforts. The result of this work, UML 1.1, was submitted to the OMG in August 1997 and adopted by the OMG in November 1997.
Model-driven engineering (MDE) is a software development methodology that focuses on creating and exploiting domain models, which are conceptual models of all the topics related to a specific problem. Hence, it highlights and aims at abstract representations of the knowledge and activities that govern a particular application domain, rather than the computing concepts.
Executable UML is both a software development method and a highly abstract software language. It was described for the first time in 2002 in the book "Executable UML: A Foundation for Model-Driven Architecture". The language "combines a subset of the UML graphical notation with executable semantics and timing rules." The Executable UML method is the successor to the Shlaer–Mellor method.
Telelogic AB was a software business headquartered in Malmö, Sweden. Telelogic was founded in 1983 as a research and development arm of Televerket, the Swedish department of telecom. It was later acquired by IBM Rational, and exists under the IBM software group.
Rational Rose was a development environment for Unified Modeling Language. It integrates with Microsoft Visual Studio .NET and Rational Application Developer. The Rational Software division of IBM, which previously produced Rational Rose, wrote this software.
Rational Rhapsody, a modeling environment based on UML, is a visual development environment for systems engineers and software developers creating real-time or embedded systems and software. Rational Rhapsody uses graphical models to generate software applications in various languages including C, C++, Ada, Java and C#.

Rational Software Modeler (RSM), made by IBM's Rational Software division, is a Unified Modeling Language (UML) 2.0-based visual modeling and design tool. Rational Software Modeler is based on the Eclipse open-source software framework and is used for visual modeling and model-driven development (MDD) with UML for creating applications and web services. IBM ceased marketing Rational Software Modeler in 2010 and ended support for it in 2015. Much of the same functionality is now available through Rational Software Architect.
Rational Synergy is a software tool that provides software configuration management (SCM) capabilities for all artifacts related to software development including source code, documents and images as well as the final built software executable and libraries. Rational Synergy also provides the repository for the change management tool known as Rational Change. Together these two tools form an integrated configuration management and change management environment that is used in software development organizations that need controlled SCM processes and an understanding of what is in a build of their software.
UML state machine, formerly known as UML statechart, is an extension of the mathematical concept of a finite automaton in computer science applications as expressed in the Unified Modeling Language (UML) notation.

QP is a family of open source real-time embedded frameworks (RTEFs) and runtime environments based on active objects (actors) and hierarchical state machines. The QP family consists of the lightweight QP/C and QP/C++ frameworks, written in C (C99) and C++ (C++11), respectively.
Schindler&Schill GmbH is a German software company, founded 2008 in Regensburg by two experts on Windows based software. The company also trades under EasyLogix.
Rational Dynamic Object Oriented Requirements System (DOORS) (formerly Telelogic DOORS) is a requirements management tool. It is a client–server application, with a Windows-only client and servers for Linux, Windows, and Solaris. There is also a web client, DOORS Web Access.

YAKINDU Statechart Tools (YAKINDU SCT) is a tool for the specification and development of reactive, event-driven systems with the help of finite-state machines. It comprises a tool for the graphical editing of statecharts and provides validation, simulation, and source code generators for various target platforms and programming languages. YAKINDU Statechart Tools are available with standard and professional editions, with no-cost licenses for non-commercial resp. academic usage. Users are coming from both industry and academia.
TeleSoft, Inc. was an American software development company founded in 1981 and based in San Diego, California, that specialized in development tools for the Ada programming language.






