| IGHG2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | IGHG2 , immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 2 (G2m marker) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 147110 GeneCards: IGHG2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ig gamma-2 chain C region is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGHG2 gene. [3]
| IGHG2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | IGHG2 , immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 2 (G2m marker) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 147110 GeneCards: IGHG2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ig gamma-2 chain C region is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGHG2 gene. [3]

An antibody (Ab) is the secreted form of a B cell receptor; the term immunoglobulin (Ig) can refer to either the membrane-bound form or the secreted form of the B cell receptor, but they are, broadly speaking, the same protein, and so the terms are often treated as synonymous. Antibodies are large, Y-shaped proteins belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which are used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that cause disease. Antibodies can recognize virtually any size antigen with diverse chemical compositions from molecules. Each antibody recognizes one or more specific antigens. Antigen literally means "antibody generator", as it is the presence of an antigen that drives the formation of an antigen-specific antibody. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope that specifically binds to one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing the two molecules to bind together with precision. Using this mechanism, antibodies can effectively "tag" a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly.

Immunoglobulin D (IgD) is an antibody isotype that makes up about 1% of proteins in the plasma membranes of immature B-lymphocytes where it is usually co-expressed with another cell surface antibody called IgM. IgD is also produced in a secreted form that is found in very small amounts in blood serum, representing 0.25% of immunoglobulins in serum. The relative molecular mass and half-life of secreted IgD is 185 kDa and 2.8 days, respectively. Secreted IgD is produced as a monomeric antibody with two heavy chains of the delta (δ) class, and two Ig light chains.
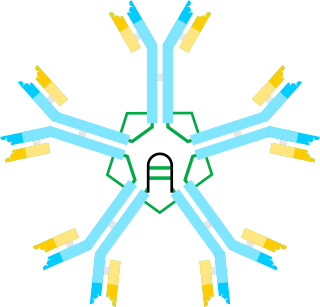
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is the largest of several isotypes of antibodies that are produced by vertebrates. IgM is the first antibody to appear in the response to initial exposure to an antigen; causing it to also be called an acute phase antibody. In humans and other mammals that have been studied, plasmablasts in the spleen are the main source of specific IgM production.

The immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) is the large polypeptide subunit of an antibody (immunoglobulin). In human genome, the IgH gene loci are on chromosome 14.

Immunoglobulin class switching, also known as isotype switching, isotypic commutation or class-switch recombination (CSR), is a biological mechanism that changes a B cell's production of immunoglobulin from one type to another, such as from the isotype IgM to the isotype IgG. During this process, the constant-region portion of the antibody heavy chain is changed, but the variable region of the heavy chain stays the same. Since the variable region does not change, class switching does not affect antigen specificity. Instead, the antibody retains affinity for the same antigens, but can interact with different effector molecules.

The word allotype comes from two Greek roots, allo meaning 'other or differing from the norm' and typos meaning 'mark'. In immunology, allotype is an immunoglobulin variation that can be found among antibody classes and is manifested by heterogeneity of immunoglobulins present in a single vertebrate species. The structure of immunoglobulin polypeptide chain is dictated and controlled by number of genes encoded in the germ line. However, these genes, as it was discovered by serologic and chemical methods, could be highly polymorphic. This polymorphism is subsequently projected to the overall amino acid structure of antibody chains. Polymorphic epitopes can be present on immunoglobulin constant regions on both heavy and light chains, differing between individuals or ethnic groups and in some cases may pose as immunogenic determinants. Exposure of individuals to a non-self allotype might elicit an anti- allotype response and became cause of problems for example in a patient after transfusion of blood or in a pregnant woman. However, it is important to mention that not all variations in immunoglobulin amino acid sequence pose as a determinant responsible for immune response. Some of these allotypic determinants may be present at places that are not well exposed and therefore can be hardly serologically discriminated. In other cases, variation in one isotype can be compensated by the presence of this determinant on another antibody isotype in one individual. This means that divergent allotype of heavy chain of IgG antibody may be balanced by presence of this allotype on heavy chain of for example IgA antibody and therefore is called isoallotypic variant. Especially large number of polymorphisms were discovered in IgG antibody subclasses. Which were practically used in forensic medicine and in paternity testing, before replaced by modern day DNA fingerprinting.

In immunology, antibodies are classified into several types called isotypes or classes. The variable (V) regions near the tip of the antibody can differ from molecule to molecule in countless ways, allowing it to specifically target an antigen . In contrast, the constant (C) regions only occur in a few variants, which define the antibody's class. Antibodies of different classes activate distinct effector mechanisms in response to an antigen . They appear at different stages of an immune response, differ in structural features, and in their location around the body.

Ig mu chain C region is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGHM gene.

Ig gamma-1 chain C region is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGHG1 gene.

Immunoglobulin heavy constant alpha 1 is a immunoglobulin gene with symbol IGHA1. It encodes a constant (C) segment of Immunoglobulin A heavy chain. Immunoglobulin A is an antibody that plays a critical role in immune function in the mucous membranes. IgA shows the same typical structure of other antibody classes, with two heavy chains and two light chains, and four distinct domains: one variable region, and three variable regions. As a major class of immunoglobulin in body secretions, IgA plays a role in defending against infection, as well as preventing the access of foreign antigens to the immunologic system.
Immunoglobulin heavy locus, also known as IGH, is a region on human chromosome 14 that contains a gene for the heavy chains of human antibodies.

Ig epsilon chain C region is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGHE gene.

Ig alpha-2 chain C region is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGHA2 gene.
Immunoglobulin lambda locus, also known as IGL@, is a region on the q arm of human chromosome 22, region 11.22 (22q11.22) that contains genes for the lambda light chains of antibodies.

Immunoglobulin iota chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VPREB1 gene. VPREB1 has also recently been designated CD179A.
Ig heavy chain V-III region VH26 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGHV@ gene.

Ig gamma-3 chain C region is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGHG3 gene.

Fc fragment of IgA receptor (FCAR) is a human gene that codes for the transmembrane receptor FcαRI, also known as CD89. FcαRI binds the heavy-chain constant region of Immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibodies. FcαRI is present on the cell surface of myeloid lineage cells, including neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, and eosinophils, though it is notably absent from intestinal macrophages and does not appear on mast cells. FcαRI plays a role in both pro- and anti-inflammatory responses depending on the state of IgA bound. Inside-out signaling primes FcαRI in order for it to bind its ligand, while outside-in signaling caused by ligand binding depends on FcαRI association with the Fc receptor gamma chain.

Ig gamma-4 chain C region is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGHG4 gene.
Antibody structure is made up of two heavy-chains and two light-chains. These chains are held together by disulfide bonds. The arrangement or processes that put together different parts of this antibody molecule play important role in antibody diversity and production of different subclasses or classes of antibodies. The organization and processes take place during the development and differentiation of B cells. That is, the controlled gene expression during transcription and translation coupled with the rearrangements of immunoglobulin gene segments result in the generation of antibody repertoire during development and maturation of B cells.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of May 2024 (link)